Lipoma and Angiolipoma
Key Facts
Terminology
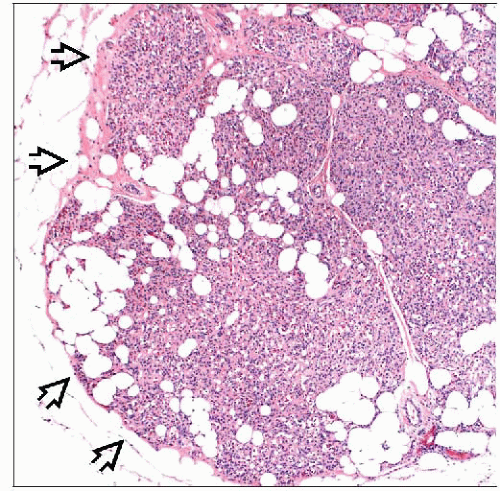
Benign neoplasms consisting of mature adipose cells and blood vessels
Clinical Issues
Lipomas and angiolipomas form soft palpable circumscribed masses
Lesions are benign, and no treatment is necessary
Image Findings
Lipomas consist entirely of adipose tissue and are radiolucent with a thin capsule
Do not require biopsy
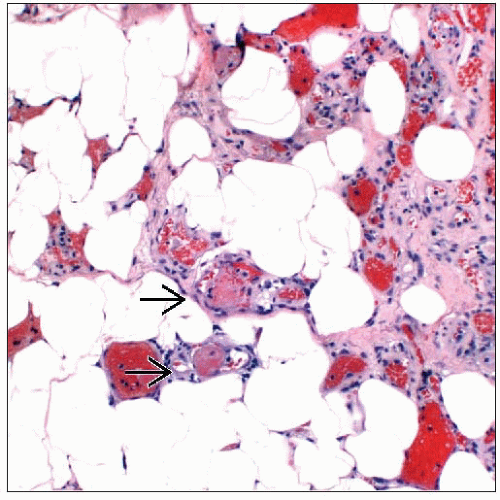
Angiolipomas form dense masses
Generally require biopsy for definitive diagnosis
Microscopic Pathology
Mature adipose tissue without epithelial elements
Adipose cells are uniform in size throughout lesion
After trauma, may show varying degrees of fibrosis, myxoid change, and calcification
Top Differential Diagnoses
Myofibroblastoma/spindle cell lipoma
Hamartoma
Hibernoma
Liposarcoma or angiosarcoma
Reporting Considerations
Histologic findings on fine needle aspiration, core needle biopsy, or in fragmented specimens are nonspecific for lipomas
Clinical, radiologic, and pathologic correlation is often necessary for diagnosis
TERMINOLOGY
Definitions
Benign neoplasms consisting of mature adipose cells and blood vessels
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Age
Most lipomas become clinically apparent in patients 40-60 years old
Presentation
Lipomas and angiolipomas form soft palpable circumscribed masses
Typically present as slowly growing solitary lesions
Also detected at screening mammography
Treatment
Surgical approaches
Lesions are benign, and no treatment is necessary
Palpable masses, or those that are clinically apparent, may be excised for cosmetic reasons or due to patient preference
Superficial or subcutaneous lesions are more likely to be clinically apparent and undergo excision
Prognosis
Benign lesions without risk of local recurrence
Core Needle Biopsies
Histologic features of lipoma on core needle biopsy are nondiagnostic
Radiologic correlation is necessary for a final diagnosis
Lipomas are rarely biopsied as imaging findings are usually diagnostic
Angiolipomas can be diagnosed on core needle biopsies
More commonly biopsied than lipomas due to dense appearance that can mimic carcinomas
IMAGE FINDINGS
Mammographic Findings
Lipomas and angiolipomas form oval, round, or lobulated masses
Lipomas consist entirely of adipose tissue and are radiolucent with thin capsule
Masses with typical appearance of lipoma need not be biopsied
Angiolipomas form dense masses
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree