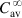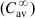Practice Problems
The chapter contains a number of practice problems, for which step-to-step answers are provided in Appendix I. Many of the problems are based on experimental data that have been extracted from original research publications. However, in all cases, the original data have been modified in order to emphasize the teaching on pharmacokinetics and the mathematics and models applied. The aim is to help the student understand the rather abstract mammillary model and how it can be applied in the development of pharmaceutical products.
Keywords
Bioavailability; clearance; kinetic rate constants; pharmaceutical availability; protein binding; sustained release; urinary data
Some of the following problems are based on experimental data extracted from original research publications in international peer-reviewed journals. In all cases, the data have been modified from the original data, and thus do not show the normal experimental variations.
7.1
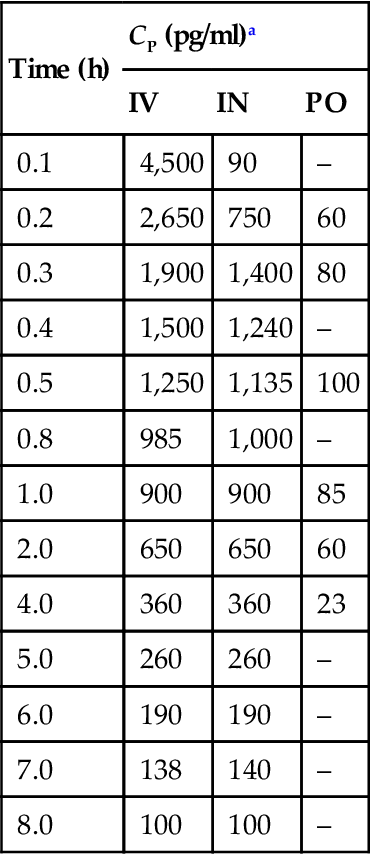
Scopolamine was administered to 12 healthy men (31.0±4.5 years, 78.2±7.2 kg) as nasal spray (IN), oral tablet (PO), and intravenous (IV) bolus injection [1]. The dose was, in all three cases, 0.40 mg (D0=0.40 mg). Blood samples were collected and the plasma scopolamine concentration (CP) determined at various time points (t).
| Time (h) | CP (pg/ml)a | ||
| IV | IN | PO | |
| 0.1 | 4,500 | 90 | – |
| 0.2 | 2,650 | 750 | 60 |
| 0.3 | 1,900 | 1,400 | 80 |
| 0.4 | 1,500 | 1,240 | – |
| 0.5 | 1,250 | 1,135 | 100 |
| 0.8 | 985 | 1,000 | – |
| 1.0 | 900 | 900 | 85 |
| 2.0 | 650 | 650 | 60 |
| 4.0 | 360 | 360 | 23 |
| 5.0 | 260 | 260 | – |
| 6.0 | 190 | 190 | – |
| 7.0 | 138 | 140 | – |
| 8.0 | 100 | 100 | – |
7.2
Phenytoin follows nonlinear pharmacokinetics at the therapeutic dosing range. The patient (70 kg) received phenytoin as IV bolus injections at dosing rates (R) of 4.3 and 5.0 mg/kg/day that gave steady-state plasma concentration (CSS) of 8.0 and 20 µg/ml, respectively.
A. Determine Vmax and Km in this patient.
B. The therapeutic window of phenytoin is between 10 and 20 µg/ml (see Figure 5.1). Determine the dosing rate that gives a CSS of 15 µg/ml.
C. Determine the ClT of phenytoin in this patient when CSS is 15 µg/ml.
7.3
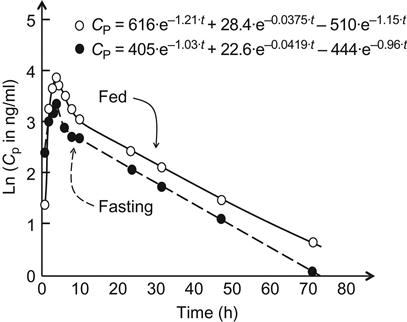
Itraconazole follows the two-compartment open model after administration of oral itraconazole solution [2]. Six healthy male volunteers received itraconazole (D0=40 mg) as an oral solution under both fed ( ) and fasting (
) and fasting ( ) conditions. Blood samples were collected and the average itraconazole plasma concentration determined up to 72 h after administration of the drug. The obtained ln CP versus time profile is shown below.
) conditions. Blood samples were collected and the average itraconazole plasma concentration determined up to 72 h after administration of the drug. The obtained ln CP versus time profile is shown below.