Lipid-associated Lymphadenopathy
Tariq Muzzafar, MBBS
Key Facts
Terminology
Lymphadenopathy characterized by accumulation of endogenous or exogenous lipids
Etiology/Pathogenesis
Endogenous
Diabetes mellitus, hyperlipidemia, hepatobiliary diseases
Exogenous
Total parenteral nutrition
Mineral oil ingestion
Lipid vehicles used for radiologic imaging or treatment
Clinical Issues
No impact on prognosis
No specific therapy required
Image Findings
± lymphadenopathy; often small or modest
Microscopic Pathology
Overall lymph node architecture is intact
Lipid droplets represented by variably sized empty spaces within histiocytes
Droplets surrounded by histiocytes and multinucleated giant cells of foreign body type
Often marked sinus histiocytosis is present
No well-defined granulomas, fibrosis, or scarring identified
Morphologic changes may persist for years
Ancillary Tests
Sudan black and oil Red-O demonstrate lipid globules on frozen sections
TERMINOLOGY
Definitions
Lymphadenopathy characterized by accumulation of endogenous or exogenous lipids
Can result in foreign body giant cell reaction and lipogranulomas
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Endogenous Etiology
Diabetes mellitus, hyperlipidemia
Hepatobiliary diseases
Cholelithiasis, chronic cholecystitis, xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis
Affects lymph nodes draining biliary system
Lymph node atrophy and fatty replacement in
Physiologic regression with age, obesity, radiation therapy
Miscellaneous
Hematomas, cholesterol deposits, xanthomatous lesions, mucinous tumors, fat emboli, necrotic fat
Exogenous Sources
Total parenteral nutrition
Lipid constituents accumulate in macrophages leading to
Splenomegaly, hepatomegaly, lymphadenopathy
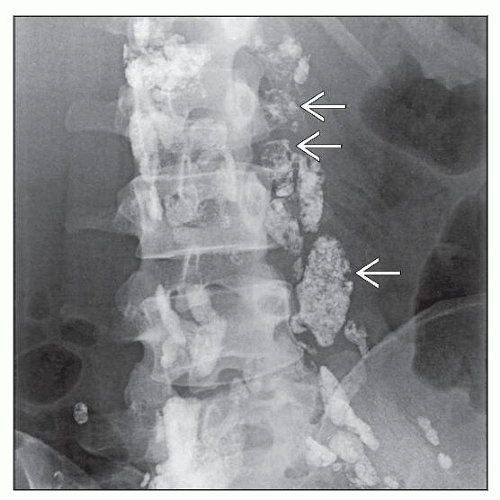
Lipid vehicles used in contrast media of bipedal lymphography
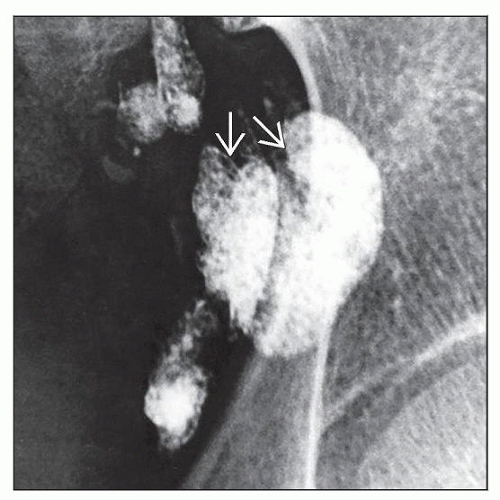
In past, standard for assessing & staging abdominal & pelvic lymph nodes (e.g., lymphangiogram)
Ethiodol (iodinated ethyl ester of fatty acids of poppy seed oil)
Lipiodol (iodinated glycerol ester)
Lipid vehicles used in injected sustained release depot drug preparations
Sclerosing agents injected into hemorrhoids
Mineral oil
Ingestion in industrialized countries
Mesenteric, celiac, portohepatic, paraaortic, mediastinal lymph nodes
CLINICAL ISSUES
Site
Lymph nodes
Liver, spleen, bone marrow can also be affected
Treatment
No specific therapy required
Prognosis
No impact on prognosis
IMAGE FINDINGS
Radiographic Findings
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree