QUESTION 20.2
A. Coxsackievirus
B. Epstein-Barr virus
C. Human immunodeficiency virus
D. Human papillomavirus
E. Paramyxovirus
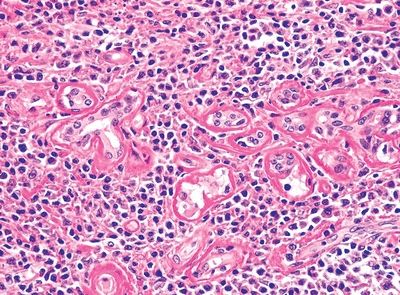
3. A 46-year-old male presents with an ulcer on the hard palate. A biopsy reveals necrosis of salivary gland parenchyma, chronic inflammation, and foci of squamous epithelium admixed with mucous acini. Squamous cells exhibit nuclear pleomorphism and mitotic activity. The lesion displays a lobular architecture, as demonstrated in this picture. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
QUESTION 20.3
A. Acute viral sialadenitis
B. Chronic sialadenitis
C. Mucoepidermoid carcinoma
D. Necrotizing sialometaplasia
E. Squamous cell carcinoma
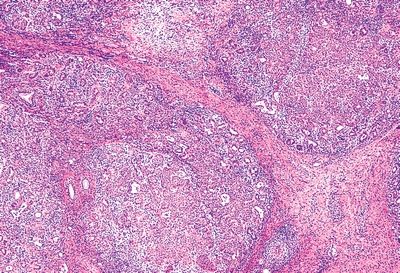
4. A 40-year-old man presents with 1-year history of swelling of the right submandibular gland. On palpation, a slightly tender, very firm mass is appreciated. Fearing a malignancy, the submandibular gland is removed, and the lesion has the histologic features shown in this picture. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
QUESTION 20.4
A. Acute viral sialadenitis
B. Chronic sclerosing sialadenitis
C. Granulomatous sialadenitis
D. Necrotizing sialometaplasia
E. Sjögren syndrome
5. A 40-year-old woman presents with enlargement of the left parotid gland and dryness of the eyes and mouth. A biopsy of the parotid and minor salivary glands shows the histologic changes represented in this picture. Laboratory studies reveal high titers of circulating antibodies to ribonucleoproteins (RNP), including SS-A (Ro) and SS-B (La). This patient has an increased risk of developing which type of lymphoma?
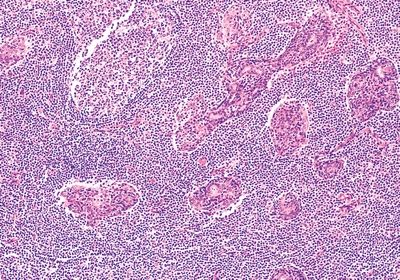
QUESTION 20.5
A. Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
B. Follicular lymphoma
C. Mantle cell lymphoma
D. Marginal zone lymphoma
E. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma
6. A well-demarcated slowly growing 4-cm tumor is resected from the left parotid gland of a 45-year-old female patient. Its cut surface is variegated, with myxoid and blue-gray areas. The microscopic appearance of the tumor is demonstrated in this picture. If properly resected, the recurrence rate of this tumor is:
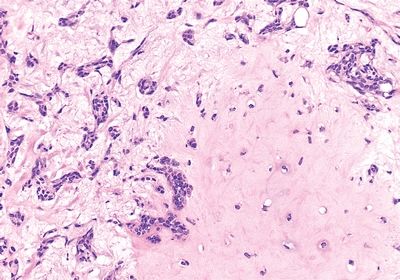
QUESTION 20.6
A. 2%
B. 10%
C. 20%
D. 30%
E. 40%
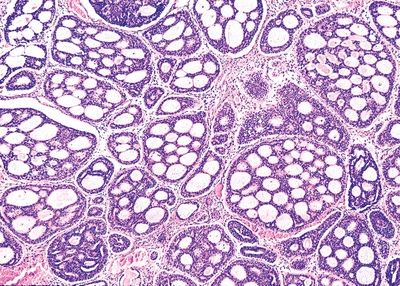
7. A 60-year-old man presents with bilateral painless swelling of the parotid gland. Image studies reveal a 1.5-cm mass in the right parotid and a 2.0-cm mass in the left parotid. Both tumors are resected and appear to have similar microscopic appearance, which is shown in this picture. Which of the following is the strongest predisposing condition for the development of this tumor?
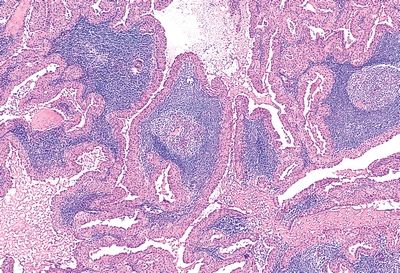
QUESTION 20.7
A. Epstein-Barr virus infection
B. HIV infection
C. Radiation
D. Sjögren syndrome
E. Smoking
8. This picture demonstrates the typical microscopic features of a well-circumscribed, encapsulated mass removed from the parotid of a 65-year-old woman. Which of the following subtypes has a 25% recurrence rate?
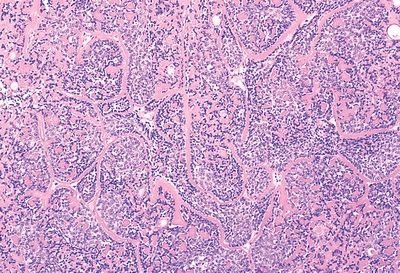
QUESTION 20.8
A. Membranous
B. Solid
C. Trabecular
D. Tubular
E. All of the above
9. The most common location of the salivary gland tumor depicted in this photomicrograph is:
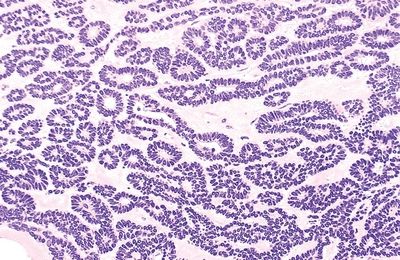
QUESTION 20.9
A. Hard palate
B. Parotid
C. Sublingual
D. Submandibular
E. Upper lip
10. The tumor shown in this photomicrograph was removed from the parotid gland of a 38-year-old woman. Which of the following is the most important risk factor for this neoplasm?
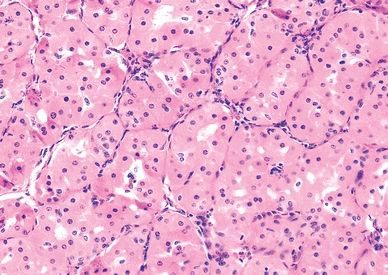
QUESTION 20.10
A. Chronic sclerosing sialadenitis
B. Family history
C. Radiation
D. Sjögren syndrome
E. Smoking
11. Of the five salivary gland neoplasms shown in these photomicrographs, which one is always found in the parotid and periparotid region?
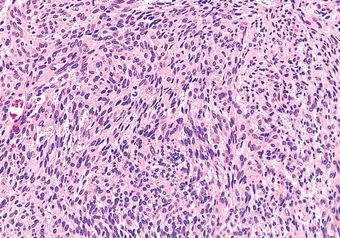
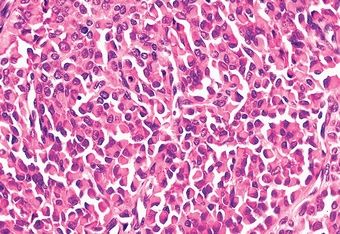
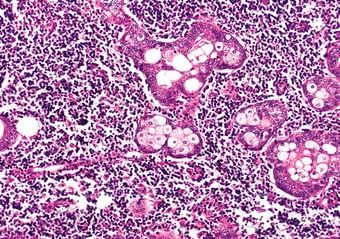
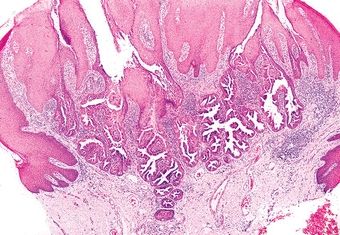
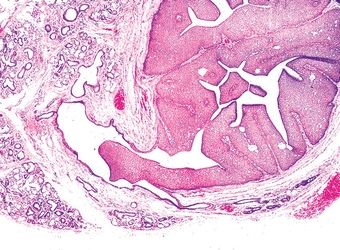
QUESTION 20.11
A. Association with Sjögren syndrome
B. Cytoplasm packed with mitochondria
C. Good long-term prognosis
D. Highest prevalence in the parotid gland
E. Prominent perineural invasion
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree