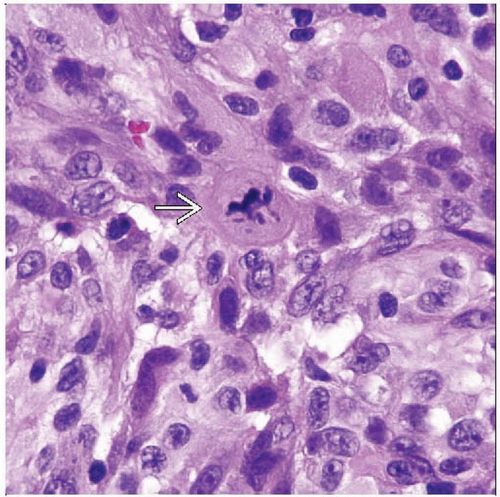
Interdigitating Reticulum Cell Sarcoma
Wesley O. Greaves, MD
L. Jeffrey Medeiros, MD
Cyril Fisher, MD, DSc, FRCPath
Key Facts
Clinical Issues
Wide age range
Single lymph nodes most commonly involved
Cervical, axillary, or inguinal groups
Slow-growing, asymptomatic mass
Rare cases associated with B- or T-cell lymphomas or leukemias
Microscopic Pathology
Partial or complete replacement of lymph node architecture
Sheets, whorls, nests, or fascicles
Spindle-shaped or epithelioid cells
Cytologic atypia can be mild or prominent
Ancillary Tests
Immunohistochemistry
S100 strongly positive
Fascin(+)
CD68, CD45, lysozyme variable
Molecular genetics
HUMARA has shown clonality in small subset of cases tested
Antigen receptor genes are usually in germline configuration
No chromosomal translocations
IDC sarcoma in patients with follicular lymphoma carry IgH rearrangements and t(14;18)/IgH-BCL2
Top Differential Diagnoses
Langerhans cell sarcoma
Follicular dendritic cell sarcoma
Histiocytic sarcoma
Melanoma
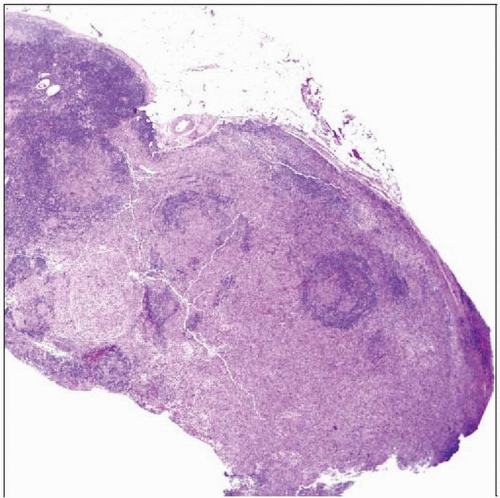 Interdigitating dendritic cell sarcoma subtotally replacing lymph node shows that the neoplasm tends to spare lymphoid follicles. The neoplasm was S100 protein(+). |
TERMINOLOGY
Synonyms
Interdigitating dendritic cell (IDC) tumor
Interdigitating dendritic reticulum cell sarcoma
Definitions
Neoplastic proliferation of cells with immunophenotype similar to normal IDCs
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Postulated Normal Cell Counterpart is IDC
Antigen-presenting cell involved in T-cell immunity
Derived from CD34(+) lymphoid/myeloid progenitor cell in bone marrow that homes to lymph node
Normally found in
T-cell regions of lymph node
Periarteriolar lymphoid sheaths
Interfollicular areas of extranodal lymphoid tissue
Concept of “Transdifferentiation”
Rare patients with histiocytic neoplasms also have clonally related B-cell lymphoma
Usually B-cell lymphoma precedes histiocytic neoplasm
IDC sarcoma and follicular lymphoma
Histiocytic sarcoma and follicular lymphoma
IDC sarcoma and chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma
Histiocytic sarcoma and splenic marginal zone lymphoma
Histiocytic neoplasms associated with follicular lymphoma share
t(14;18)(q32;q21)/BCL2-IgH &/or identical IgH gene rearrangements
Histiocytic tumors and nonfollicular B-cell lymphomas share identical IgH gene rearrangements
B-cell lymphoma might transform to histiocytic phenotype via “transdifferentiation”
Possibly due to loss of key components of B-cell differentiation
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
Very rare
Age
Most patients are adults; median: 6th-7th decade
Youngest patient reported was 2 years old
Gender
Male to female ratio = 1.2:1
Site
Lymph node
Most commonly a single lymph node is involved
Cervical, axillary, or inguinal lymph node groups most often affected
Extranodal sites can be involved
Skin and soft tissue most common
Liver and spleen
Gastrointestinal tract, lung, kidney
Bone marrow is involved in < 20% of patients
Presentation
Slow-growing, asymptomatic mass is most common
Systemic symptoms occur in subset
Fever, night sweats, fatigue
Some have IDC sarcoma and another hematopoietic neoplasm including
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma
Mycosis fungoides
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (mostly of T-cell lineage)
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree