Occurs via portal vein, arterial system, or bile ducts
Diagnostic Checklist
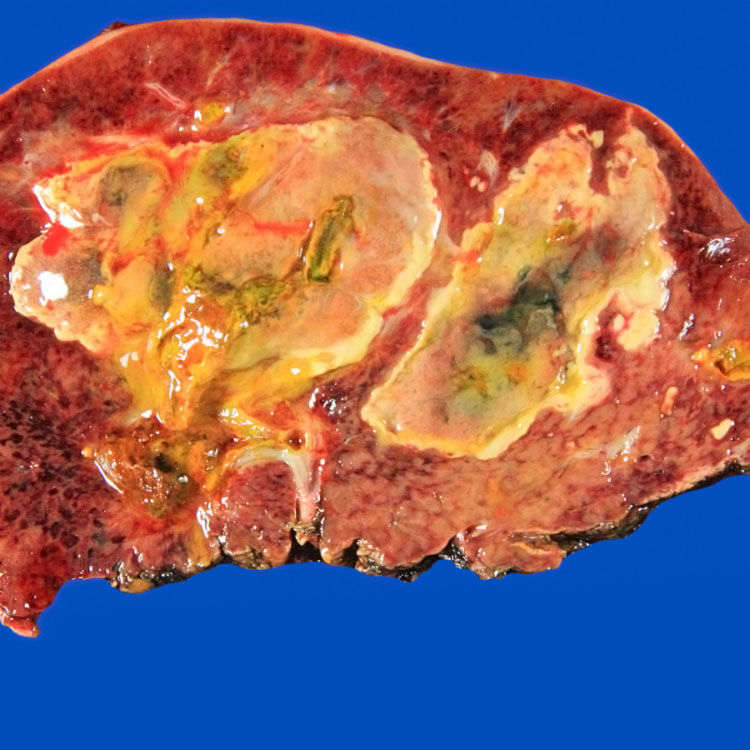
This partial hepatectomy specimen shows 2 large, irregular, yellow-tan abscesses with central green bile-stained necrosis.
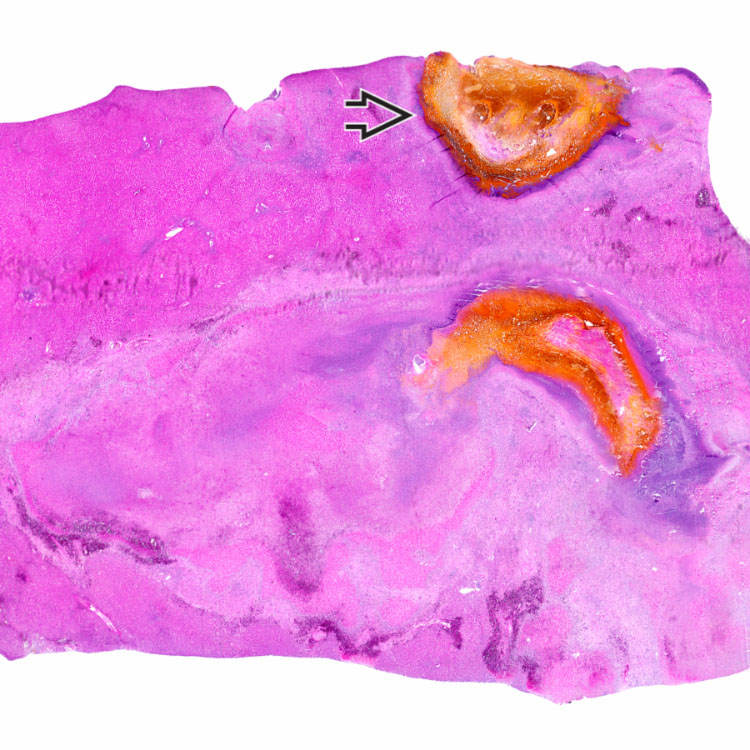
This section of a large liver abscess shows irregular zones of inflammation and necrosis with associated bile. Another smaller abscess containing bile is present at the top of the section
 .
.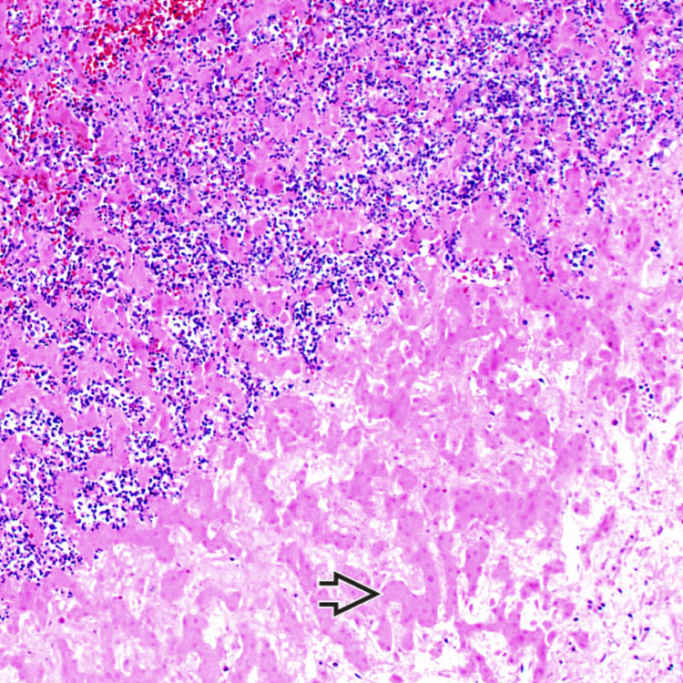
In this region of the abscess, necrotic liver parenchyma is identifiable by the ghosts of residual hepatic plate architecture
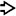 . The necrotic parenchyma is infiltrated with neutrophils.
. The necrotic parenchyma is infiltrated with neutrophils.ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Predisposing Conditions
• Diabetes is major risk factor
 Other predisposing conditions include malignancy, alcohol abuse, cirrhosis, hypertension, recent surgery, immunosuppression
Other predisposing conditions include malignancy, alcohol abuse, cirrhosis, hypertension, recent surgery, immunosuppression
 Other predisposing conditions include malignancy, alcohol abuse, cirrhosis, hypertension, recent surgery, immunosuppression
Other predisposing conditions include malignancy, alcohol abuse, cirrhosis, hypertension, recent surgery, immunosuppressionEpidemiology
• Bacterial abscesses are most common in Western countries




Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree









 , as seen in this actinomycotic abscess. Marked acute and chronic inflammation are also present.
, as seen in this actinomycotic abscess. Marked acute and chronic inflammation are also present.


