Chapter 10 State law identifies those health care providers who are authorized to write prescriptions. This fact is because of the state-by-state variation in prescriptive authority. Traditionally, physicians have had full prescriptive authority, dentists and podiatrists have had prescriptive authority for a limited formulary, and veterinarians have had the ability to prescribe, dispense, and administer a variety of medications. State laws have been amended in every state to provide prescriptive authority to certain other providers, such as doctors of osteopathy, physician assistants (PAs), advanced practice nurses (APNs), or specifically nurse practitioners (NPs), certified nurse-midwives (CNMs), certified registered nurse anesthetists (CRNAs), and in some states clinical nurse specialists (CNSs). Prescriptive authority may be granted directly to these providers or indirectly through delegated authority from a physician (see Chapter 2 for information on APNs and PAs). Each state determines the qualifications and credentials that are essential for a provider to obtain prescriptive authority; these may include specific courses in pharmacology before prescriptive authority is granted, as well as ongoing requirements for continuing education in pharmacology. The DEA oversees controlled substances. This agency attempts to limit professionals who may prescribe controlled substances to those who are authorized and competent to do so and to monitor the activity of such individuals to make certain they are in conformance with federal law. Such monitoring is essential because of the potential for misuse and abuse of these substances by both patients and providers. The DEA does not define who is to receive DEA numbers but relies on the states for this information (U.S. Department of Justice, DEA, 2006). States issue a state-controlled substance license. This number seems to have little purpose other than to document for the DEA that the applicant is recognized as a prescriber within the state and is eligible for the federal DEA number. The DEA website lists the controlled substance authority for midlevel practitioners by discipline in the state in which they practice (http://www.deadiversion.usdoj.gov/drugreg/practioners/index.html). The health care provider who seeks a federal DEA number may obtain an application by calling 202-307-7255; by going to the DEA website at www.DEADiversion.usdoj.gov; or by writing to the Drug Enforcement Administration Registration Division, Washington, DC 20537, and submitting the appropriate information and fees. Fees are sufficiently high to deter casual acquisition. Currently the rate for pharmacies, hospitals/clinics, practitioners, teaching institutions, or midlevel practitioners is $731, which covers 3 years. Providers must indicate on the application the specific schedules of drugs that they are authorized by the state to prescribe. Physician numbers begin with A if they have had the DEA number for some time or with F if they are a new registration. Nonphysician prescribers are required to fill out a specific addendum to the DEA application to validate state authority to engage in the prescription of controlled substances. DEA numbers issued to “midlevel providers” begin with the letter M, followed by a number that corresponds to the first letter of the last name (i.e., E for Edwards) and a computer-generated sequence of numbers. Physician and midlevel practitioners’ manuals, available by special request, contain essential rules and regulations related to use or misuse of the DEA number. If applicants meet the DEA requirements, they are issued a number. One exception is that military and U.S. Public Health Service physicians are exempt from registration. This number is valid for 3 years and then may be renewed. This federal number is also reported to the state and is included in the materials distributed to pharmacists in that state (U.S. Department of Justice, DEA, 2006). Drugs in Schedule I have the highest potential for abuse, and their use is limited to research protocols, instructional purposes, or chemical analysis. Ongoing research may eventually establish a medical role for some of these substances under selected circumstances. On the other end of the spectrum, Schedule V drugs are available by prescription or may be sold over the counter in some states, depending on state law (U.S. Department of Justice, DEA, 2012). See Table 10-1 for a sample Schedule of Controlled Drugs. TABLE 10-1 Federal Schedule of Controlled Drugs From U.S. Department of Justice, DEA: Prescribers’ manual, Washington, DC, 2008, U.S. Department of Justice. Although state law may mandate the specifics of what is required on a prescription, there is general agreement about some things that should be included, whether required by law or not and whether a preprinted prescription pad is used or the prescription is transmitted electronically. Most states insist that the hospital name or the imprinted name of the prescriber, along with credentials, address, and telephone number, must be preprinted on the prescription pad for controlled substances but not for noncontrolled drugs. It is important, however, for the pharmacist to be able to easily contact the prescriber. In institutions where there are many prescribers, an institutional prescription pad may allow the prescriber to use a number rather than having all prescriber names printed on the pad. Prescriptions must be preprinted, typed, or written in ink and must be signed by an authorized prescriber to be valid. For a good example of a prescription, see Figure 10-1. • Name and address of the patient—Most states require the address if the prescription is written for a controlled substance. It is always a good idea to include the address on a prescription; this will help the pharmacist to make certain that the correct person is picking up the drug. • Date that the prescription is written—By law, a patient usually has up to 120 days to fill a prescription for a controlled or a noncontrolled drug. Medicaid or Medical Assistance prescriptions often must be filled within a shorter period, usually 10 days, although states may vary on their specific practices. The date on the prescription helps the pharmacist to determine if the patient waited too long to fill the prescription. Some patients hold a prescription in case they need it at another time. This is equivalent to giving patients an inappropriate ability to diagnose and prescribe for themselves in the future. • Age and weight of the patient—The pharmacist needs this information to assess the accuracy of the prescription as written. Dosage modifications based on age and weight may be suggested or validated by the pharmacist with this information, particularly for pediatric and geriatric patients. 1. Superscription—The symbol “Rx” from the Latin recipe meaning “take” is included. 2. Inscription—Drug ingredients and their quantities, strength, or concentration are specified. 3. Drug—The full name of the medication is written clearly and specifically. Do not use abbreviations. If handwriting legibility is an issue, print or type the information required. There must be no question as to the meaning of what is written. Some pharmaceutical companies supply preprinted pads for certain prescriptions, reducing the chance for error (and encouraging the prescribing of their product) (Jayawardena et al, 2007; Mills, 2007; Varkey et al, 2007). 4. Strength or concentration—The dose of the medication to be dispensed must be specified. 5. Signature—This usually is indicated by an “S,” representing the Latin signa, which means “mark.” Other individuals use “Sig.,” which means “Directions for use.” Thus, the signature includes instructions to be placed on the outside of the package to direct the patient how and when to take the medicine and in what quantities. The signature component of the prescription should not be confused with the prescriber’s signature that is placed at the bottom of the form. It is especially important to be complete in writing instructions for how the medication should be taken. First, it is important for the patient to understand how to take the medication. The prescription should be specific about this and should not just indicate “Take as directed.” Research has shown that failure to write instructions clearly is responsible for many of the medication errors that patients make. Patients often do not understand instructions, become confused over time, or fail to make changes when therapy is modified (Aspinall et al, 2007). The imprecision of poorly written directions can also influence a patient’s ability to comply. To improve patient recall and reduce administration errors, patients require explicit directions. A high percentage of reported administrative errors result from the direct failure of patients to comprehend the directions on the prescription label (Cohen, 2007). In one study, when given a prescription for tetracycline 250 mg with the directions “Take 1 capsule every 6 hours,” only 36% of 67 participants interpreted the directions to mean around the clock, for a total of 4 doses in 24 hours. Approximately 25% would have been noncompliant by omitting the late-night dose because they would have divided the day into three 6-hour periods while they were awake. Although in this instance, the pharmacist has adequate information to counsel the patient, the example demonstrates the importance of prescription writing and labeling (Aspinall et al, 2007). Caregivers express greater satisfaction with the prescribing experience when they are given the rationale for and more informative dosing information, especially when caring for pediatric patients (Barrett et al, 2011). Second, clarity and precision in writing instructions also help the pharmacist. Federal regulations now mandate that pharmacists must provide education and counseling to patients regarding their medication. Having specific information about why the patient is taking the medication and how the patient should take the medication allows the pharmacist to help reinforce the provider’s directions, discover errors in the writing or the filling of the prescription, and obtain feedback about how patients think they should take the medication. Given the growing number of new drugs on the market, identifying the symptom, indication, or intended effect for which the medication is being prescribed becomes more important and can be added in just a few words—for example, “for nausea,” “at headache onset,” and so on. This additional information allows the pharmacist who is dispensing the prescription to help assess compliance and reinforce the provider’s instructions. An example of this can be seen with propranolol, which may be used to treat several different problems. It would be nonsensical for a pharmacist to explain how important it is for a patient to take the medication to control high blood pressure when the patient is being treated for migraine headaches. Knowing the intent of the treatment will aid the pharmacist in communicating with the patient and providing feedback to the provider (Bernstein et al, 2007). Finally, specific instructions on the container assist the prescriber in reviewing medications ordered by other prescribers. Patients should always bring all medications they are taking to each office visit. Errors may be detected more easily when instructions on each container are examined. The number of tablets/capsules/teaspoons is designated by small roman numerals—for example, one = i, two = ii, three = iii, and so on. Examples of instructions might include “Take i tablet 1 hour before eating or 2 hours after eating 3 times a day”; “Mix i teaspoon in a full glass of orange juice to be taken morning and evening”; or “Take ii capsules with food each morning.” See Table 10-2 for examples of abbreviations commonly used in prescribing medications. TABLE 10-2 Abbreviations Commonly Used in Prescription Writing • Subscription—The pharmacist is instructed on how to compound the medicine. Although compounding pharmacies still exist, the advent of modern pharmaceutical packaging and unit dosing means that this component of the prescription usually is met by specifying the dosage form (e.g., capsule, tablet, liquid, suspension, cream, ointment) and the amount to be dispensed. The prescriber may specify that the product is to be taken PO, IV, IM, and so on (Bridge, 2007). The abbreviation “D” preceding the amount to be dispensed is used to indicate “Give.” • Quantity or volume—This indicates how much medication is to be dispensed. Order enough for the standard course of the medication or enough to last until the next scheduled visit. Order standard volumes when writing for liquids. The Physicians’ Drug Reference or package insert lists standard volumes under “How Supplied.” Sometimes, the volume or number of doses that may be ordered is limited by how much will be paid for by a prescription reimbursement plan. • To summarize—In writing this part of the prescription, the first line usually contains the drug name and strength. The second line contains the instructions for taking the drug. The third line tells the pharmacist how much and in what form the medication should be dispensed.
Practical Tips on Writing Prescriptions
Who May Write Prescriptions?
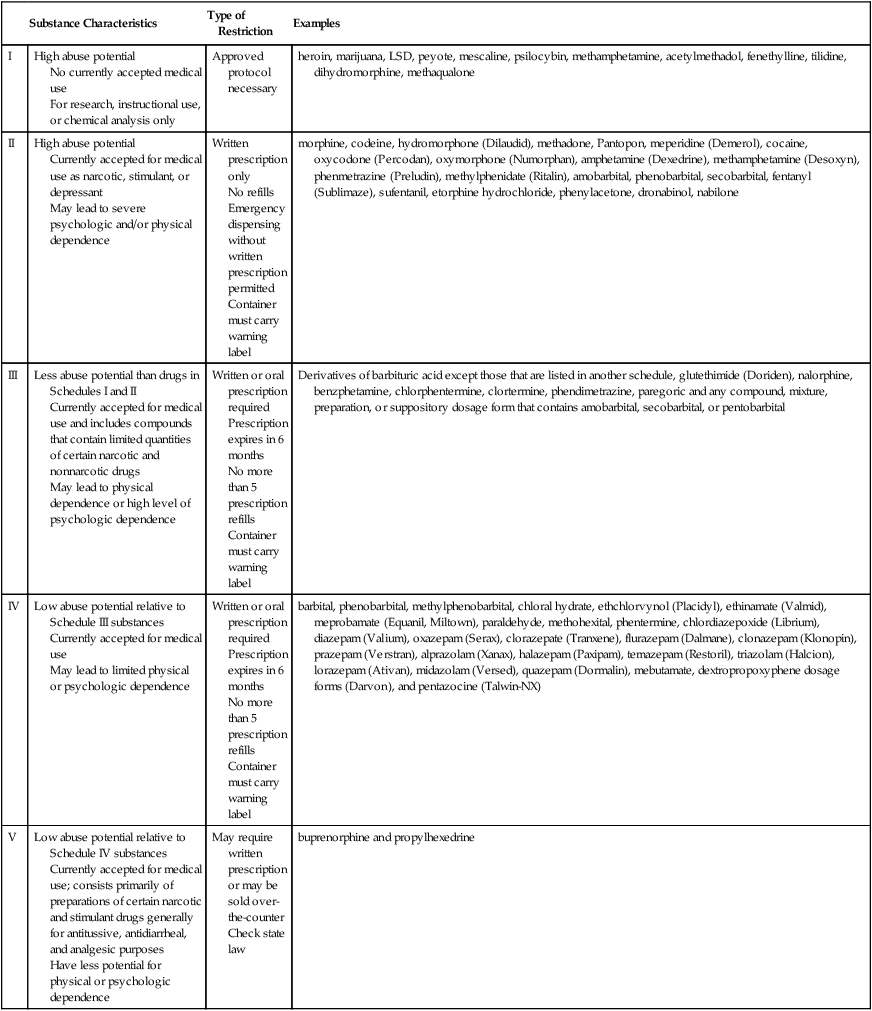
Drug Schedules
Substance Characteristics
Type of Restriction
Examples
I
High abuse potential
No currently accepted medical use
For research, instructional use, or chemical analysis only
Approved protocol necessary
heroin, marijuana, LSD, peyote, mescaline, psilocybin, methamphetamine, acetylmethadol, fenethylline, tilidine, dihydromorphine, methaqualone
II
High abuse potential
Currently accepted for medical use as narcotic, stimulant, or depressant
May lead to severe psychologic and/or physical dependence
Written prescription only
No refills
Emergency dispensing without written prescription permitted
Container must carry warning label
morphine, codeine, hydromorphone (Dilaudid), methadone, Pantopon, meperidine (Demerol), cocaine, oxycodone (Percodan), oxymorphone (Numorphan), amphetamine (Dexedrine), methamphetamine (Desoxyn), phenmetrazine (Preludin), methylphenidate (Ritalin), amobarbital, phenobarbital, secobarbital, fentanyl (Sublimaze), sufentanil, etorphine hydrochloride, phenylacetone, dronabinol, nabilone
III
Less abuse potential than drugs in Schedules I and II
Currently accepted for medical use and includes compounds that contain limited quantities of certain narcotic and nonnarcotic drugs
May lead to physical dependence or high level of psychologic dependence
Written or oral prescription required
Prescription expires in 6 months
No more than 5 prescription refills
Container must carry warning label
Derivatives of barbituric acid except those that are listed in another schedule, glutethimide (Doriden), nalorphine, benzphetamine, chlorphentermine, clortermine, phendimetrazine, paregoric and any compound, mixture, preparation, or suppository dosage form that contains amobarbital, secobarbital, or pentobarbital
IV
Low abuse potential relative to Schedule III substances
Currently accepted for medical use
May lead to limited physical or psychologic dependence
Written or oral prescription required
Prescription expires in 6 months
No more than 5 prescription refills
Container must carry warning label
barbital, phenobarbital, methylphenobarbital, chloral hydrate, ethchlorvynol (Placidyl), ethinamate (Valmid), meprobamate (Equanil, Miltown), paraldehyde, methohexital, phentermine, chlordiazepoxide (Librium), diazepam (Valium), oxazepam (Serax), clorazepate (Tranxene), flurazepam (Dalmane), clonazepam (Klonopin), prazepam (Verstran), alprazolam (Xanax), halazepam (Paxipam), temazepam (Restoril), triazolam (Halcion), lorazepam (Ativan), midazolam (Versed), quazepam (Dormalin), mebutamate, dextropropoxyphene dosage forms (Darvon), and pentazocine (Talwin-NX)
V
Low abuse potential relative to Schedule IV substances
Currently accepted for medical use; consists primarily of preparations of certain narcotic and stimulant drugs generally for antitussive, antidiarrheal, and analgesic purposes
Have less potential for physical or psychologic dependence
May require written prescription or may be sold over-the-counter
Check state law
buprenorphine and propylhexedrine
Components of the Traditional Prescription

Top Portion
Middle Portion
Abbreviation
Meaning
sig
Directions for use
qam
Every morning
bid
Two times daily while awake
tid
Three times daily while awake
qid
Four times daily while awake
q8h
Every 8 hours around the clock
ac
Before meals
pc
After meals
hs
At hour of sleep or bedtime
tsp
Teaspoon
prn
As needed
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


Practical Tips on Writing Prescriptions
Only gold members can continue reading. Log In or Register to continue
