QUESTION 35.2
A. Acinar cells
B. Ductal cells
C. Hepatocytes
D. Mesothelial cells
3. A subtotal pancreatic resection is performed in a patient with malabsorption. The histopathologic changes are shown in this picture. There is apparent hyperplasia of the islets of Langerhans. Which of the following is the most common complication of this condition?
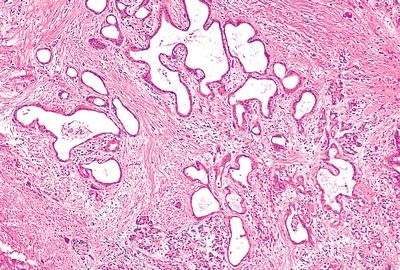
QUESTION 35.3
A. Diabetes mellitus
B. Ductal adenocarcinoma
C. Migratory thrombophlebitis
D. Obstructive jaundice
E. Pancreatic pseudocyst
4. A 69-year-old man presents with chronic diarrhea, steatorrhea, weight loss, and painless jaundice. A CT scan reveals diffuse, sausage-shaped enlargement of the pancreas with narrowing of the main duct. His serum IgG4 level is elevated. Out of concern for possible cancer, a biopsy of the pancreas is performed, revealing the histologic changes shown in this picture. Also, the inflammatory reaction is noted to involve veins, producing a picture of obliterative phlebitis. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
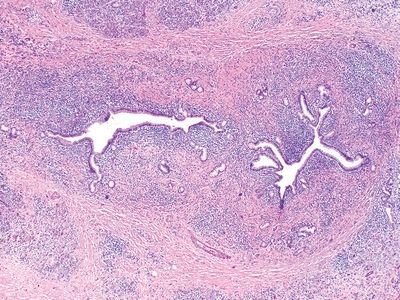
QUESTION 35.4
A. Autoimmune pancreatitis, type 1
B. Autoimmune pancreatitis, type 2
5. This photomicrograph shows a specific histologic change in a pancreatic biopsy from a patient thought to have autoimmune pancreatitis (AIP). Which of the following types of AIP does this patient have?
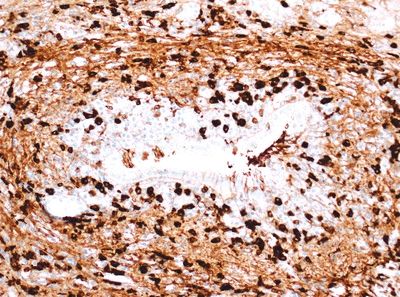
QUESTION 35.5
A. Autoimmune pancreatitis, type 1
B. Autoimmune pancreatitis, type 2
6. A pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) shows the microscopic features highlighted in this picture. Which variant of PDAC is this?
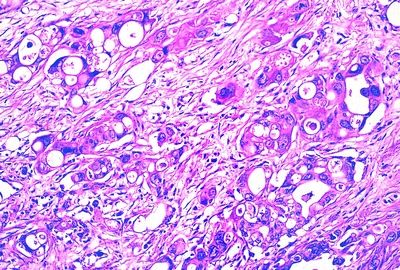
QUESTION 35.6
A. Foamy gland
B. Large duct
C. Poorly cohesive
D. Vacuolated/cribriform
7. An ultrasound-guided FNA of a pancreatic lesion reveals the cell clusters shown in this picture. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
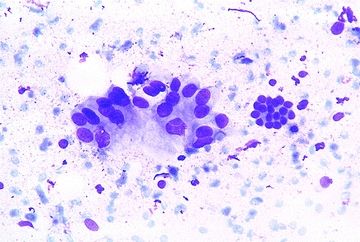
QUESTION 35.7
A. Acinar cells
B. Ductal cells
C. Hepatocytes
D. Mesothelial cells
E. Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
8. All of the following features are helpful in the differential diagnosis between PDAC and benign noninvasive ducts, EXCEPT:
A. Corpora amylacea–like secretions
B. Haphazard distribution and contour irregularities of ducts
C. Intraluminal debris, partial duct rupture, and vacuolation
D. Presence of myoepithelial or basal cells
E. Unusual location of ducts
9. This photomicrograph shows the FNA of a pancreatic mass. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
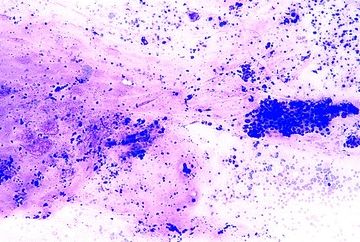
QUESTION 35.9
A. Adenosquamous carcinoma
B. Colloid carcinoma
C. Ductal carcinoma
D. Medullary carcinoma
E. Undifferentiated carcinoma
10. Which of the following histologic types of pancreatic carcinoma is associated with microsatellite instability (MSI)?
A. Adenosquamous carcinoma
B. Colloid carcinoma
C. Medullary carcinoma
D. Undifferentiated carcinoma
E. Undifferentiated carcinoma with osteoclast-like giant cells
11. A pancreatic tumor shows a mixture of different neoplastic components including areas that appear as in this low-power picture admixed with areas of glandular differentiation. There are large cells with bizarre multilobulated nuclei and atypical mitotic figures. Which of the following features is characteristic of this neoplasm?
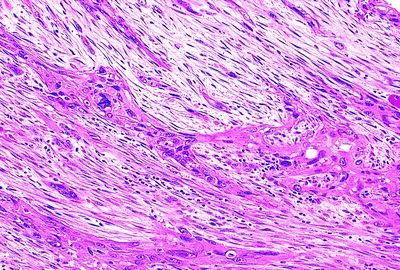
QUESTION 35.11
A. Butyrate esterase reaction
B. Evidence of neuroendocrine differentiation
C. Female predilection
D. Keratin expression
E. Origin from acinar cells
12. Which of the following types of PanIN is most commonly found with a coexisting invasive ductal adenocarcinoma?
A. PanIN-1A
B. PanIN-1B
C. PanIN-2
D. PanIN-3
13. This photomicrograph shows a lesion that was removed from the head of the pancreas in a patient who suffered from acute pancreatitis. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
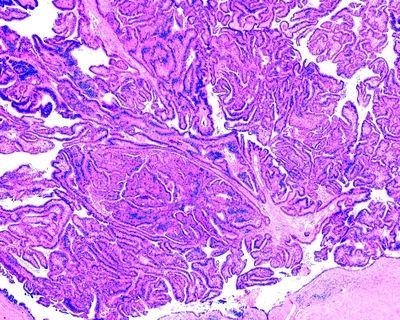
QUESTION 35.13
A. Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm (IPMN)
B. Intraductal tubulopapillary neoplasm (ITPN)
C. Mucinous cystic neoplasm
D. PanIN-3
14. The multiloculated cystic tumor shown in this picture is almost exclusively found in perimenopausal women. Which one is it?
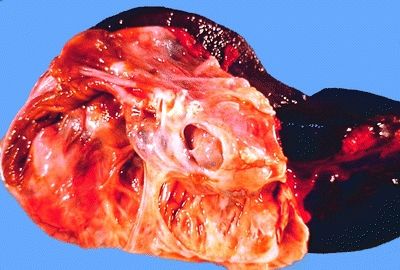
QUESTION 35.14
A. Acinar cell carcinoma
B. Mucinous cystic neoplasm
C. Pancreatoblastoma
D. Serous cystadenoma
E. Solid pseudopapillary neoplasm
15. A pancreatic tumor is found at the autopsy of a 75-year-old woman who died of a myocardial infarction. On the cut surface, the tumor shows small cysts filled with serous fluid. Histologically, the septa between cysts are lined by cuboidal cells with clear cytoplasm and contain scattered islets of Langerhans. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


