QUESTION 28.3
A. Bronchogenic cyst
B. Cystic hygroma
C. Enteric cyst
D. Pericardial cyst
E. Unilocular thymic cyst
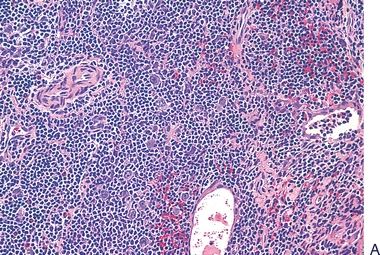
4. These photomicrographs show the histopathologic features of a cystic mass in the mediastinum of a 20-year-old man who presented with chest pain and dyspnea. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
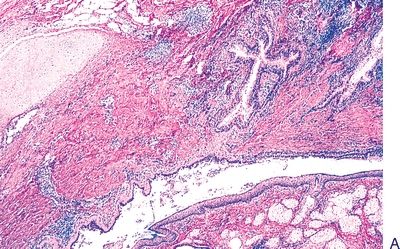
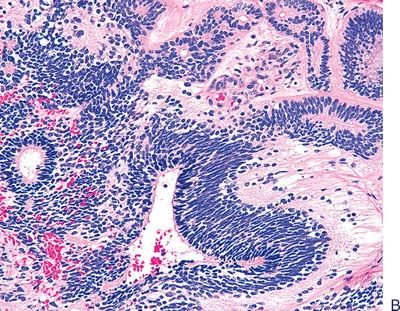
QUESTION 28.4
A. Ganglioneuroma
B. Immature teratoma
C. Malignant mixed germ cell tumor
D. Mature teratoma
E. Thymic carcinoma
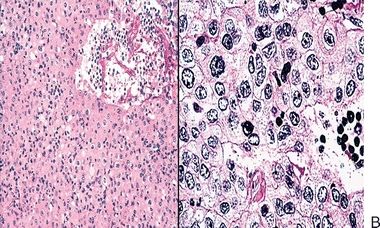
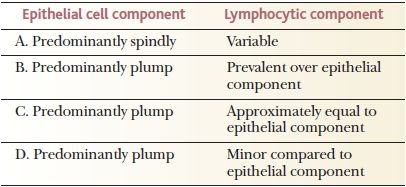
5. A 40-year-old patient undergoes surgery for resection of a mediastinal multicystic mass. The tumor is surrounded by a thick capsule. Histologically, the mass has the microscopic appearance shown in this picture. These features are most consistent with:
QUESTION 28.5
A. Cystic thymoma
B. Lymphoblastic lymphoma
C. Seminoma
D. Thymic carcinoid
E. Thymic cyst
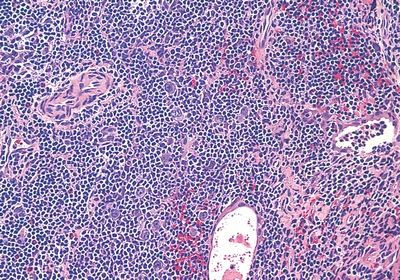
6. Various histologic classifications of lymphoma have been proposed that are usually based on morphologic features of epithelial neoplastic cells (spindle vs. plump shape) and prevalence of lymphoid versus epithelial cells. The following table lists several types of thymomas that differ in such histologic parameters. Which of these cases is associated with the best prognosis?
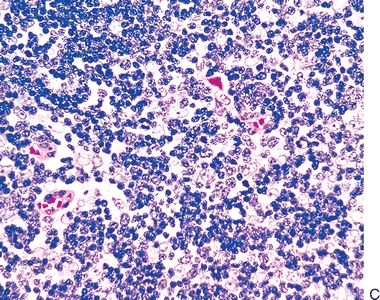
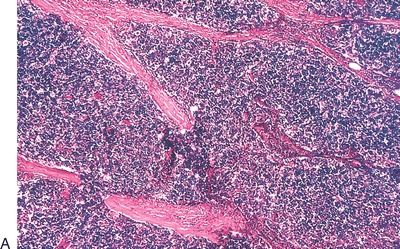
15. A thymic biopsy reveals the histopathologic changes depicted in this photomicrograph. This lesion is associated with:
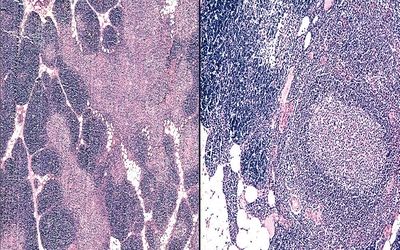
QUESTION 28.15
A. Castleman disease
B. DiGeorge syndrome
C. Hodgkin disease
D. Myasthenia gravis
E. Seminoma
16. A 33-year-old woman with myasthenia gravis undergoes resection of an enlarged thymic gland. Which of the following features favors lymphocyte-predominant thymoma over thymic hyperplasia?
A. Effacement of thymic architecture
B. Foci of medullary differentiation
C. Keratin immunoreactivity in an arborizing pattern
D. Serum lakes in perivascular location
E. All of the above
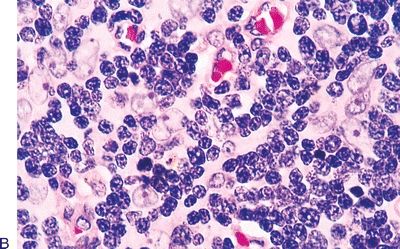
17. A mediastinal lesion comes to the pathologist’s attention. The patient has fever, anemia, weight loss, and hypergammaglobulinemia. Histologically, the specimen displays the features shown in this photomicrograph. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
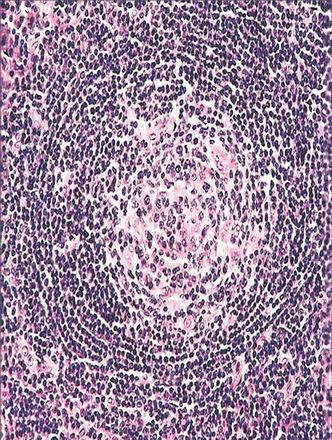
QUESTION 28.17
A. Castleman disease
B. Lymphocyte-predominant thymoma
C. Lymphoid hyperplasia
D. Normal thymus
E. Thymic carcinoma
18. A 33-year-old man presents with a thymic mass and an elevated white blood cell count. A thymic resection shows histologic features highly suggestive of lymphocyte-predominant thymoma, but lymphoblastic lymphoma cannot be ruled out. Which of the following immunostains is most helpful in this differential diagnosis?
A. CD3
B. CD43
C. CD99 (MIC-2)
D. Cytokeratin
E. Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase
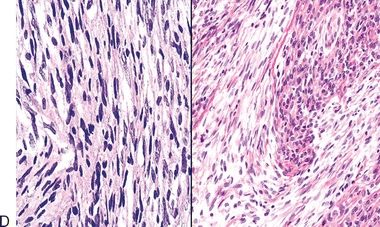
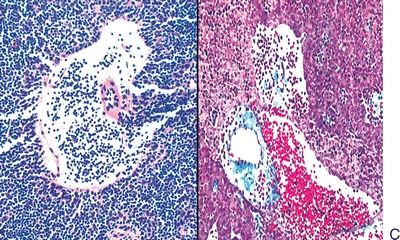
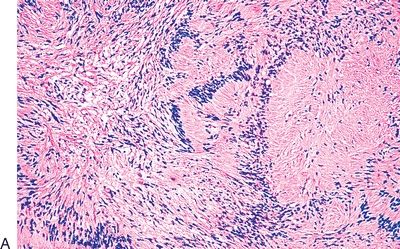
19. The histologic type of thymoma shown in this photomicrograph has a strong resemblance to:
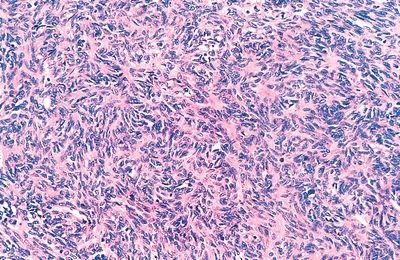
QUESTION 28.19
A. Atypical carcinoid
B. Castleman disease
C. Fibrous histiocytoma
D. Schwannoma (neurilemmoma)
E. Solitary fibrous tumor
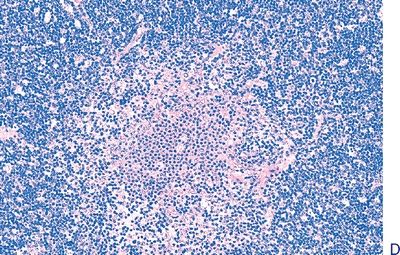
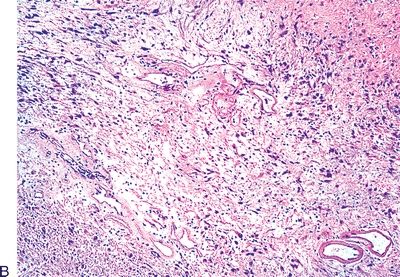
20. The histologic type of thymoma shown in this photomicrograph has a strong resemblance to:
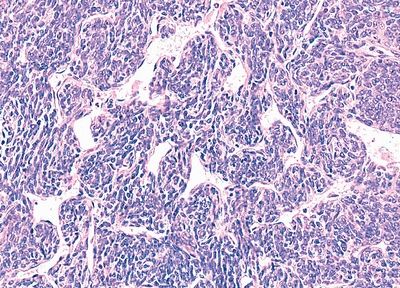
QUESTION 28.20
A. Atypical carcinoid
B. Castleman disease
C. Fibrous histiocytoma
D. Schwannoma (neurilemmoma)
E. Solitary fibrous tumor
A. Early clinical manifestations
B. Lack of well-defined capsule
C. Large size and prominent regressive changes
D. Poorer prognosis compared to retroperitoneal location
E. Presence of clusters of well-differentiated ganglion cells
22. An adult patient presents with Cushing syndrome. Radiologic investigations lead to identification of a mediastinal tumor, which is excised. Histologically, the tumor has the features shown in this photomicrograph. Which of the following supports a diagnosis of small cell neuroendocrine carcinoma over basaloid carcinoma?
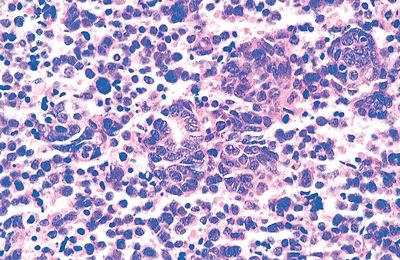
QUESTION 28.22
A. Association with cyst remnants, nucleoli, and deposits of basement membrane-like material
B. Nuclear molding, finely dispersed chromatin, and inconspicuous nucleoli
23. The microscopic appearance of a posterior mediastinal mass in a 5-year-old child is demonstrated in this picture. The differential diagnosis includes neuroblastoma, primitive neuroectodermal tumor (PNET), and rhabdomyosarcoma. Which of the following would support the diagnosis of PNET and rule out the other tumors?
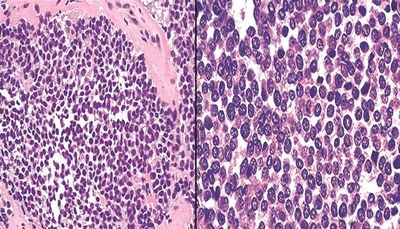
QUESTION 28.23
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree