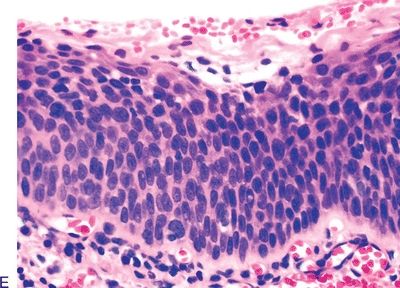
QUESTION 19.1
A. Granular cell tumor
B. Masson hemangioma
C. Peripheral giant cell granuloma
D. Pyogenic granuloma
E. Verruciform xanthoma
2. The majority of solitary papillomas of the oral cavity are associated with:
A. Frank koilocytosis
B. HPV types 6 and 11
C. HPV types 16 and 18
D. Progression to carcinoma
E. Squamous dysplasia
3. With respect to risk factors, the majority of cases of oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma in the United States are associated with:
A. Chronic trauma
B. Iron deficiency
C. Lifestyle
D. Occupation
E. Viruses
4. A 40-year-old man undergoes resection of a tumor located in the right palatine tonsil, which histologically is a squamous cell carcinoma (SCC). The patient does not smoke or drink alcohol. Further investigations reveal presence of HPV DNA in the tumor. Which of the following is correct regarding this form of SCC?
A. Aberrant overexpression of p16 is usually present.
B. Buccal mucosa is the most frequent site.
C. HPV types 6 and 11 are most frequently associated.
D. It has a worse prognosis compared to smoking-related SCC.
E. Its incidence is declining in the United States.
5. Which of the following is the most frequent morphologic type of HPV-related OPC?
A. Keratinizing squamous cell carcinoma
B. Nonkeratinizing squamous cell carcinoma
C. Nonkeratinizing squamous cell carcinoma with maturation
D. Undifferentiated carcinoma
E. Other types
6. A 55-year-old man presents with the oral lesion shown in this photograph. The lesion cannot be scraped off or can be attributed to a known condition. Which of the following is the most frequent histologic substrate of this lesion?
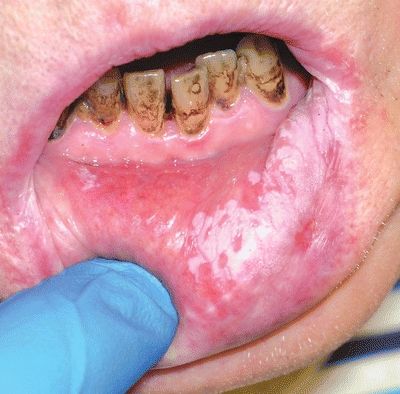
QUESTION 19.6
A. Hyperkeratosis
B. Dysplasia
C. Carcinoma in situ
D. Invasive carcinoma
7. A 60-year-old man presents with the oral lesion shown in this picture. Which of the following is the most frequent histologic substrate of this lesion?
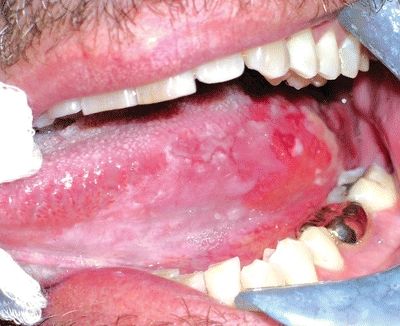
QUESTION 19.7
A. Hyperkeratosis
B. Dysplasia
C. Carcinoma in situ
D. Invasive carcinoma
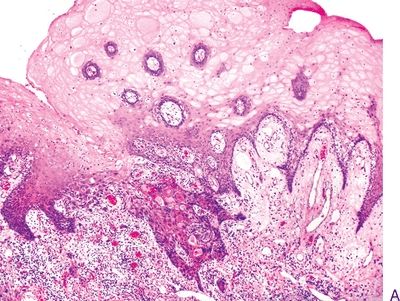
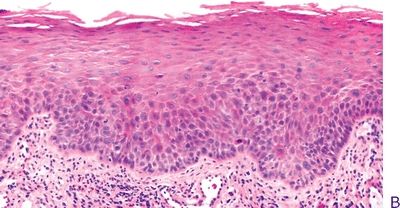
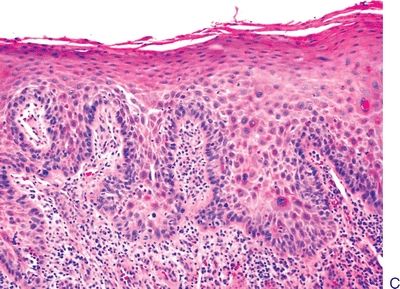
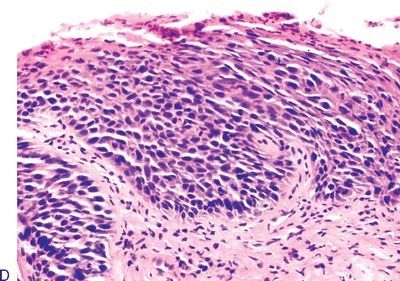
Questions 8–13. Match the microscopic diagnosis with the corresponding oral epithelial lesion in the photomicrograph.
14. Of the histopathologic parameters listed below, which one is the most significant predictor of regional lymph node metastasis in oropharyngeal SCC?
A. Host response
B. Lymph node reaction pattern
C. Pattern of invasion
D. Perineural invasion
E. Tumor grade
15. Which of the following is true about evaluation of resection margins in the surgical treatment of oropharyngeal carcinoma?
A. Intraoperative assessment is not reliable in assessing margins.
B. Postoperative radiation therapy is ineffectual when margins are positive.
C. Positive margins are associated with 10% recurrence rate.
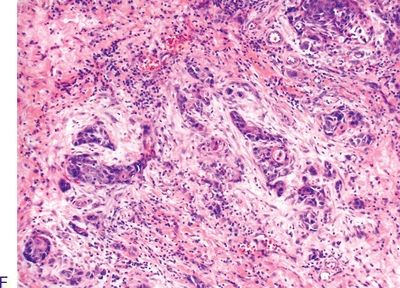
16. An elderly patient presents with a large fungating mass growing from the lower lip and invading contiguous soft tissues and the mandible. Grossly, the lesion appears as a raised, plaque-like mass with white and red areas, as shown in this photograph. These characteristics are most consistent with:
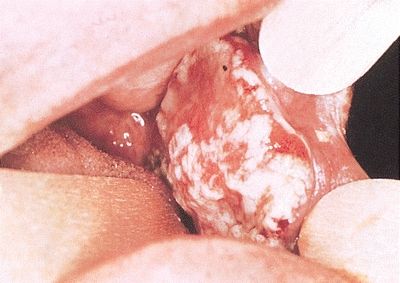
QUESTION 19.16
A. Adenosquamous cell carcinoma
B. Basaloid squamous cell carcinoma
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree