QUESTION 50.2
A. Cord torsion
B. Oligohydramnios
C. Placenta previa
D. Premature rupture of membranes
E. Vasa previa
3. The umbilical cord of a placenta from a preterm delivery is narrow and wrinkled. A 10-cm segment adjacent to the placental disc is flattened. Which of the following conditions is most likely associated with these changes?
A. Abruptio placentae
B. Ectopic implantation
C. Infection
D. Maternal history of cocaine abuse
E. Oligohydramnios
4. A 35-year-old pregnant woman presents with fever, uterine tenderness, and leukocytosis. She delivers a male baby at 30-week gestation. Histologic examination of the placenta and amniotic sac reveals the changes shown in this picture. Which of the following is the most likely infectious agent of this condition?
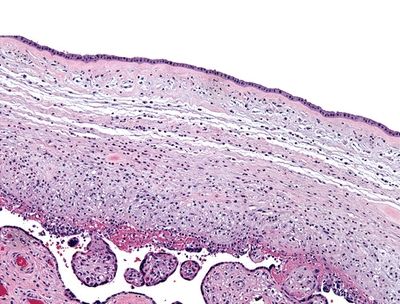
QUESTION 50.4
A. Bacteroides fragilis
B. Chlamydia trachomatis
C. Escherichia coli
D. Fusobacterium
E. Group B streptococci
5. Microscopic examination of a term placenta reveals a diffuse neutrophilic infiltration of villi and intervillous spaces, with scattered microabscesses. This histologic presentation is usually caused by:
A. Cytomegalovirus
B. Group B streptococci
C. Listeria monocytogenes
D. Syphilis
E. Toxoplasma
6. The cause of villitis of unknown etiology (VUE) is in most cases due to:
A. Ascending infection
B. Chronic hypoxia
C. Hematogenous infection
D. Immunologic reaction
E. Malformative process
7. Which of the following conditions results in the abnormalities of villous maturation illustrated in this picture?
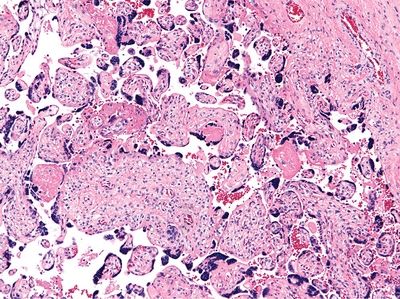
QUESTION 50.7
A. Chorangiosis
B. Generalized villous dysmaturity
C. Meconium exposure
D. Placental malperfusion
E. Villitis of unknown etiology
8. A placenta is submitted for gross and histologic evaluation in a case of clinically diagnosed abruptio placentae. Which of the following microscopic findings is most compatible with this diagnosis?
A. Intravillous and intervillous hemorrhage
B. Meconium-laden macrophages in amniotic membrane
C. Neutrophil-rich infiltration of membranes
D. Myocytes and hemorrhage in the maternal plate
E. Thrombi in fetal blood vessels
9. In this photomicrograph, chorionic villi display a change that may be produced by chronic fetal–placental hypoxia. Which of the following is it?
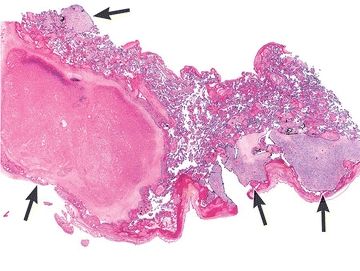
QUESTION 50.9
A. Chorangiomatosis
B. Chorioamnionitis
C. Intravillous hemorrhage
D. Villitis of unknown origin
E. Villous dysmaturity
10. Which of the following types of multiple pregnancies is associated with the highest risk of twin-to-twin-transfusion syndrome?
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


