Top Differential Diagnoses
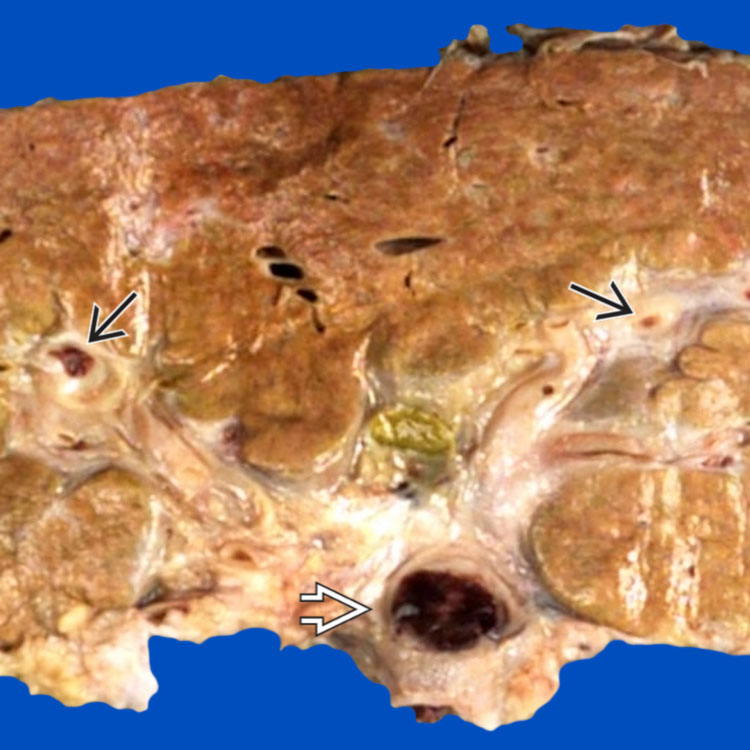
Gross photograph of this liver explant shows a large portal vein thrombus
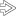 in the hilar region. Propagation into smaller intrahepatic portal veins
in the hilar region. Propagation into smaller intrahepatic portal veins 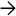 is also grossly noticed.
is also grossly noticed.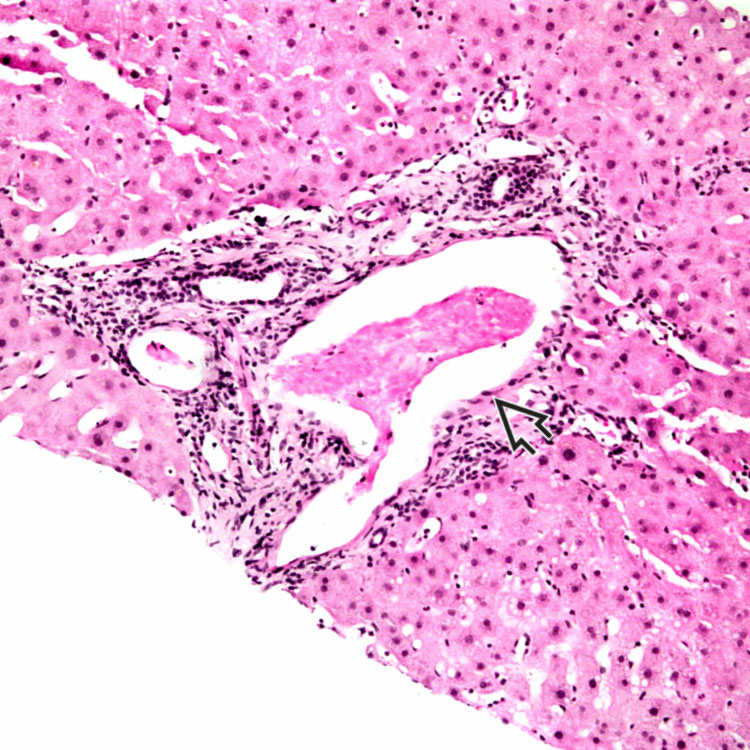
This microphotograph shows a markedly dilated portal venule
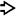 in the setting of portal vein thrombosis. Note the presence of fibrin thrombus in the lumen.
in the setting of portal vein thrombosis. Note the presence of fibrin thrombus in the lumen.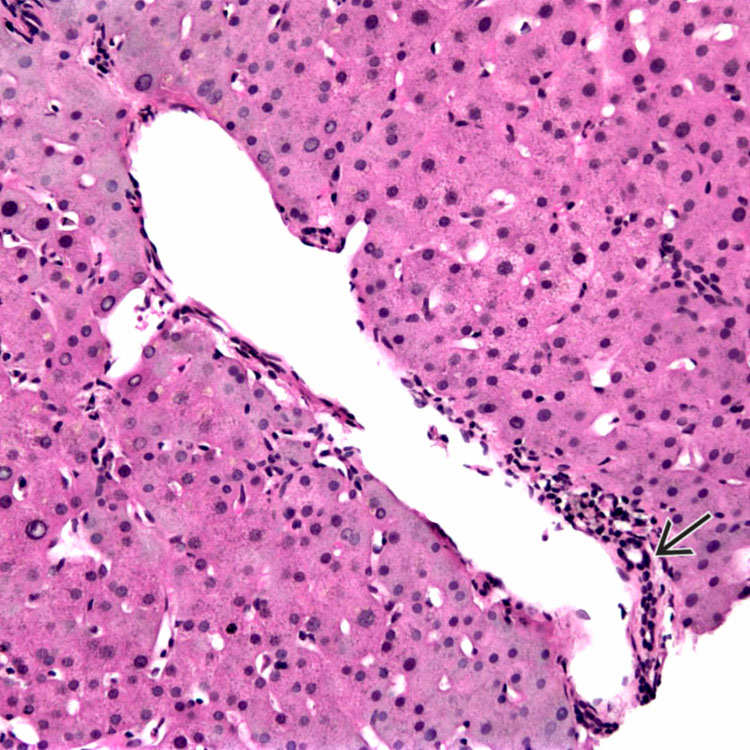
Typical changes in portal venous obstruction include dilated portal venules with “herniation” of the vessel into the surrounding parenchyma. Note the presence of a bile duct
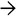 in compressed portal stroma.
in compressed portal stroma.TERMINOLOGY
Synonyms
• Idiopathic portal hypertension




Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree

















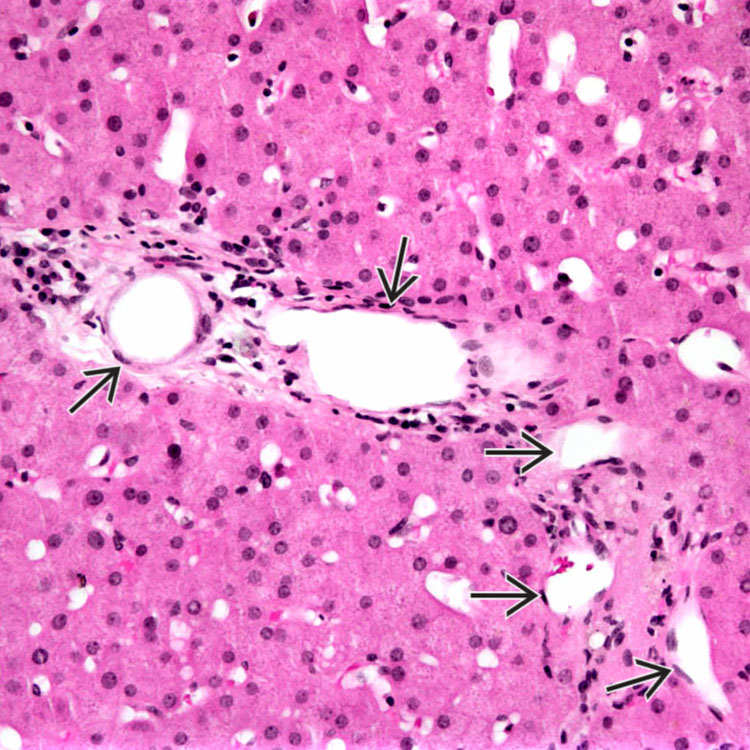
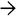 are present in this portal tract in a case of portal venous obstruction indicating elevated portal pressures.
are present in this portal tract in a case of portal venous obstruction indicating elevated portal pressures.