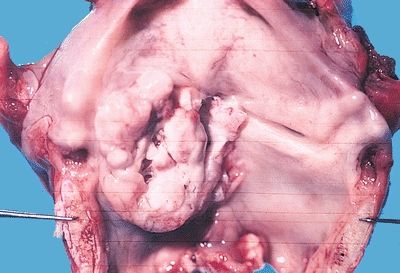
QUESTION 22.2
A. Exposure to alcohol
B. Exposure to cigarette smoking
C. Inherited mutations of the epidermal growth factor receptor gene
D. Viral infection
E. Voice overuse
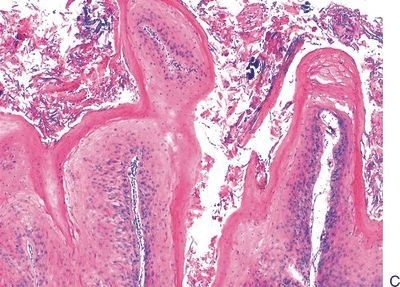
3. The following photomicrographs (A through E) demonstrate various squamous intraepithelial lesions detected by biopsy of the laryngeal mucosa. Arrange the pictures in the following order: hyperplasia, mild dysplasia, moderate dysplasia, severe dysplasia, and carcinoma in situ.
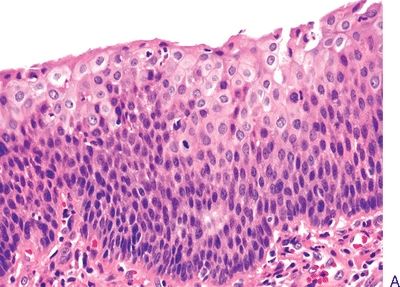
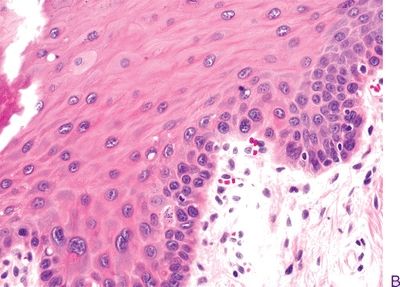
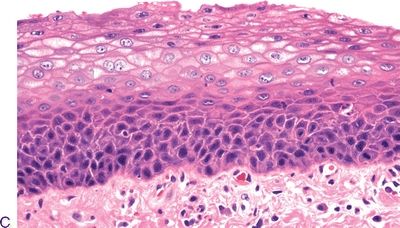
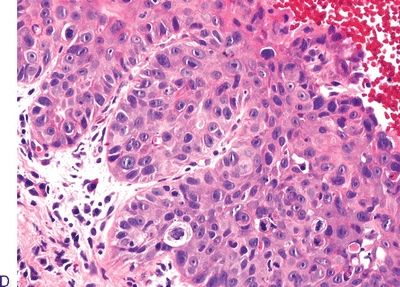
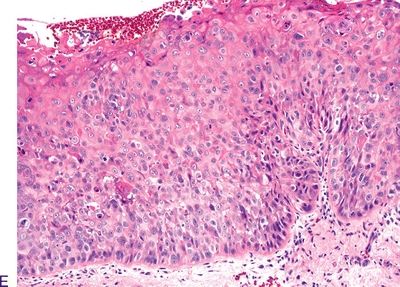
QUESTION 22.3
A. Glottic
B. Subglottic
C. Supraglottic
D. Transglottic
5. Which of the following histologic parameters is of prognostic significance in laryngeal SCC and should be documented in the pathology report?
A. Angiolymphatic invasion
B. Grade
C. Margin status
D. Perineural infiltration
E. All of the above
Questions 6–8. The following three photomicrographs show three different variants of laryngeal SCC. Match each description with the corresponding variant.
A. Papillary squamous cell carcinoma
B. Spindle cell carcinoma
C. Verrucous carcinoma
6. An exophytic tumor typically involving the vocal cords, characterized by a verrucous-like surface with abundant keratosis and parakeratosis. There is little atypia. It is deeply infiltrating and locally destructive but does not metastasize. Excellent prognosis.
7. A usually glottic tumor that exhibits a mesenchymal, sarcomatoid appearance and brisk mitotic activity. It shows immunoreactivity for keratin in up to 75%.
8. A tumor resembling laryngeal papilloma and composed of filiform fronds covered by stratified squamous epithelium showing full-thickness dysplasia. Prognosis is better than conventional SCC.
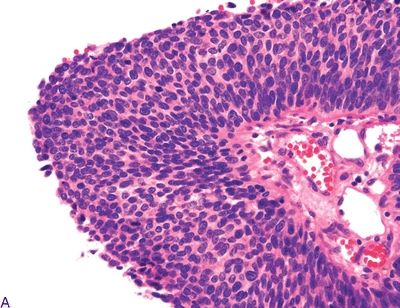
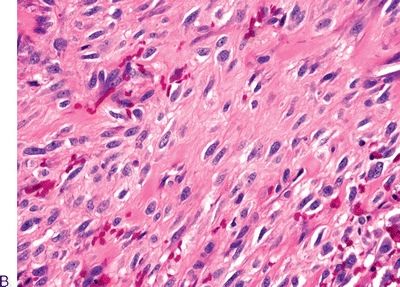
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree