Mycobacterial Pseudotumor
Elizabeth A. Montgomery, MD
Key Facts
Terminology
Exuberant spindle cell lesion, usually involving lymph nodes, induced by mycobacteria
Clinical Issues
Immunocompromised patients
Majority have AIDS and often also have evidence of systemic infection with Mycobacterium avium complex organisms
Microscopic Pathology
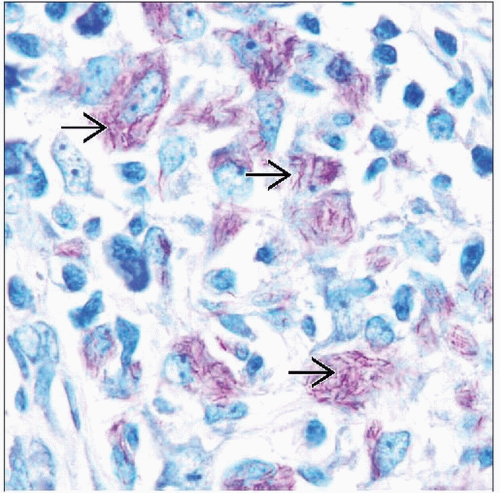
Spindle cells and admixed lymphocytes and plasma cells
Occasional multinucleated histiocytes
Delicate mycobacterial forms can be seen on both PAS and acid-fast stains
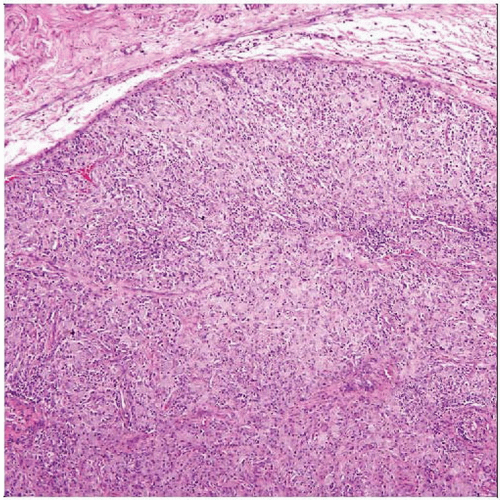 Hematoxylin & eosin at low magnification of a mycobacterial spindle cell tumor shows a loosely lobulated proliferation of epithelioid cells with a background of lymphoplasmacytic cells. |
TERMINOLOGY
Definitions
Exuberant spindle cell lesion, usually involving lymph nodes, induced by mycobacteria
CLINICAL ISSUES
Presentation
Immunocompromised patients
Majority have AIDS
Often also have evidence of systemic infection with Mycobacterium avium complex organisms
Examples reported in individuals with immune comprise from entities other than AIDS
e.g., lupus on long-term steroid treatment
Seldom encountered in USA recently since many patients are better treated for their HIV disease
Reports peaked in early 1990s
Treatment
Drugs
Antimycobacterial drugs
Prognosis
Good after treatment of infection
MACROSCOPIC FEATURES