• Lateral and medial femoral condyles palpable on lateral and medial aspects of knee • Tibial condyles—medial and lateral rounded projections at its proximal end • Medial malleolus—medial projection of tibia at its distal end • Lateral malleolus—expanded distal end of fibula • Tuberosity of 5th metatarsal • Quadriceps femoris—muscle mass of anterior thigh (see Section 7.2, Lower Limb: Hip and Thigh) • Gastrocnemius muscle—muscle mass of posterior leg (see Section 7.4, Lower Limb: Leg) • Palpable as a mass arising from ischial tuberosity • Palpable as medial and lateral superior borders of popliteal fossa • Calcaneal tendon (Achilles tendon) • Tendon of fibularis brevis—palpable at its attachment of base of 5th metatarsal • Tendons of extensor hallucis longus and extensor digitorum longus—visible when toes are forcibly extended • Dilated superficial veins most commonly seen in the posteromedial parts of the lower limb • Result from absent or faulty valves in the communicating veins between the deep and superficial venous systems of the limb • Secondary failure of the saphenofemoral valve may occur. • Stagnation of blood in these vessels predisposes to thrombosis and subsequent inflammation (thrombophlebitis). • Multiaxial, ball-and-socket synovial joint • Acetabulum (see Section 5-2, Bones and Ligaments) • Composed of contributions from ilium, ischium, pubis • Deepened by incomplete ring of fibrocartilaginous labrum, which is attached to bony rim • Ring completed by transverse acetabular ligament, which spans acetabular notch • Attaches to acetabular labrum, transverse acetabular ligament, intertrochanteric line of femur • Lower third of neck of femur is extracapsular. • Blood supply (see Section 7.6, Lower Limb: Neurovasculature) Longest and heaviest bone in body Neck is angled at 115 to 140 degrees (average 126 degrees) relative to long axis of shaft • Contains variable amounts of fat • Cutaneous nerves, such as saphenous and sural • Superficial veins, such as great and small saphenous • Separates subcutaneous tissue from muscles • Prevents bulging of muscles during contraction, which improves efficiency of pumping blood through veins back to the heart • Attaches to inguinal ligament, iliac crests, and sacrum superiorly and is continuous with crural fascia inferiorly (see Section 7.4, Lower Limb: Leg) • Fascial septa from fascia lata divide thigh into three compartments: anterior, medial, and posterior • Lateral thickening of fascia lata • Conjoint aponeurosis of tensor fasciae lata and gluteus maximus muscles • Attaches to tubercle on lateral condyle of tibia (Gerdy tubercle) • Saphenous opening in fascia lata • Extensor of hip: gluteus maximus • Most important function of these muscles: contract to prevent sagging of unsupported side of hip during locomotion, enabling opposite foot to swing through (e.g., Trendelenburg test) • Anterior (= extensor) compartment • Extensor of knee: quadriceps femoris, composed of • Rectus femoris (also flexes hip) • Vastus medialis (also stabilizes patella) • Medial (= adductor) compartment • Obturator externus—laterally rotates hip • Posterior (= flexor) compartment • Biceps femoris—also laterally rotates knee • Semitendinosus—also medially rotates knee • Semimembranosus—also medially rotates knee • Together extend hip (except short head of biceps femoris) and flex knee • Hamstring part of adductor magnus—extends hip • Femoral nerve (descends outside of femoral sheath) • Potential space about 1.5 cm long • Contains loose connective tissue, lymphatic vessels, a deep inguinal lymph node (of Cloquet) • Femoral ring: abdominal entrance to femoral canal, closed by fatty tissue and parental peritoneum • Hernia occurs when part of an abdominal viscus or fat protrudes into the femoral canal through its opening, the femoral ring. • More common in women because of wider femoral ring • Present as a mass (often tender) inferolateral to the pubic tubercle • May enlarge by passing through the saphenous opening • Are at a high risk of strangulation because of hard margins of femoral ring • Common in the elderly, particularly women with osteoporotic bone • Can occur as the result of high-impact accident, such as head-on car collision • May damage branches of medial circumflex femoral artery supplying the femoral head • Results in bleeding into the hip joint and avascular necrosis of the head of the femur
Lower Limb Study Guide
7.1 Topographic Anatomy
Guide
Bony Landmarks
Muscles and Tendons
Clinical Points
Varicose Veins
7.2 Hip and Thigh
Guide
Hip Joint
Femur
Ligament
Attachments
Function
Iliofemoral
ASIS and acetabulum → intertrochanteric line (strong, Y-shaped ligament)
Prevents hyperextension
Ischiofemoral
Acetabular rim → circles superiorly and laterally to medial base of greater trochanter
Prevents hyperextension
Screws femoral head into acetabulum
Pubofemoral
Pubic ramus → laterally and inferiorly to joint capsule
Tightens during extension and abduction
Limits abduction
Transverse acetabular
Joins inferior ends of labrum, crosses acetabular notch
Completes the acetabular ring
Ligament of head of femur
Acetabular notch → fovea of femur (intracapsular but extrasynovial)
Contains artery to head of femur (minute in adults)
Fascial Compartments of the Thigh
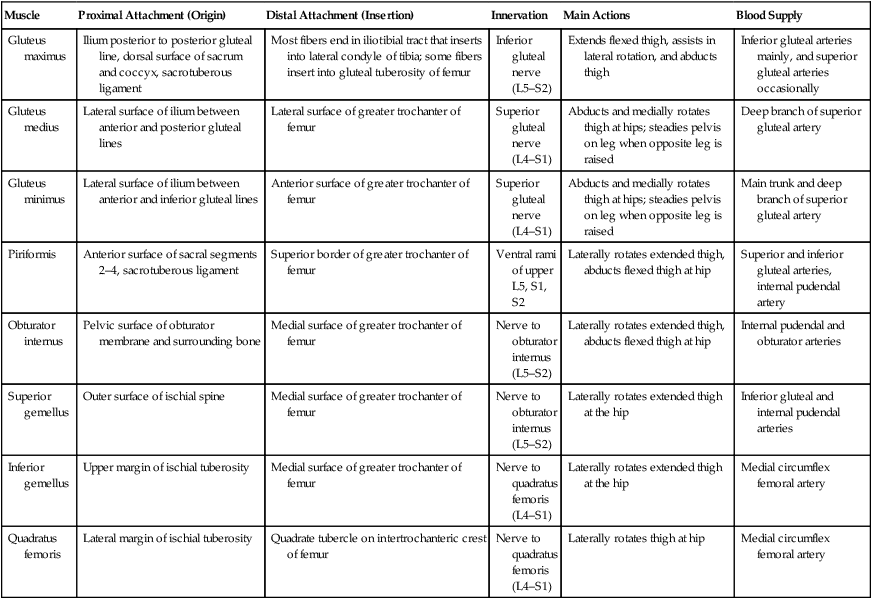
Muscles of the Gluteal Region
Muscle
Proximal Attachment (Origin)
Distal Attachment (Insertion)
Innervation
Main Actions
Blood Supply
Gluteus maximus
Ilium posterior to posterior gluteal line, dorsal surface of sacrum and coccyx, sacrotuberous ligament
Most fibers end in iliotibial tract that inserts into lateral condyle of tibia; some fibers insert into gluteal tuberosity of femur
Inferior gluteal nerve (L5–S2)
Extends flexed thigh, assists in lateral rotation, and abducts thigh
Inferior gluteal arteries mainly, and superior gluteal arteries occasionally
Gluteus medius
Lateral surface of ilium between anterior and posterior gluteal lines
Lateral surface of greater trochanter of femur
Superior gluteal nerve (L4–S1)
Abducts and medially rotates thigh at hips; steadies pelvis on leg when opposite leg is raised
Deep branch of superior gluteal artery
Gluteus minimus
Lateral surface of ilium between anterior and inferior gluteal lines
Anterior surface of greater trochanter of femur
Superior gluteal nerve (L4–S1)
Abducts and medially rotates thigh at hips; steadies pelvis on leg when opposite leg is raised
Main trunk and deep branch of superior gluteal artery
Piriformis
Anterior surface of sacral segments 2–4, sacrotuberous ligament
Superior border of greater trochanter of femur
Ventral rami of upper L5, S1, S2
Laterally rotates extended thigh, abducts flexed thigh at hip
Superior and inferior gluteal arteries, internal pudendal artery
Obturator internus
Pelvic surface of obturator membrane and surrounding bone
Medial surface of greater trochanter of femur
Nerve to obturator internus (L5–S2)
Laterally rotates extended thigh, abducts flexed thigh at hip
Internal pudendal and obturator arteries
Superior gemellus
Outer surface of ischial spine
Medial surface of greater trochanter of femur
Nerve to obturator internus (L5–S2)
Laterally rotates extended thigh at the hip
Inferior gluteal and internal pudendal arteries
Inferior gemellus
Upper margin of ischial tuberosity
Medial surface of greater trochanter of femur
Nerve to quadratus femoris (L4–S1)
Laterally rotates extended thigh at the hip
Medial circumflex femoral artery
Quadratus femoris
Lateral margin of ischial tuberosity
Quadrate tubercle on intertrochanteric crest of femur
Nerve to quadratus femoris (L4–S1)
Laterally rotates thigh at hip
Medial circumflex femoral artery
Muscles of the Thigh
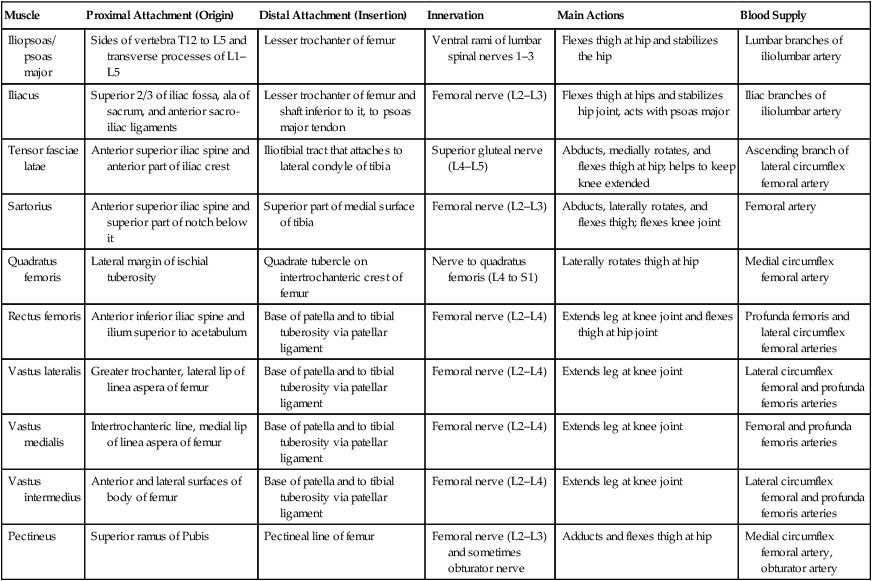
Muscle
Proximal Attachment (Origin)
Distal Attachment (Insertion)
Innervation
Main Actions
Blood Supply
Iliopsoas/ psoas major
Sides of vertebra T12 to L5 and transverse processes of L1–L5
Lesser trochanter of femur
Ventral rami of lumbar spinal nerves 1–3
Flexes thigh at hip and stabilizes the hip
Lumbar branches of iliolumbar artery
Iliacus
Superior 2/3 of iliac fossa, ala of sacrum, and anterior sacro-iliac ligaments
Lesser trochanter of femur and shaft inferior to it, to psoas major tendon
Femoral nerve (L2–L3)
Flexes thigh at hips and stabilizes hip joint, acts with psoas major
Iliac branches of iliolumbar artery
Tensor fasciae latae
Anterior superior iliac spine and anterior part of iliac crest
Iliotibial tract that attaches to lateral condyle of tibia
Superior gluteal nerve (L4–L5)
Abducts, medially rotates, and flexes thigh at hip; helps to keep knee extended
Ascending branch of lateral circumflex femoral artery
Sartorius
Anterior superior iliac spine and superior part of notch below it
Superior part of medial surface of tibia
Femoral nerve (L2–L3)
Abducts, laterally rotates, and flexes thigh; flexes knee joint
Femoral artery
Quadratus femoris
Lateral margin of ischial tuberosity
Quadrate tubercle on intertrochanteric crest of femur
Nerve to quadratus femoris (L4 to S1)
Laterally rotates thigh at hip
Medial circumflex femoral artery
Rectus femoris
Anterior inferior iliac spine and ilium superior to acetabulum
Base of patella and to tibial tuberosity via patellar ligament
Femoral nerve (L2–L4)
Extends leg at knee joint and flexes thigh at hip joint
Profunda femoris and lateral circumflex femoral arteries
Vastus lateralis
Greater trochanter, lateral lip of linea aspera of femur
Base of patella and to tibial tuberosity via patellar ligament
Femoral nerve (L2–L4)
Extends leg at knee joint
Lateral circumflex femoral and profunda femoris arteries
Vastus medialis
Intertrochanteric line, medial lip of linea aspera of femur
Base of patella and to tibial tuberosity via patellar ligament
Femoral nerve (L2–L4)
Extends leg at knee joint
Femoral and profunda femoris arteries
Vastus intermedius
Anterior and lateral surfaces of body of femur
Base of patella and to tibial tuberosity via patellar ligament
Femoral nerve (L2–L4)
Extends leg at knee joint
Lateral circumflex femoral and profunda femoris arteries
Pectineus
Superior ramus of Pubis
Pectineal line of femur
Femoral nerve (L2–L3) and sometimes obturator nerve
Adducts and flexes thigh at hip
Medial circumflex femoral artery, obturator artery
Muscle
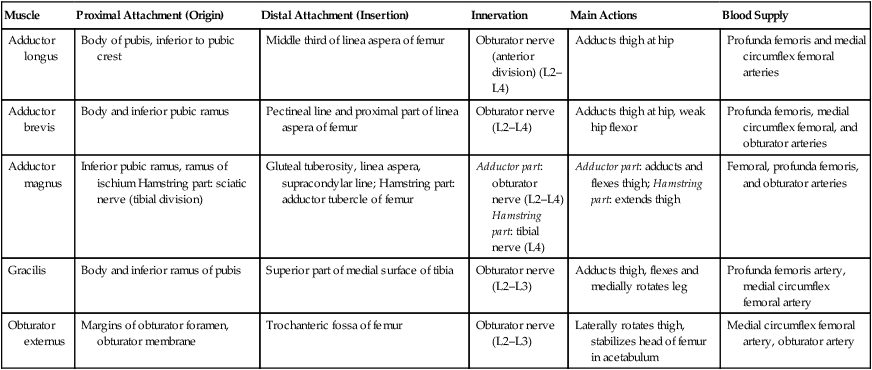
Proximal Attachment (Origin)
Distal Attachment (Insertion)
Innervation
Main Actions
Blood Supply
Adductor longus
Body of pubis, inferior to pubic crest
Middle third of linea aspera of femur
Obturator nerve (anterior division) (L2–L4)
Adducts thigh at hip
Profunda femoris and medial circumflex femoral arteries
Adductor brevis
Body and inferior pubic ramus
Pectineal line and proximal part of linea aspera of femur
Obturator nerve (L2–L4)
Adducts thigh at hip, weak hip flexor
Profunda femoris, medial circumflex femoral, and obturator arteries
Adductor magnus
Inferior pubic ramus, ramus of ischium Hamstring part: sciatic nerve (tibial division)
Gluteal tuberosity, linea aspera, supracondylar line; Hamstring part: adductor tubercle of femur
Adductor part: obturator nerve (L2–L4)
Hamstring part: tibial nerve (L4)
Adductor part: adducts and flexes thigh; Hamstring part: extends thigh
Femoral, profunda femoris, and obturator arteries
Gracilis
Body and inferior ramus of pubis
Superior part of medial surface of tibia
Obturator nerve (L2–L3)
Adducts thigh, flexes and medially rotates leg
Profunda femoris artery, medial circumflex femoral artery
Obturator externus
Margins of obturator foramen, obturator membrane
Trochanteric fossa of femur
Obturator nerve (L2–L3)
Laterally rotates thigh, stabilizes head of femur in acetabulum
Medial circumflex femoral artery, obturator artery
Muscle
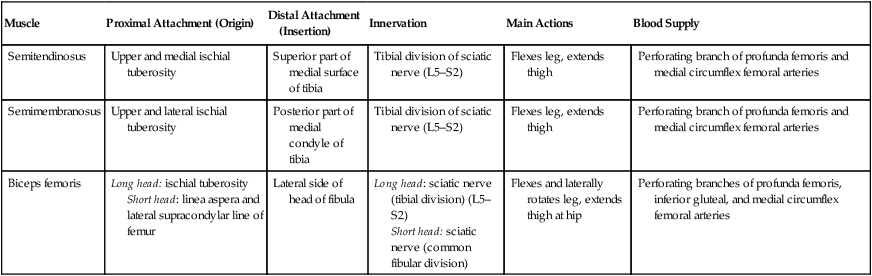
Proximal Attachment (Origin)
Distal Attachment (Insertion)
Innervation
Main Actions
Blood Supply
Semitendinosus
Upper and medial ischial tuberosity
Superior part of medial surface of tibia
Tibial division of sciatic nerve (L5–S2)
Flexes leg, extends thigh
Perforating branch of profunda femoris and medial circumflex femoral arteries
Semimembranosus
Upper and lateral ischial tuberosity
Posterior part of medial condyle of tibia
Tibial division of sciatic nerve (L5–S2)
Flexes leg, extends thigh
Perforating branch of profunda femoris and medial circumflex femoral arteries
Biceps femoris
Long head: ischial tuberosity
Short head: linea aspera and lateral supracondylar line of femur
Lateral side of head of fibula
Long head: sciatic nerve (tibial division) (L5–S2)
Short head: sciatic nerve (common fibular division)
Flexes and laterally rotates leg, extends thigh at hip
Perforating branches of profunda femoris, inferior gluteal, and medial circumflex femoral arteries
Femoral Triangle
Clinical Points
Femoral Hernia
Fractured Neck of Femur (“Broken Hip”)
Basicmedical Key
Fastest Basicmedical Insight Engine



