Mycobacterial Spindle Cell Pseudotumor
Tariq Muzzafar, MBBS
Key Facts
Clinical Issues
Rare entity; predominantly in young men
History of immunosuppression and HIV infection
Microscopic Pathology
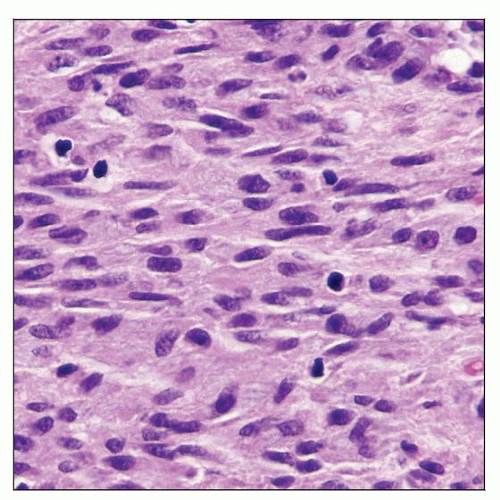
Spindle cells arranged in fascicles and storiform arrays with eosinophilic to granular cytoplasm
Clusters of epithelioid histiocytic cells with similar cytoplasmic features
Acid-fast stain shows numerous bacilli within spindled and epithelioid cells
CD68(+), lysozyme(+), vimentin(+)
CD31(-), CD34(-)
Ancillary Tests
Culture essential for confirmation
Top Differential Diagnoses
Kaposi sarcoma
Slit-like spaces with erythrocyte extravasation
Cytoplasmic eosinophilic globules
Presence of mitoses
Human herpes virus 8(+)
CD31(+), CD34(+)
Palisaded myofibroblastoma
Amianthoid fibers, scattered hemorrhagic foci, pseudocapsule
Smooth muscle actin(+), myosin(+), vimentin(+)
Inflammatory pseudotumor of lymph node
Hilum, trabeculae, and capsule of lymph node
Abundant lymphocytes, plasma cells, neutrophils
Vascular proliferation, flattened endothelial cells
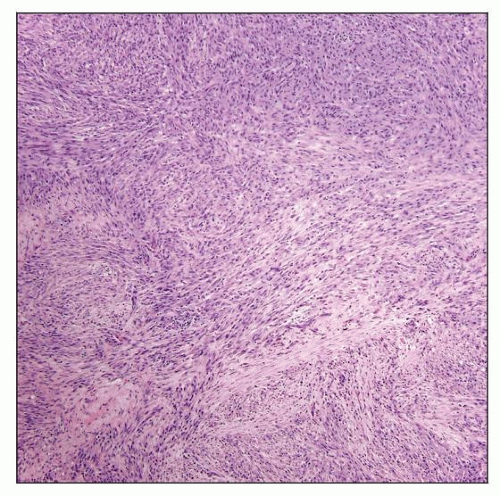 Mycobacterial spindle cell pseudotumor involving lymph node. Fascicles and storiform arrays of spindle cells efface nodal architecture. |
TERMINOLOGY
Definitions
Tumor-like lesion composed of elongated spindle cells infected by Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare (MAI)
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Infectious Agents
Mycobacterium avium–intracellulare
Cause of distinctive tumor-like appearance is unknown
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
Rare entity; ˜ 20 cases reported in literature
Occur in immunocompromised patients
Particularly in those with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS)
Age
Predominantly affects young individuals
Gender
Predominantly affects males
Site
Lymph nodes most common
Other sites: Spleen, skin, bone marrow, lung, and brain
Laboratory Tests
Traditional media
Lowenstein-Jensen media
Agar-based Middlebrook medium
Growth of organisms is slow
Visible colony growth can take up to 6 weeks
Liquid media (growth takes ˜ 2 weeks)
BACTEC
Mycobacteria growth indicator tubes
Treatment
Drugs
HIV(+): Clarithromycin or azithromycin + ethambutol
HIV(-): Clarithromycin or azithromycin plus rifampin or rifabutin and ethambutol
Prognosis
Anti-MAI drugs are effective, particularly if immunosuppression can be reversed
IMAGE FINDINGS
Radiographic Findings
Lymphadenopathy
MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY
Histologic Features
Lymph node architecture effaced by elongated spindle cells (histiocytes)
Arranged in short fascicles and storiform arrays
Histiocytes have bland nuclei, eosinophilic to granular cytoplasm
Admixed small lymphocytes
No significant mitotic activity
Acid-fast (Ziehl-Neelsen) stain demonstrates numerous bacilli within cells
Cytologic Features
In Wright-Giemsa touch imprints
Bland histiocytes
Negative outlines of MAI bacilli in cytoplasm
Immunohistochemistry
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree