Juvenile Granulosa Cell Tumor
Steven S. Shen, MD, PhD
Jae Y. Ro, MD, PhD
Key Facts
Terminology
Testicular tumor that is multicystic and composed of multiple follicles lined by granulosa and theca-like cells
Clinical Issues
Rare, but is most common congenital testicular neoplasm (6.6 % of all prepubertal testicular tumors)
Infants younger than 2 years old; most common testis tumor in infants < 6 months
Macroscopic Features
Well-circumscribed or partially encapsulated multicystic mass with solid yellow and papillary areas
Microscopic Pathology
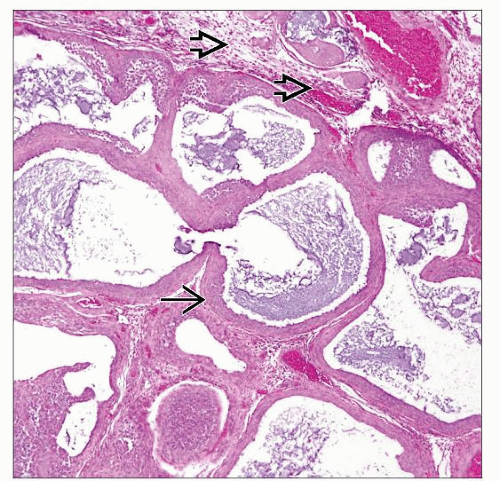
Multiple irregular cystic areas interspersed with solid areas
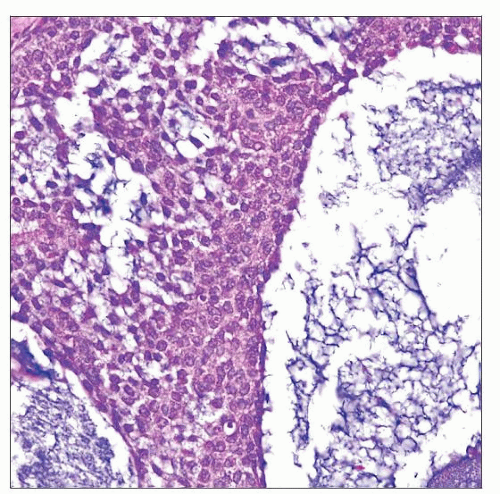
Variably sized follicles lined by bland-looking oval round cells arranged in single or multiple layers with outer layers resembling theca cells
Granulosa cells have round to ovoid nuclei, inconspicuous nucleoli, scanty, vacuolated cytoplasm
Mitotic activity is usually evident and often prominent
Basophilic to faintly eosinophilic fluid within follicles
Call-Exner bodies and nuclear grooves, often seen in adult GCT are absent
Ancillary Tests
Positive for Cam5.2, vimentin, S100; focal actin-sm, inhibin-α, CD99
Negative for EMA/MUC1, cytokeratin, α-fetoprotein, PLAP, Podoplanin(D2-40), Oct3/4, SALL4, glypican-3, CD45(LCA)
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Juvenile granulosa cell tumor (JGCT)
Definitions
Testicular tumor that is multicystic and composed of multiple follicles lined by granulosa and theca-like cells occurring predominantly in infants
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
Extremely rare in testis
Most common testicular tumor in infants
6.6% of all prepubertal testicular tumors
Age
Infants younger than 2 years (most younger than 6 months)
Rarely occurs in adults
Presentation
Painless scrotal or abdominal mass
Associations
Undescended testes
Gonadal dysgenesis with chromosomal abnormality affecting Y chromosome or 45X/46XY mosaicism (Denys-Drash syndrome)
Contralateral testis is often undescended
No known presentation with gynecomastia or endocrine disorders
Treatment
Surgical approaches
Orchiectomy is curative
Partial orchiectomy (testis sparing) may be option
Prognosis
Clinically benign
Malignant behavior or metastasis has not been reported
IMAGE FINDINGS
General Features
Complex, multiseptated, hypoechoic mass on ultrasonography
MACROSCOPIC FEATURES
General Features
Well-circumscribed or partially encapsulated multicystic mass with solid yellow and papillary areas
Size
Range: 0.8-6.0 cm
MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY
Histologic Features
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree