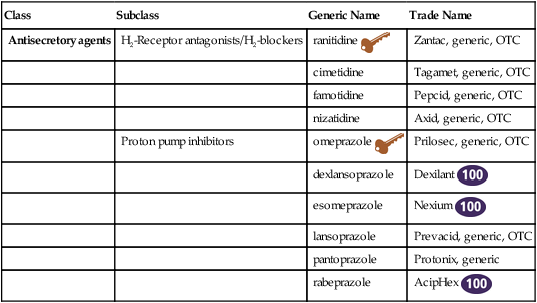
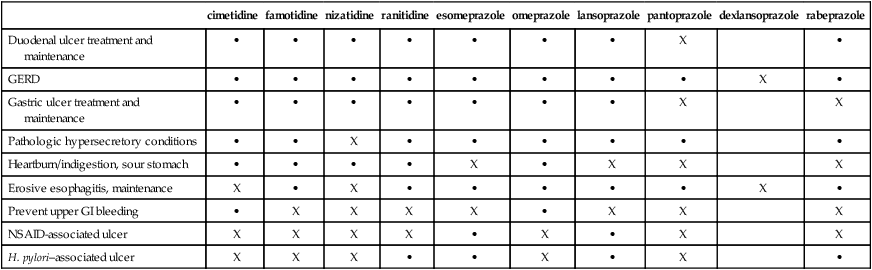
Chapter 27 H2-blockers (H2-receptor antagonists) and PPIs block acid secretion in the stomach but do so via different mechanisms of action. In general, all H2-blockers, except cimetidine, are considered equally effective and have similar side effect profiles. The indications and off-label uses for each agent are listed in Table 27-1. These distinctions are not always observed in practice. TABLE 27-1 Indications and Unlabeled Uses for H2-Blockers and PPIs
Histamine2-Blockers and Proton Pump Inhibitors
Class
Subclass
Generic Name
Trade Name
Antisecretory agents
H2-Receptor antagonists/H2-blockers
ranitidine ![]()
Zantac, generic, OTC
cimetidine
Tagamet, generic, OTC
famotidine
Pepcid, generic, OTC
nizatidine
Axid, generic, OTC
Proton pump inhibitors
omeprazole ![]()
Prilosec, generic, OTC
dexlansoprazole
Dexilant ![]()
esomeprazole
Nexium ![]()
lansoprazole
Prevacid, generic, OTC
pantoprazole
Protonix, generic
rabeprazole
AcipHex ![]()
cimetidine
famotidine
nizatidine
ranitidine
esomeprazole
omeprazole
lansoprazole
pantoprazole
dexlansoprazole
rabeprazole
Duodenal ulcer treatment and maintenance
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
X
•
GERD
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
X
•
Gastric ulcer treatment and maintenance
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
X
X
Pathologic hypersecretory conditions
•
•
X
•
•
•
•
•
•
Heartburn/indigestion, sour stomach
•
•
•
•
X
•
X
X
X
Erosive esophagitis, maintenance
X
•
X
•
•
•
•
•
X
•
Prevent upper GI bleeding
•
X
X
X
X
•
X
X
X
NSAID-associated ulcer
X
X
X
X
•
X
•
X
X
H. pylori–associated ulcer
X
X
X
•
•
X
•
X
•
< div class='tao-gold-member'>
Histamine2-Blockers and Proton Pump Inhibitors
Only gold members can continue reading. Log In or Register to continue

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


