QUESTION 21.1
A. Actinomycosis
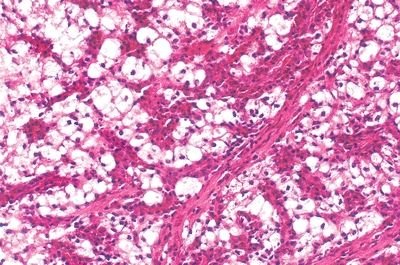
B. Aspergillosis
C. Mucormycosis
D. Myospherulosis
E. Rhinosporidiosis
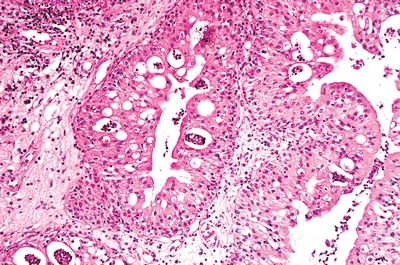
2. A 40-year-old man presents with destructive ulcerative lesions of the nasal and nasopharyngeal cavities. Biopsies show extensive chronic inflammatory infiltrates, mostly consisting of foamy macrophages and plasma cells, as shown in this picture. A Steiner stain identifies small rods within macrophages. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
QUESTION 21.2
A. Leprosy
B. Rhinoscleroma
C. Sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphade- nopathy
D. Tuberculosis
E. Wegener granulomatosis
3. Which of the following statements best describes “midfacial necrotizing lesion” (lethal midline granuloma)?
A. Angiotropic lymphoma involving the nasal cavity
B. Complication of chronic cocaine abuse
C. Destructive lesion due to large cell lymphoma
D. Syndrome encompassing different pathologic conditions
E. Synonym of aggressive Wegener granulomatosis
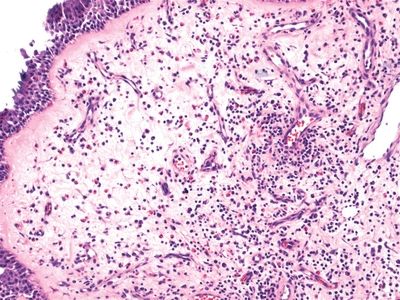
4. A 35-year-old male undergoes resection of a nasal polyp, which reveals the histologic features shown in this picture. Which of the following is most likely to be associated with this kind of polyp?
QUESTION 21.4
A. Asthmatic attacks on aspirin ingestion
B. Cystic fibrosis
C. Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infection
D. Occupational risk
E. Origin in the maxillary antrum
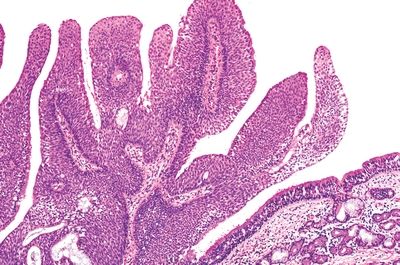
5. A 35-year-old man presents with unilateral nasal obstruction. Inspection reveals an exophytic growth filling the right nasal fossa. The lesion is removed. Its microscopic appearance is shown in this picture. Which of the following is true about this polyp?
QUESTION 21.5
A. Associated with Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)
B. Associated with human papillomavirus (HPV)
C. Associated with 10% risk of invasive carcinoma
D. Develops from the lateral nasal wall
E. Develops in the vestibule
6. This photomicrograph shows a papilloma removed from the nasal fossa of a 50-year-old man who presented with epistaxis. Which of the following is true about this lesion?
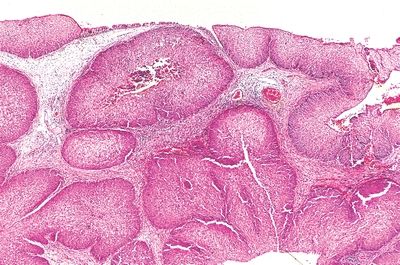
QUESTION 21.6
A. Develops from the lateral nasal wall.
B. HPV is found in the majority of cases.
C. Not associated with risk of invasive carcinoma.
D. Recurrence rate is 5% with simple excision.
E. Women are affected more often than men.
A. Inflammatory
B. Schneiderian, fungiform type
C. Schneiderian, inverted type
D. Schneiderian, oncocytic type
E. Squamous
8. A 58-year-old male with history of chronic rhinosinusitis undergoes resection of a polypoid lesion growing in the posterior nasal septum. The microscopic appearance of the lesion is demonstrated in this low-power photomicrograph. On high power, the epithelium lining the glands resembles respiratory epithelium. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
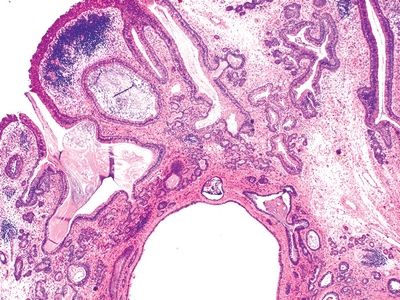
QUESTION 21.8
A. Chondromesenchymal hamartoma
B. Inflammatory polyp
C. Low-grade adenocarcinoma
D. Respiratory epithelial adenomatoid hamartoma
E. Schneiderian, fungiform type
9. A 65-year-old man undergoes resection of an infiltrative mass within the maxillary antrum. The microscopic features of the mass are shown in this picture. This type of neoplasm arising at this site is associated with:
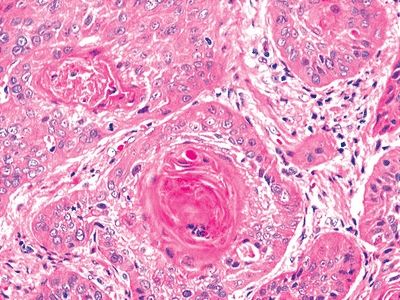
QUESTION 21.9
A. Epstein-Barr virus
B. Human papillomavirus
C. Second primary in the contralateral antrum
D. Second primary in the head and neck
E. Smoking history
10. A 14-year-old boy undergoes biopsy of a nasopharyngeal lesion near the eustachian tube opening. The microscopic appearance of the lesion is shown in this picture. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
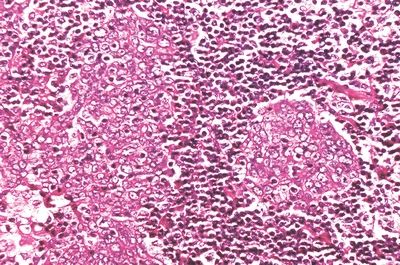
QUESTION 21.10
A. Squamous cell carcinoma, keratinizing
B. Squamous cell carcinoma, nonkeratinizing
C. Undifferentiated carcinoma, Regaud pattern
D. Undifferentiated carcinoma, Schmincke pattern
11. A midline sinonasal tumor from a 25-year-old woman consists of sheets of poorly cohesive cells with scanty cytoplasm and uniform nuclei with prominent nucleoli, as shown in picture A. Mitotic figures and apoptotic bodies are numerous. Scattered throughout the tumor are foci of abrupt keratinization, as demonstrated in picture B. This tumor is most likely to express:
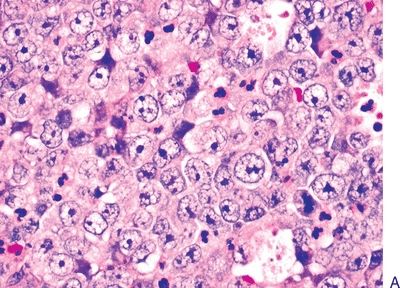
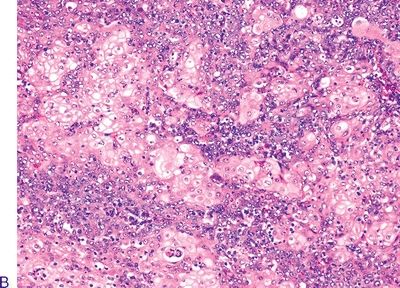
QUESTION 21.11
A. CD45
B. CD99
C. HMB45
D. NUT protein
E. Synaptophysin
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree