Chapter 4 Immunopathology
2 List key facts about T lymphocytes
 The specific surface antigen is antigen-specific T-cell receptor (TCR), which can be composed of αβ (95% of T cells) or γσ heterodimers. Each T cell has a unique TCR, reflecting a unique rearrangement of the genes (marker of clonality).
The specific surface antigen is antigen-specific T-cell receptor (TCR), which can be composed of αβ (95% of T cells) or γσ heterodimers. Each T cell has a unique TCR, reflecting a unique rearrangement of the genes (marker of clonality). The common surface marker present on all T lymphocytes is nonvariable CD3 protein (pan T-cell marker).
The common surface marker present on all T lymphocytes is nonvariable CD3 protein (pan T-cell marker). There is functional diversity of T-cell populations; CD4+ helper/inducer cells constitute approximately 60% of mature T lymphocytes, and CD8+ suppressor/cytotoxic cells constitute approximately 30% of mature T lymphocytes. Furthermore, CD4+ cells differ in their ability to secrete cytokines: The TH1 subset secretes IL-2 and IFN-γ, whereas TH2 secretes IL-4 and IL-5.
There is functional diversity of T-cell populations; CD4+ helper/inducer cells constitute approximately 60% of mature T lymphocytes, and CD8+ suppressor/cytotoxic cells constitute approximately 30% of mature T lymphocytes. Furthermore, CD4+ cells differ in their ability to secrete cytokines: The TH1 subset secretes IL-2 and IFN-γ, whereas TH2 secretes IL-4 and IL-5.3 List key features of B lymphocytes
 Antigen-specific surface immunoglobulin M (IgM) is the consequence of the unique gene rearrangements and a marker of B-cell clonality.
Antigen-specific surface immunoglobulin M (IgM) is the consequence of the unique gene rearrangements and a marker of B-cell clonality. Two more nonvariable transmembrane proteins (Igα and Igβ) form a heterodimer that is a part of the B-cell receptor complex.
Two more nonvariable transmembrane proteins (Igα and Igβ) form a heterodimer that is a part of the B-cell receptor complex.4 List key features of natural killer (NK) cells
 They are CD3 negative and do not rearrange the CD3 gene but do express some surface T-cell markers. They express receptors for Fc of IgG (also known as CD16), which enables them to lyse IgG-coated target cells.
They are CD3 negative and do not rearrange the CD3 gene but do express some surface T-cell markers. They express receptors for Fc of IgG (also known as CD16), which enables them to lyse IgG-coated target cells. They can kill a variety of virus-infected cells and some tumor cells without prior sensitization (i.e., “natural” killer). NK cells express inhibiting receptors for class I major histocompatability complex (MHC) molecules present on all nucleated cells. If a virus or a neoplastic transformation altered the expression of MHC class I molecules, the inhibition is interrupted and the NK cell attacks the altered cell (causing cell lysis).
They can kill a variety of virus-infected cells and some tumor cells without prior sensitization (i.e., “natural” killer). NK cells express inhibiting receptors for class I major histocompatability complex (MHC) molecules present on all nucleated cells. If a virus or a neoplastic transformation altered the expression of MHC class I molecules, the inhibition is interrupted and the NK cell attacks the altered cell (causing cell lysis).7 List key features of cytokines
 Cytokines are soluble signaling molecules secreted by a variety of cells, both of the immune and the nonimmune system.
Cytokines are soluble signaling molecules secreted by a variety of cells, both of the immune and the nonimmune system. They can act on the same cell that secreted them (autocrine effect), on the cells in close proximity (paracrine effect), or on remote cells after being transported through the bloodstream (endocrine effect).
They can act on the same cell that secreted them (autocrine effect), on the cells in close proximity (paracrine effect), or on remote cells after being transported through the bloodstream (endocrine effect).10 What is the pathogenesis of hypersensitivity reactions?
 Binding of antibodies to the antigens on the cell surface, predisposing them to lysis of phagocytosis (type II)
Binding of antibodies to the antigens on the cell surface, predisposing them to lysis of phagocytosis (type II)11 What are the characteristics of type I hypersensitivity (anaphylactic) reactions?
 Develop rapidly (within minutes) following exposure to the antigen in a previously sensitized individual
Develop rapidly (within minutes) following exposure to the antigen in a previously sensitized individual12 Are the type I hypersensitivity reactions localized or systemic?
Type I hypersensitivity reaction may cause a localized or a systemic reaction.
 Localized reaction: If the allergen is confined to the site of contact, localized edema and inflammation typically develop (e.g., hives and rhinitis). This reaction causes only minor discomfort, but it may also be life threatening if it involves the larynx or the bronchial tree (e.g., bronchial asthma).
Localized reaction: If the allergen is confined to the site of contact, localized edema and inflammation typically develop (e.g., hives and rhinitis). This reaction causes only minor discomfort, but it may also be life threatening if it involves the larynx or the bronchial tree (e.g., bronchial asthma).13 What is the pathogenesis of localized type I hypersensitivity reactions?
These reactions involve the interaction of three cell types:
 TH2 lymphocytes: Helper T lymphocytes produce IL-4, which is necessary for stimulation of IgE-secreting B cells.
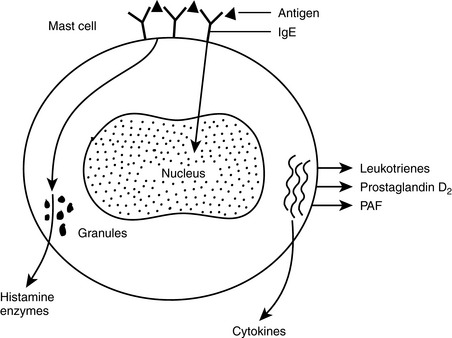
TH2 lymphocytes: Helper T lymphocytes produce IL-4, which is necessary for stimulation of IgE-secreting B cells.First exposure leads to a sensitization and priming of the T and B cells, which interact and produce IgE that binds to the surface of mast cells in tissues. Upon second exposure to the same antigen, cross-linking of IgE on the mast cells occurs. Cell surface changes stimulate two sets of reactions (Fig. 4-1).
 Delayed reaction: This reaction is mediated by substances that need to be synthesized, and their release occurs several hours after the initiation of the immune reaction.
Delayed reaction: This reaction is mediated by substances that need to be synthesized, and their release occurs several hours after the initiation of the immune reaction.14 What occurs during the immediate degranulation of mast cells?
 Biogenic amines: Histamine, the primary mediator of this group, will increase vascular permeability (→ edema) and stimulate smooth muscle contraction (bronchospasm) and secretion of mucus or gastric juices.
Biogenic amines: Histamine, the primary mediator of this group, will increase vascular permeability (→ edema) and stimulate smooth muscle contraction (bronchospasm) and secretion of mucus or gastric juices. Enzymes: Hydrolytic enzymes (e.g., chymase and tryptase) contribute to inflammation by activating kinins and the complement system. Fragments of complement proteins have a chemotactic action and recruit other cells to the site of inflammation.
Enzymes: Hydrolytic enzymes (e.g., chymase and tryptase) contribute to inflammation by activating kinins and the complement system. Fragments of complement proteins have a chemotactic action and recruit other cells to the site of inflammation.15 Which mediators are released from mast cells in a delayed manner?
These mediators, known as secondary mediators and released 6 to 12 hours later, include:
 Lipid-derived mediators: Antigen binding to mast cells triggers an activation of phospholipase A2 that generates arachidonic acid from intracellular lipids. Arachidonic acid is further metabolized into leukotrienes and prostaglandins. Platelet-activating factor (PAF) is also formed.
Lipid-derived mediators: Antigen binding to mast cells triggers an activation of phospholipase A2 that generates arachidonic acid from intracellular lipids. Arachidonic acid is further metabolized into leukotrienes and prostaglandins. Platelet-activating factor (PAF) is also formed.16 What are the symptoms associated with type I hypersensitivity reactions?
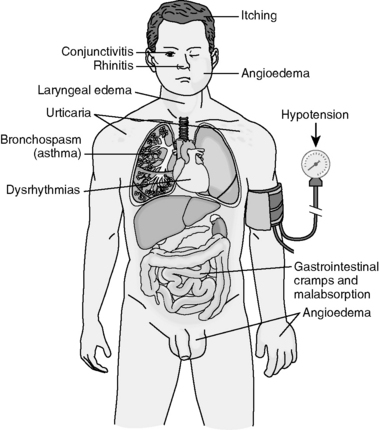
The symptoms depend on the route of exposure, dose of antigen, and the target organ sensitivity (Fig. 4-2).
 Systemic allergen presentation: Typically this reaction occurs upon injection of drugs, hormones, or antisera into a previously sensitized person. Clinically, an anaphylactic shock develops, which is characterized by hypotension due to widespread vascular dilatation, widespread edema, difficulty breathing due to laryngospasm, laryngeal and pulmonary edema, and cardiac dysrhythmia.
Systemic allergen presentation: Typically this reaction occurs upon injection of drugs, hormones, or antisera into a previously sensitized person. Clinically, an anaphylactic shock develops, which is characterized by hypotension due to widespread vascular dilatation, widespread edema, difficulty breathing due to laryngospasm, laryngeal and pulmonary edema, and cardiac dysrhythmia. Localized reactions: Antigen entering the body through the skin, by inhalation, or through ingestion evokes a reaction usually limited to one organ system.
Localized reactions: Antigen entering the body through the skin, by inhalation, or through ingestion evokes a reaction usually limited to one organ system. Upper respiratory tract reactions: Seasonal upper respiratory allergies caused by pollens (>10μm) evoke hay fever. Similar but prolonged allergic rhinitis may result from sensitization to dust mites. In both instances, there is nasal congestion, watery discharge, itching, sneezing, and cough.
Upper respiratory tract reactions: Seasonal upper respiratory allergies caused by pollens (>10μm) evoke hay fever. Similar but prolonged allergic rhinitis may result from sensitization to dust mites. In both instances, there is nasal congestion, watery discharge, itching, sneezing, and cough. Gastrointestinal reactions: Ingestion of allergens may lead to diarrhea, malabsorption syndrome, and protein-losing enteropathy. Massive hypoproteinemia may even cause shock.
Gastrointestinal reactions: Ingestion of allergens may lead to diarrhea, malabsorption syndrome, and protein-losing enteropathy. Massive hypoproteinemia may even cause shock. Bronchopulmonary reactions: Asthma is an example of hypersensitivity of small airways to inhaled allergens. It presents with bronchospasm causing wheezing, hypersecretion of mucus, and coughing. Death due to asphyxia may result from extreme bronchoconstriction and plugging of bronchi with mucus (status asthmaticus).
Bronchopulmonary reactions: Asthma is an example of hypersensitivity of small airways to inhaled allergens. It presents with bronchospasm causing wheezing, hypersecretion of mucus, and coughing. Death due to asphyxia may result from extreme bronchoconstriction and plugging of bronchi with mucus (status asthmaticus).17 What are the characteristics of type II hypersensitivity (cytolytic) reactions?
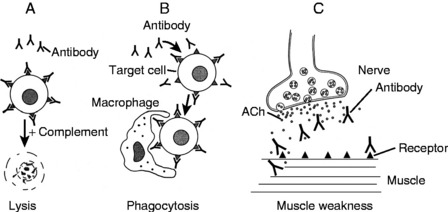
Antigen is present on the surface of the target cell. It may be intrinsic antigen (e.g., Rh D blood antigen) or antigen adsorbed on the cell surface from the environment (e.g., drugs acting as haptens). The antibody interaction with the antigen elicits three reactions (Fig. 4-3):
 Complement-activated cell lysis: Binding of antibody (primarily IgM) to the antigen on the cell surface leads to an activation of complement-activated cell lysis and the formation of the cytolytic membrane attack complex (MAC), which destroys cells (e.g., acute hemolytic transfusion reaction).
Complement-activated cell lysis: Binding of antibody (primarily IgM) to the antigen on the cell surface leads to an activation of complement-activated cell lysis and the formation of the cytolytic membrane attack complex (MAC), which destroys cells (e.g., acute hemolytic transfusion reaction). Antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC): Binding of low-density (primarily IgG) antibodies that act as opsonins is followed by phagocytosis of damaged cells. ADCC typically mediates autoimmune hemolytic anemia and thrombocytopenia.
Antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC): Binding of low-density (primarily IgG) antibodies that act as opsonins is followed by phagocytosis of damaged cells. ADCC typically mediates autoimmune hemolytic anemia and thrombocytopenia. Antibody-mediated cell dysfunction: Binding of stimulatory antibodies to receptors for thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) on thyroid cells may stimulate hypersecretion of thyroid hormones in Graves disease. Binding of antiacetylcholine receptor antibodies at the neuromuscular junction may block nerve transmission and the cause of muscle weakness in myasthenia gravis.
Antibody-mediated cell dysfunction: Binding of stimulatory antibodies to receptors for thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) on thyroid cells may stimulate hypersecretion of thyroid hormones in Graves disease. Binding of antiacetylcholine receptor antibodies at the neuromuscular junction may block nerve transmission and the cause of muscle weakness in myasthenia gravis.18 List important diseases caused by type II hypersensitivity cytotoxic reactions
 Transfusion reaction: This is caused by a mismatched blood transfusion. An infusion of blood of an A blood group donor into a B blood group recipient will result in a massive hemolytic reaction mediated by the natural anti-A blood group antigen in the recipient.
Transfusion reaction: This is caused by a mismatched blood transfusion. An infusion of blood of an A blood group donor into a B blood group recipient will result in a massive hemolytic reaction mediated by the natural anti-A blood group antigen in the recipient. Hemolytic disease of the newborn (erythroblastosis fetalis): This reaction occurs transplacentally and is mediated by maternal IgG antibodies to the fetal Rh+ positive red blood cells (RBCs). It occurs only in Rh− mothers who have been immunized to Rh blood group antigen during the first pregnancy by an Rh+ fetus.
Hemolytic disease of the newborn (erythroblastosis fetalis): This reaction occurs transplacentally and is mediated by maternal IgG antibodies to the fetal Rh+ positive red blood cells (RBCs). It occurs only in Rh− mothers who have been immunized to Rh blood group antigen during the first pregnancy by an Rh+ fetus. Autoimmune hemolytic anemia: This disease results from the production of anti-RBC antibodies that bind to RBC and cause hemolysis. The causes of such an immune reaction are not known.
Autoimmune hemolytic anemia: This disease results from the production of anti-RBC antibodies that bind to RBC and cause hemolysis. The causes of such an immune reaction are not known. Pemphigus vulgaris: This blistering skin disease is caused by antibodies to the proteins forming the intercellular junctions (desmosomes) of the epidermis.
Pemphigus vulgaris: This blistering skin disease is caused by antibodies to the proteins forming the intercellular junctions (desmosomes) of the epidermis.19 What are the characteristics of immune complex–mediated hypersensitivity (type III) reactions?
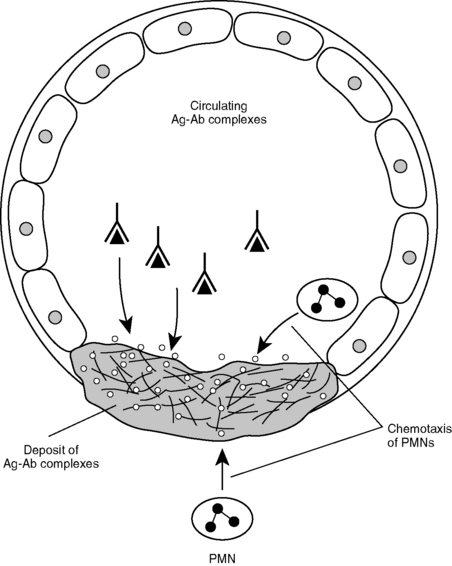
 Binding of antibody to the antigen forms complexes that are not cleared by the reticuloendothelial system but instead are deposited in tissues where they elicit an inflammatory reaction through activation of complement (Fig. 4-4).
Binding of antibody to the antigen forms complexes that are not cleared by the reticuloendothelial system but instead are deposited in tissues where they elicit an inflammatory reaction through activation of complement (Fig. 4-4). Complexes may be formed locally in the tissue or in the circulation and then deposited in various tissues. Either way, aggregated Fc regions of IgG antibodies activate the complement pathway, leading to increased vascular permeability, activation of neutrophils, and tissue necrosis.
Complexes may be formed locally in the tissue or in the circulation and then deposited in various tissues. Either way, aggregated Fc regions of IgG antibodies activate the complement pathway, leading to increased vascular permeability, activation of neutrophils, and tissue necrosis. Antigens capable of inducing type III hypersensitivity reaction may be exogenous (e.g., streptococcal antigens, hepatitis B virus, and heroin) or endogenous (e.g., immunoglobulins and nuclear antigens).
Antigens capable of inducing type III hypersensitivity reaction may be exogenous (e.g., streptococcal antigens, hepatitis B virus, and heroin) or endogenous (e.g., immunoglobulins and nuclear antigens).20 List the most important diseases caused by type III hypersensitivity reaction
 Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE): This disease is caused by circulating immune complexes that deposit in many organs, most often the skin, joints, and kidneys. Circulating blood cells are also often affected, resulting in anemia, leukopenia, and thrombocytopenia.
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE): This disease is caused by circulating immune complexes that deposit in many organs, most often the skin, joints, and kidneys. Circulating blood cells are also often affected, resulting in anemia, leukopenia, and thrombocytopenia. Polyarteritis nodosa: This disease typically affects medium-sized arteries of internal organs, skin, eye, or peripheral nerves in an unpredictable manner.
Polyarteritis nodosa: This disease typically affects medium-sized arteries of internal organs, skin, eye, or peripheral nerves in an unpredictable manner. Acute poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis: This kidney disease typically follows a streptococcal throat infection and the formation of circulating antistreptococcal antibodies, which deposit in the glomerular basement membranes.
Acute poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis: This kidney disease typically follows a streptococcal throat infection and the formation of circulating antistreptococcal antibodies, which deposit in the glomerular basement membranes. Membranous nephropathy: In some forms of this immune-mediated glomerulopathy, there are circulating antigen-antibody complexes that deposit on the epithelial side of the glomerular basement membrane. The disease typically presents as nephrotic syndrome and massive proteinuria.
Membranous nephropathy: In some forms of this immune-mediated glomerulopathy, there are circulating antigen-antibody complexes that deposit on the epithelial side of the glomerular basement membrane. The disease typically presents as nephrotic syndrome and massive proteinuria. Serum sickness: Injection of foreign serums may cause the formation of circulating immune complexes that are deposited in many organs. Most often it presents with a skin rash.
Serum sickness: Injection of foreign serums may cause the formation of circulating immune complexes that are deposited in many organs. Most often it presents with a skin rash.Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree