Histoplasma Lymphadenitis
Tariq Muzzafar, MBBS
Key Facts
Etiology/Pathogenesis
Histoplasma is endemic in
Central America
River valleys of midwestern and south-central USA
Acute disseminated disease occurs in
Immunocompromised subjects including AIDS
Very young and old patients, with fatal outcome
Clinical Issues
Commonly causes pulmonary disease in immunocompetent host
May be asymptomatic or mildly symptomatic
History of immunodeficiency including HIV infection should be sought
Lymph node involvement may be part of disseminated disease
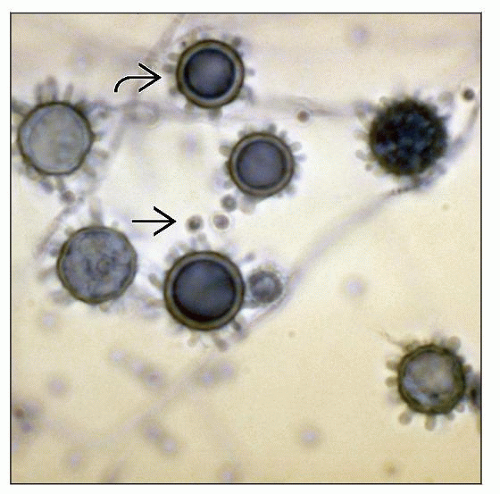
Microscopic Pathology
Granulomatous inflammation
Gomori methenamine silver (GMS) and periodic acid-Schiff (PAS) stains highlight organisms
Ancillary Tests
Culture essential for definitive identification of organism
Identification can be confirmed by DNA hybridization probe assay
Top Differential Diagnoses
Tuberculous lymphadenitis
Sarcoidosis
Kikuchi-Fujimoto lymphadenitis
Infarcted necrotizing lymphadenitis
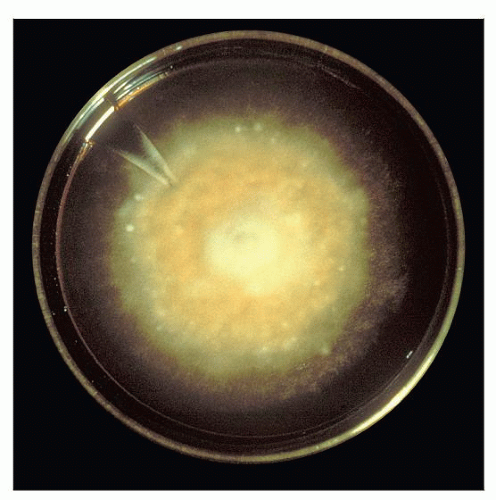 Sabouraud dextrose agar plate culture of Histoplasma capsulatum shows typical fuzzy appearance of mold colony. (CDC Public Health Image Library, #290.) |
TERMINOLOGY
Definitions
Inflammation of lymph nodes due to Histoplasma capsulatum infection
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Worldwide distribution
Endemic in Central America and river valleys of midwestern and south-central USA
More than 80% of population in endemic regions exposed
Natural habitat is acidic soil with high organic content
Bird and bat excrement in soil enhance fungal growth
Soil disruption, demolition, and repair of buildings increase risk of exposure
Acute disseminated disease with fatal outcome in
Immunocompromised subjects including AIDS
Very young and old patients
Chronic disease occurs in immunocompetent middleaged to older adults
Aerosols containing microconidia (spores) of mycelial phase inhaled, causing localized pneumonitis
Hematogenous dissemination occurs until cellular immunity develops in 2-3 weeks
Reactivation may occur in immunosuppression
CLINICAL ISSUES
Presentation
Commonly causes pulmonary disease in immunocompetent host
May be asymptomatic or mildly symptomatic
Heavy exposure can cause diffuse pulmonary disease
More than 50% of adults in endemic areas previously infected
Chronic pulmonary disease occurs with preexisting emphysema and leads to
Cavitation
Bronchopleural fistulae
Pneumothorax
Other clinical presentations
Meningitis, pericarditis, endocarditis
Fibrosing mediastinitis with obstructive symptoms, adrenal involvement, rheumatologic syndromes
Laboratory Tests
Culture
Performed on Sabouraud dextrose agar
Growth can take 4-6 weeks
Organisms grow as large, cottony mycelial colonies with prominent, cross-walled hyphae
Multiple specimens cultured to achieve high yield
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree