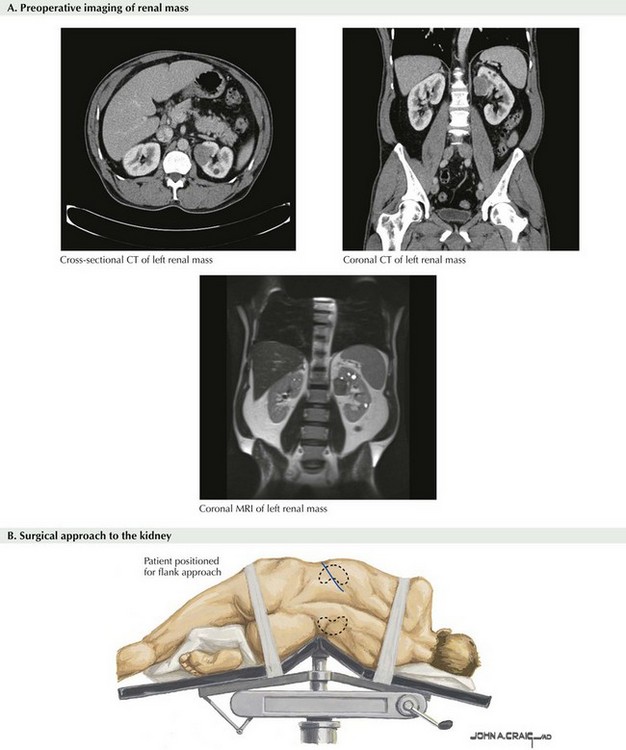
Chapter 53 Typically, a contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CT) scan or a magnetic resonance (MR) image is obtained before surgery. Although not necessarily required, CT and MRI offer precise mapping of the kidney, its vasculature, and relation to adjacent organs. Also, imaging of the renal vein and vena cava helps ensure no evidence of tumor thrombus and provides preoperative clinical staging. It is also prudent to visualize the contralateral kidney to confirm adequate function. Cross-sectional images are usually sufficient, but coronal images can be extremely helpful as well (Fig. 53-1, A). For a left radical nephrectomy, the patient is placed in the right lateral decubitus position with the left flank up (Fig. 53-1, B). The patient is centered over the break in the bed. The lower leg is bent and the top leg straight, and the dependent hip, knee, and ankle padded appropriately. Pillows can be placed between the legs. An axillary roll should be placed under the axilla, to protect from nerve damage. The patient’s lower arm is placed straight out on an arm board, and the upper arm should be secured to an upper arm board. The upper arm must be safely positioned away from the working field to ensure full access to laparoscopic instrumentation.
Laparoscopic Transperitoneal Radical Nephrectomy
Preoperative Imaging
Patient Positioning and Trocar Placement
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree