Metastatic Skin Tumors
Christine J. Ko, MD
David Cassarino, MD, PhD
Key Facts
Clinical Issues
Melanoma
Nodule, often pigmented, may be ulcerated, multiple or solitary
Nodal metastases; most commonly in regional lymph nodes
Blue nevus-like melanoma: Blue macule/papule, often near original site of primary melanoma
Survival often < 3 years, but varies
SCC and BCC: Nonspecific nodule(s), often pink to red
Merkel cell carcinoma: Nodal &/or distant metastasis common
DFSP: Essentially only the fibrosarcomatous variant
Microscopic Pathology
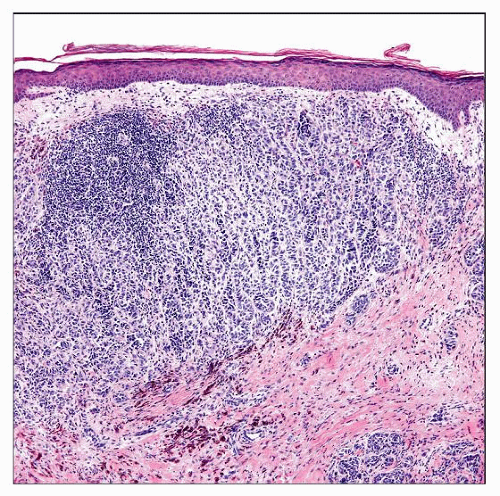
Metastatic melanoma
Nodal metastases: Micrometastasis better detected with use of stains, i.e., S100, MART-1/Melan-A, HMB-45, MITF
Cutaneous metastases generally lack an epidermal component (only rare epidermotropism)
Blue nevus-like metastatic melanoma: Virtually identical to blue nevus; history may be the key clue to diagnosis
Top Differential Diagnoses
All metastatic skin tumors: Primary skin tumor (rather than metastasis to skin from primary focus elsewhere in skin)
Nodal metastasis of melanoma: Nodal nevus (typically p16[+], low proliferation rate with Ki-67)
Merkel cell carcinoma: Other metastatic small cell neuroendocrine tumors
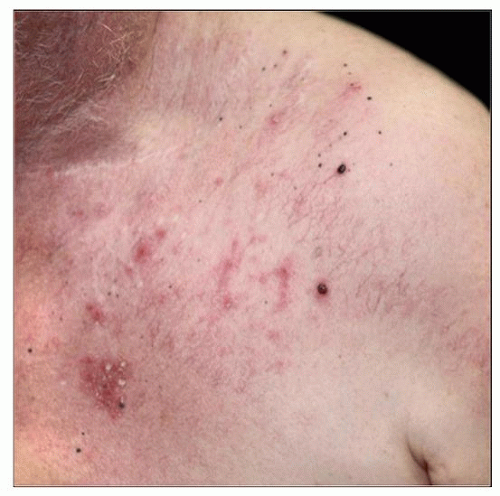 This patient with a history of melanoma on the chest has an unusual presentation of metastatic melanoma, with numerous 1-3 mm black-red papules. |
TERMINOLOGY
Definitions
Metastatic tumor originating from skin
CLINICAL ISSUES
Presentation
Melanoma
Cutaneous metastases
Nodule or papule, often pigmented, may be ulcerated, multiple or solitary
Rarely the presenting sign of disease
Occasionally primary tumor site cannot be determined
Nodal metastases
Most commonly in regional, draining lymph nodes
Distant metastases
Any site, including bone, gastrointestinal tract, lung, brain
Blue nevus-like melanoma
Blue macule/papule, often near original site of primary melanoma
Merkel cell carcinoma
Spreads to lymph nodes in up to 50-75% of cases
Distant metastasis in up to 30-50% of cases
Other sites of metastasis include liver, lungs, bone, brain
Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC)
Nonspecific nodules, often pink to red
Rarely zosteriform pattern
Basal cell carcinoma (BCC)
Very rarely metastasizes to other sites (lymph nodes, bone, parotid, lungs, other internal organs)
Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans (DFSP)
Essentially only fibrosarcomatous cases
Often history of multiple local recurrences
Rarely metastasizes
Lung most common site; also lymph nodes, bone, soft tissue
Many other cutaneous malignancies may metastasize
Adnexal carcinomas
Sebaceous carcinoma: Relatively high incidence of metastasis
Microcystic adnexal carcinoma (extremely rare, with history of multiple recurrences)
Apocrine and eccrine carcinomas
Aggressive digital papillary adenocarcinoma (typically to lungs)
Sarcomas that involve dermis
Treatment
Melanoma
Nodal metastasis
Excision if possible (lymph node dissection)
Observation, clinical trial, interferon-α, &/or radiation
Distant metastasis
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree