Infectious Mononucleosis
Pei Lin, MD
Key Facts
Etiology/Pathogenesis
Epstein-Barr virus infection
Clinical Issues
Fever
Pharyngitis
Lymphadenopathy
Microscopic Pathology
Follicular and interfollicular hyperplasia
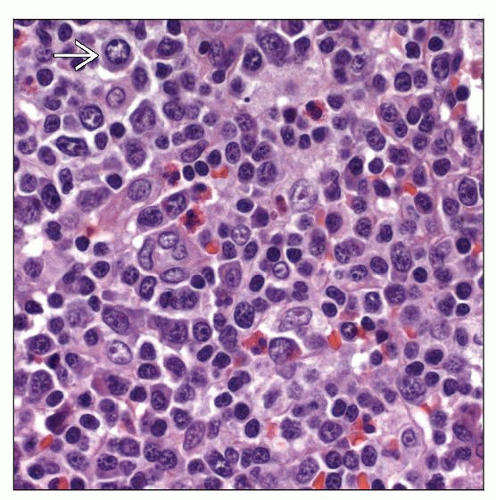
Range of cells from small mature forms to immunoblasts
Ancillary Tests
Proliferating lymphocytes in peripheral blood and lymphoid organs are largely CD3(+), CD8(+) T cells
Immunoblasts are CD30(+) and CD45(+)
EBV encoded early RNA (EBER) in situ hybridization highlights infected cells
Top Differential Diagnoses
Classical Hodgkin lymphoma
Peripheral T-cell lymphoma
Diagnostic Checklist
Symptom complex
Preserved overall architecture; marked follicular and interfollicular hyperplasia
Spectrum of small to large cells with many intermediate forms
No Reed-Sternberg cells or variants
Predominantly CD3(+),CD8(+) T cells
Positive serology or EBER
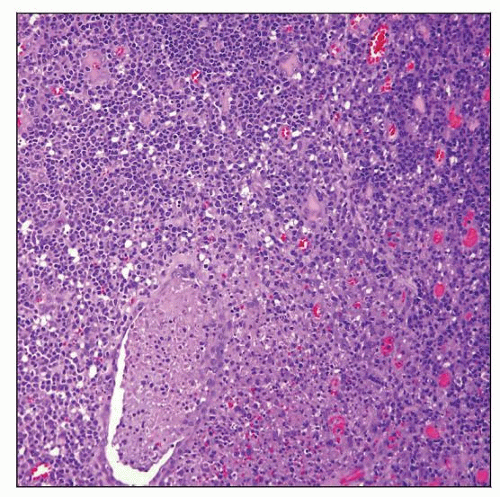 Epstein-Barr virus infection involving tonsil. Marked lymphoid hyperplasia with many tingible body macrophages, with focal karyorrhexis and exudate, are shown. |
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Infectious mononucleosis (IM)
Synonyms
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) lymphadenitis, Pfeiffer disease, glandular fever
Definitions
Acute lymphadenitis induced by EBV infection
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Infectious Agents
Epstein-Barr virus
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Age
Mostly adolescents and young adults in USA
Even younger age in developing countries
Gender
No gender preference
Presentation
Fever
Pharyngitis
Lymphadenopathy
Peripheral blood lymphocytosis of atypical lymphocytes
Laboratory Tests
Monospot test (a.k.a. heterophile antibody test)
EBV-specific antibody tests by immunofluorescence
Elevated IgM antiviral capsid antigen (VCAs) and absence of antibodies to EBV nuclear antigen (anti-EBNA) indicate acute infection
Treatment
Options, risks, complications
Observation is sufficient in most cases as disease resolves by itself
Infection may be complicated by rupture of spleen or hepatitis
Prognosis
Usually self-limited; EBV rarely fatal, mostly in patients with immunodeficiency
EBV can also cause hemophagocytic syndrome or chronic active EBV infection
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree