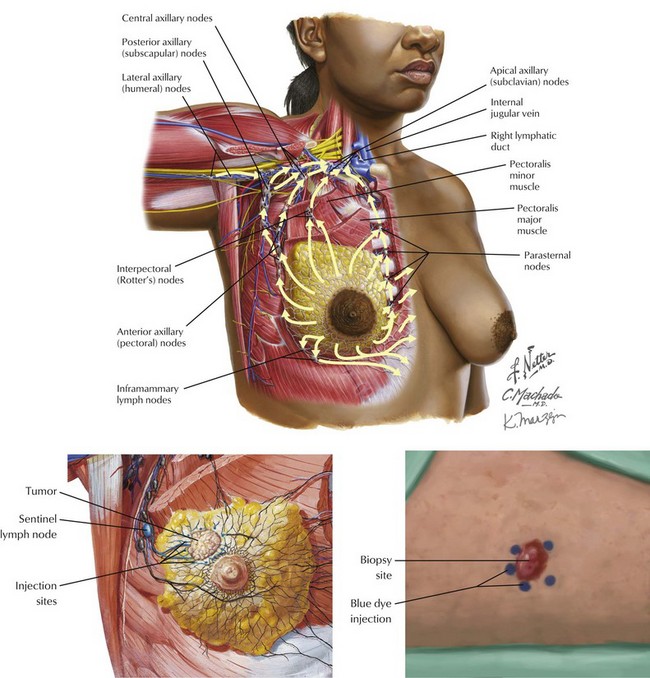
Chapter 48 The injection site for the blue dye or the radiotracer can be either over the tumor or the areola (Fig. 48-1). In the operating room the surgeon then looks for a blue lymph node (if dye is used), a radioactive lymph node (if radiotracer is used), or both. With a radiotracer, multiple nodes may be radioactive. It is important to search for the node with the highest level of radioactivity. This node, as well as all nodes with more than 10% of the highest count, should be removed for pathologic evaluation. Another important consideration is the choice of injection site. The lymphatic drainage of the breast and overlying skin are the same: both drain to the axillary lymph nodes. Therefore, intradermal injection (vs. peritumoral injection) of radiotracer is an acceptable practice. Periareolar and subareolar injections work equally well for SLNB. However, intradermal injection of blue dye may lead to skin discoloration and should be avoided in breast cancer. This approach contrasts with melanoma, in which intradermal injections are required; the discoloration of the skin is irrelevant because a wide local excision will be performed at the time of SLNB (Fig. 48-1).
Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy
Dye/Radiotracer and Injection Sites
Lymphatic Drainage
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree