QUESTION 56.4
A. Appendix
B. Colon
C. Ovary itself
D. Stomach
E. Uterus
5. The majority of ovarian infections in the United States are secondary to:
A. Acute appendicitis
B. Malakoplakia
C. Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)
D. Pelvic tuberculosis
E. Use of an intrauterine device (IUD)
6. Which of the following is the pathologic substrate of an ovarian condition known as hyperreactio luteinalis?
A. Bilateral luteinized follicle cysts
B. Decidual reaction of ovarian stroma
C. Massive ovarian edema
D. Stromal hyperplasia and hyperthecosis
E. Unilateral luteoma
7. Which of the following features is typically ABSENT in ovaries associated with polycystic ovarian disease (Stein-Leventhal syndrome)?
A. Corpora lutea and corpora albicantia
B. Cystic follicles
C. Follicle cysts
D. Luteinization of theca interna
E. Stromal hyperplasia/hyperthecosis
8. Examine these five gross pictures. Match each of the diagnoses with its corresponding picture.
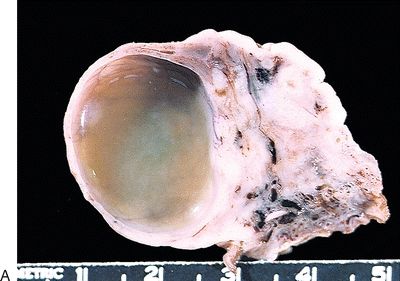
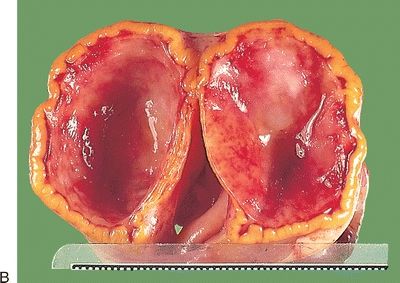
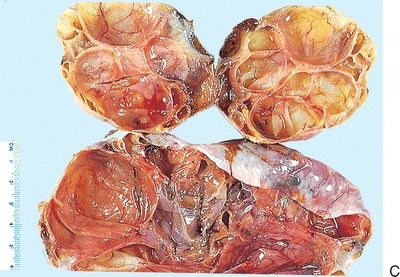
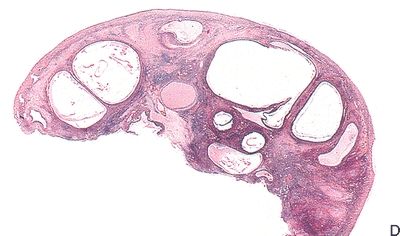

QUESTION 56.8
A. Corpus luteum
B. Fibromatosis
C. Follicle cyst
D. Hyperreactio luteinalis
E. Polycystic ovary syndrome
Answers and Explanations
1. Correct choice: B
FIBROSARCOMA—This is the most frequent of ovarian sarcomas. Leiomyosarcoma and endometrioid stromal sarcoma account for the majority of the remainder, while all other types are very rare. Morphologically, ovarian sarcomas have morphologic features that are indistinguishable from analogous tumors occurring in other locations. Fibrosarcomas lie at the malignant end of a spectrum of stromal neoplasms including fibroma, cellular fibroma, and mitotically active cellular fibroma. Ovarian fibrosarcomas usually present as large, fleshy tumors with significant nuclear atypia and high mitotic rate. Fibrosarcomas are negative for inhibin and CD10.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


