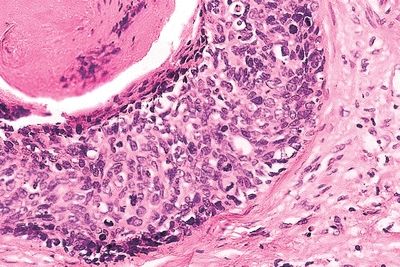
QUESTION 48.3
A. Balanitis circumscripta plasmacellularis
B. Lichen sclerosus
C. Penile melanosis
D. Peyronie disease
E. Sclerosing lymphangitis of the penis
4. Erythroplasia of Queyrat and Bowen disease refer to conditions histologically characterized by:
A. Acanthosis with spotty proliferation of atypical cells
B. Carcinoma in situ
C. Prominent koilocytic atypia
D. Squamous hyperplasia with papillomatosis
E. Superficial spreading squamous cell carcinoma
5. These three pictures show three squamous lesions associated with increased risk of penile SCC. Which one of them is most often associated with HPV infection?
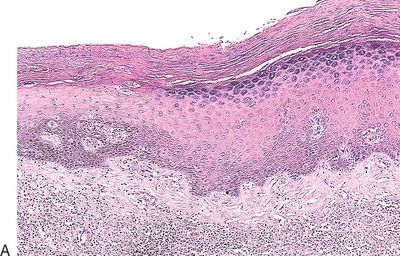
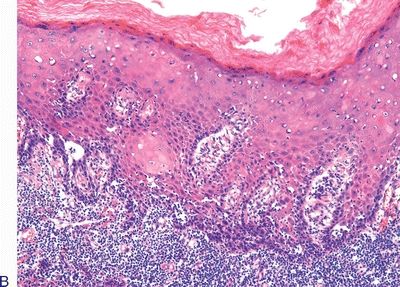
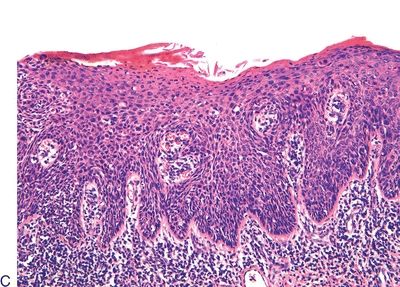
QUESTION 48.5
A. Lesion A
B. Lesion B
C. Lesion C
A. Basaloid
B. Papillary
C. Sarcomatoid
D. Usual
E. Warty
Answers and Explanations
1. Correct choice: D
FOURNIER GANGRENE—Fournier gangrene is a life-threatening necrotizing fasciitis of the genitalia. Dartos and penile fascia are preferred sites of involvement. Predisposing factors are local or perineal trauma, burns, or anorectal disease added to debilitating conditions such as diabetes, leukemia, and alcoholic cirrhosis. Streptococci and staphylococci are the most common causative agents in children, as gram-negative bacilli and anaerobic bacteria are in adults. Fournier gangrene is akin to necrotizing balanitis (Corbus disease).
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree