Medium-sized epithelioid cells, large epithelioid cells, and spindled cells
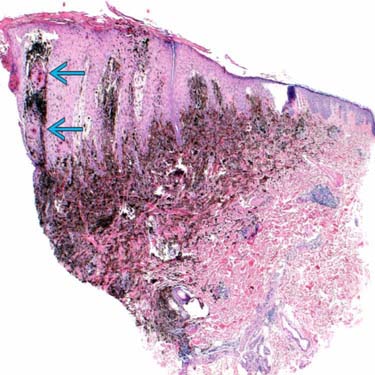
A punch biopsy from an 11-year-old girl, right posterior auricular, shows a heavily pigmented compound melanocytic tumor with overlying epidermal hyperplasia and squamous proliferation
 . Typically, pigmented epithelioid melanocytoma (PEM) is over pigmented out of proportion to the tumor.
. Typically, pigmented epithelioid melanocytoma (PEM) is over pigmented out of proportion to the tumor.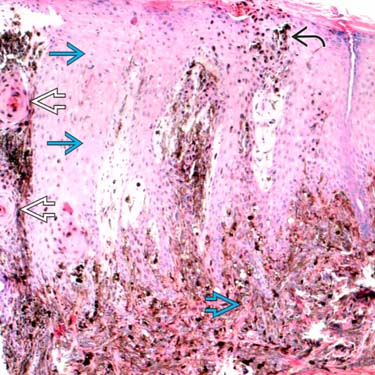
Among the epidermal psoriasiform hyperplasia
 , there lies intraepidermal melanophages
, there lies intraepidermal melanophages  . The squamous eddies
. The squamous eddies  are reactive and not neoplastic. Large epithelioid dermal cells are evident
are reactive and not neoplastic. Large epithelioid dermal cells are evident  .
.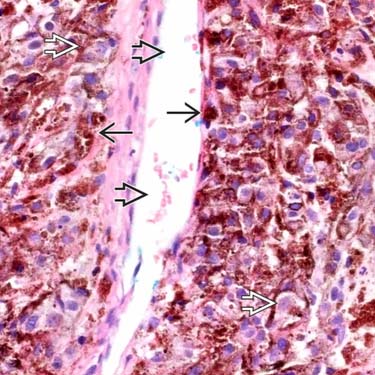
High magnification shows large epithelioid cells
 with open chromatin and cherry-red macronucleoli. The melanophages are packed with chunky clusters of melanin
with open chromatin and cherry-red macronucleoli. The melanophages are packed with chunky clusters of melanin  , masking the nuclei. The tumor cells condense around the blood vessels and lymphatics but do not invade vascular spaces
, masking the nuclei. The tumor cells condense around the blood vessels and lymphatics but do not invade vascular spaces  .
.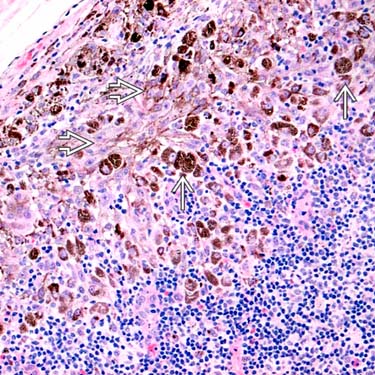
A sentinel lymph node biopsy from the 11-year-old girl diagnosed with PEM shows melanophages
 and large epithelioid tumor cells
and large epithelioid tumor cells  , seen in multiple foci throughout the lymph node.
, seen in multiple foci throughout the lymph node.MICROSCOPIC
Histologic Features
• Extends into deep reticular tissue and subcutaneous fat along adnexal structures or neurovascular bundles




Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree







