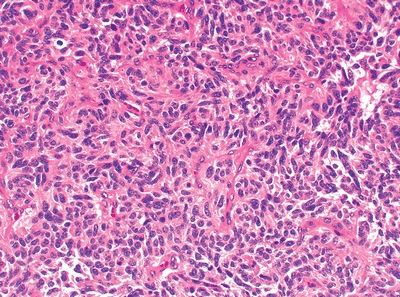
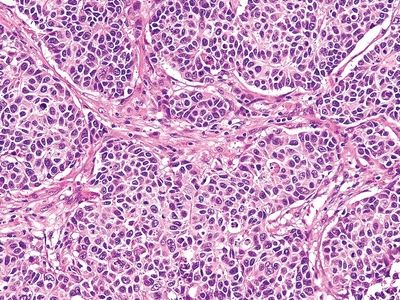
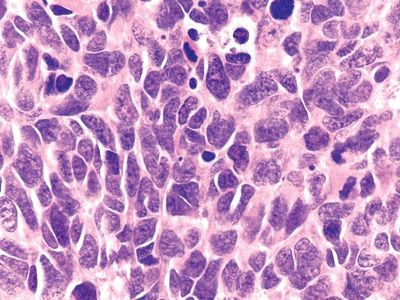
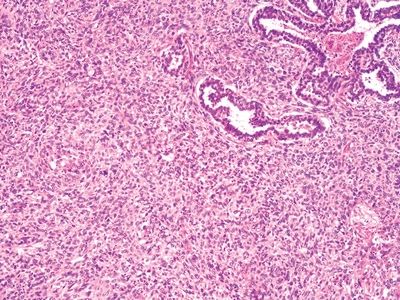
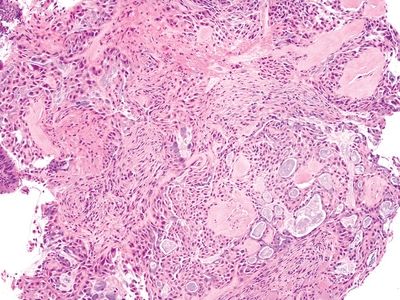
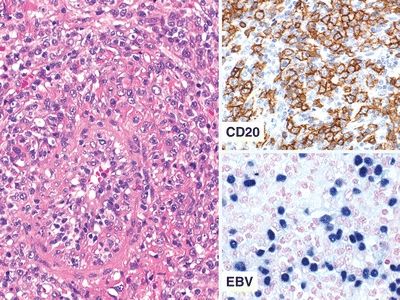
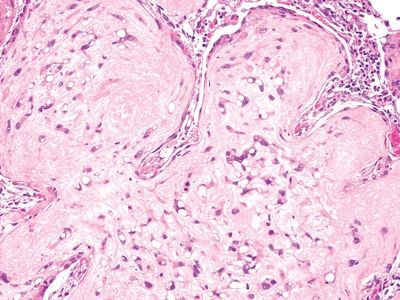
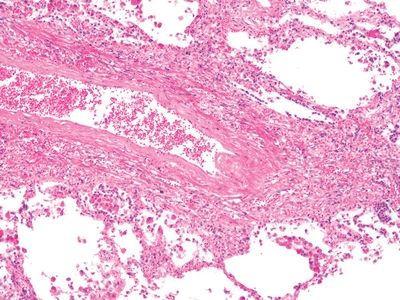
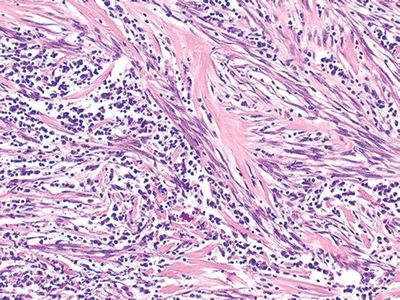
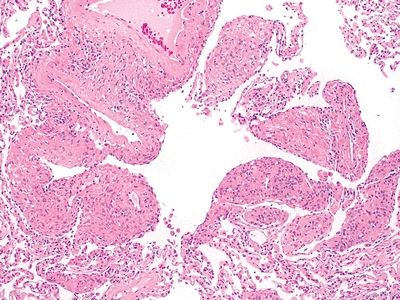
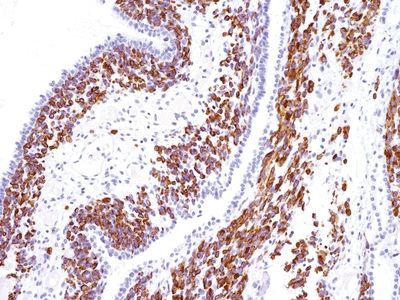
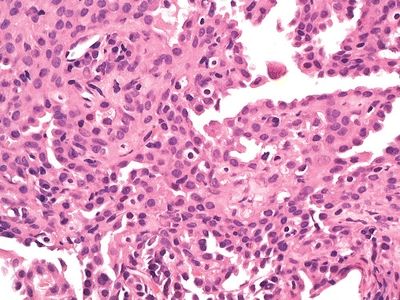
QUESTION 26.14
A. Peripheral carcinoid
B. Atypical adenomatous hyperplasia
C. Typical carcinoid
D. Paraganglioma
E. Granular cell tumor
A. Peripheral carcinoid
B. Atypical adenomatous hyperplasia
C. Typical carcinoid
D. Paraganglioma
E. Granular cell tumor
A. Peripheral carcinoid
B. Large cell carcinoma
C. Large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma
D. Poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma
E. Poorly differentiated squamous cell carcinoma
A. B-cell lymphoma
B. Mantle cell lymphoma
C. Large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma
D. Poorly differentiated squamous cell carcinoma
E. Small cell carcinoma
A. PAS
B. p63
C. CK5/CK6
D. CD56
E. Calretinin
A. Mucous gland adenoma
B. Alveolar adenoma
C. Mucoepidermoid carcinoma
D. Acinic cell tumor
E. Adenosquamous carcinoma
A. Granulomatous pulmonary arteritis (WG)
B. Lymphomatoid granulomatosis
C. Churg-Strauss arteritis
D. Found predominantly in young women
E. T-cell lymphoma
A. CD31 positive
B. BEREP4 positive
C. TTF-1 positive
D. CK5/CK6 positive
E. CK7 positive
A. HPV infection
B. EBV infestation
C. Herpesvirus infection
D. Mycobacterial infection
E. Aspergillus infection
A. Pulmonary artery sarcoma
B. Metastatic leiomyosarcoma
C. Metastatic liposarcoma
D. Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor
E. Nodular sclerosing, Hodgkin
A. Found in elderly men and women
B. HMB-45 positive
C. Perivascular epithelioid cell origin
D. ER positive
E. Associated with tuberous sclerosis
A. Is congenital cystic adenomatoid malformation
B. Is found in only in young boys
C. Is pleuropulmonary blastoma
D. Is pulmonary blastoma
E. Has a good prognosis
A. Adenocarcinoma in situ
B. Adenocarcinoma, invasive with lipidic pattern
C. Metastatic breast carcinoma
D. Sclerosing hemangioma
E. Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma
A. Metastatic renal cell carcinoma
B. Clear cell variant of large cell carcinoma
C. Atypical carcinoid
D. PECOMA
E. Paraganglioma
28. Atypical adenomatous hyperplasia is usually characterized by all except:
A. Association with adenocarcinoma
B. Less than 5 mm
C. Centriacinar localization
D. Contains ciliated and mucinous cell
E. Mild to moderate cytologic atypia
29. Squamous cell carcinoma of the lungs feature all except which of the following?
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree