Nephrogenic Adenoma of the Prostatic Urethra
Gladell P. Paner, MD
Rugvedita Parakh, MD
Bonnie L. Balzer, MD, PhD
Key Facts
Terminology
Tubulo-papillary proliferations along urothelial mucosa that resemble immature renal tubules
Etiology/Pathogenesis
Renal tubular cell seeding hypothesis
Nephrogenic metaplasia hypothesis
Microscopic Pathology
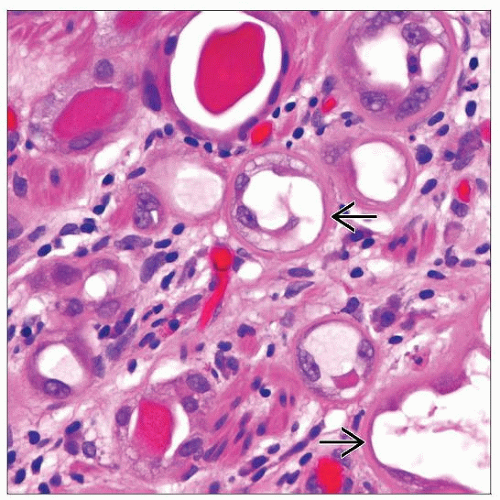
Most common as small round to oval tubules
Thickened peritubular basement membrane
May contain intraluminal basophilic or eosinophilic secretions
Other architectural patterns include cystic, papillary-polypoid, solid growth, and rare fibromyxoid subtype
Monolayer of cuboidal, flattened, or “hobnailed” cells
Scanty to modest eosinophilic to clear cytoplasm
Nuclei with minimal atypia, inconspicuous nucleoli, and absent to rare mitosis
Tubules may be very small simulating signet ring cells
Admixture of these different patterns is common
Polypoid-papillary growth when present is always seen with underlying tubular proliferation
Extension of tubules into subjacent prostate fibromuscular stroma is common
Ancillary Tests
Key immunohistochemical panel: PAN-CK(AE1/AE3) (+), pax-2(+), PSA/PAP(-) in majority of cases
Top Differential Diagnoses
Prostatic acinar adenocarcinoma
Urethral papillary neoplasms
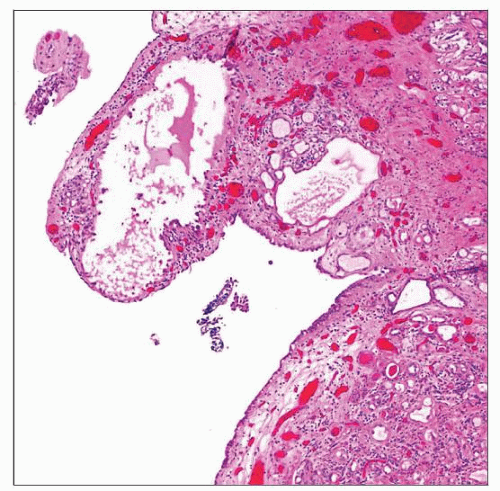 Low-power magnification of NA of the prostatic urethra shows polypoid growth with subjacent tubular and cystic proliferations in the lamina propria. |
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Nephrogenic adenoma (NA)
Synonyms
Nephrogenic metaplasia
Definitions
Benign epithelial lesion of urethra characterized by tubular, glandular, &/or papillary growth pattern that is morphologic and immunohistochemical mimic of prostatic adenocarcinoma
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Renal Tubular Cell Seeding Hypothesis
In renal transplant patients, NA cells shown to have same sex chromosome status with allografted kidneys and not with surrounding bladder tissue in opposite gender recipients
May represent seeding implantation and growth of renal tubular cells in injured urothelial mucosa
Nephrogenic Metaplasia Hypothesis
Metaplastic alteration of urothelium in response to insult or injury
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Age
Mean: 66 years; range: 21-77 years
Site
Vast majority of NA encountered in urinary bladder
Prostatic urethra is involved in approximately 15% of cases and may extend into subjacent prostate stroma
Presentation
Most are incidental findings
Mainly seen in transurethral resection of prostate (TURP) specimens for benign prostatic hyperplasia
Natural History
Majority of cases with preceding genitourinary surgery, instrumentation, urinary tract infection, or calculi
Treatment
None required
Prognosis
Benign, but with high “recurrence” rate (37%) if inciting etiology persists
MACROSCOPIC FEATURES
General Features
Only about 1/3 may assume macroscopic proportions, which may be seen at cystourethroscopically as exophytic papillary or polypoid lesions
Size
Generally < 1 cm, average 0.3 cm
MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY
Histologic Features
Architectural patterns
Most common as small round to oval tubules in laminar fashion
Some tubules characteristically have thickened or prominent peritubular basement membrane
May contain intraluminal basophilic or eosinophilic secretions, the latter imparting resemblance of tubules to thyroid follicles
Tubules may be very small, simulating signet ring cells
Extension of tubules into subjacent prostate fibromuscular stroma common
Cystically dilated tubules
Papillary-polypoid pattern, usually with minimal branching and edematous stroma
Rare solid or diffuse growth and fibromyxoid appearance with spindled cells
Admixture of these different patterns is common; polypoid-papillary, when present, is always seen with underlying tubular proliferation
Cytological features
Monolayer of bland cuboidal, flattened, or “hobnailed” cells
Scanty to modest amount of eosinophilic to clear cytoplasm
Small nuclei with minimal atypia (in range of reactive) and inconspicuous to rarely prominent nucleoli
Absent to rare mitotic figures
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree