HER2 Positive Carcinoma
Key Facts
Clinical Issues
15-20% of breast carcinomas overexpress HER2
All newly diagnosed invasive breast cancers should be evaluated for HER2
IHC, FISH, and CISH methods have received FDA approval
HER2+BC is associated with poorer prognosis
Higher incidence of lymph node metastases
Distant metastases are often to visceral sites and brain
HER2-targeted treatment is available
HER2+BC shows the highest responses to neoadjuvant therapy
HER2 status also may be predictive for response for different types of chemotherapy and endocrine therapy
Some HER2+BC is resistant to treatment or develop resistance to treatment
May be due to varying numbers of coamplified genes in different cancers or due to heterogeneity of HER2 overexpression
Microscopic Pathology
Majority of HER2+BC are of no special type (“ductal” carcinomas)
Other subtypes that can be HER2(+) are apocrine carcinoma, invasive micropapillary carcinoma, and inflammatory carcinoma
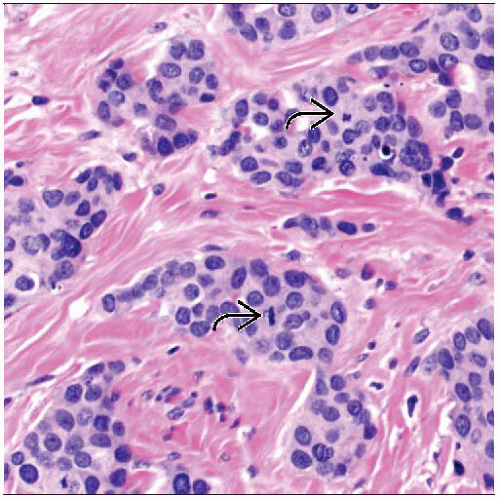
Usually poorly differentiated and have high proliferative rate
Extensive DCIS and multiple foci of invasion are more common than in other subtypes
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
HER2 positive breast cancer (HER2+BC)
Synonyms
HER2 (human epidermal growth factor receptor, HER-2/neu, c-erbB2, NEU, NGL, TKR1, CD340, ERBB2)
Definitions
Carcinomas characterized by overexpression of HER2: 15-20% of all breast carcinomas
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
HER2+BC Biology
HER2 encodes a 185 kDa membrane tyrosine kinase growth factor receptor located on chromosome 17q12
Member of family of genes that includes epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR or HER1)
Gene amplification results in increased mRNA and protein overexpression
HER2 overexpression likely plays role in carcinogenesis and tumor formation
Majority of HER2+BC continues to express HER2 with recurrence (lymph node and distant metastases)
HER2 overexpression increases receptor activation and HER receptor family signaling
Signaling promotes angiogenesis, proliferation, cell survival, invasion, and metastasis
Adjacent genes are coamplified with HER2
Carcinomas vary in number of genes amplified; at minimum 6 genes (and likely several dozen) are coamplified
Only a subset of these genes show overexpression of protein products
Variations in number of coamplified genes may explain some differences in response to HER2-targeted therapy
HER2+BC also frequently displays amplification of other DNA segments
70% of these carcinomas amplify at least 1 other DNA segment
CEP17 (chromosome 17 centromere enumeration probe) sequences are amplified in 10-20% of these carcinomas
True chromosome 17 polysomy (duplication of entire chromosome) is rare: Only 1-2% of cancers
Relationship of CEP17 amplification to HER2 overexpression is unclear
Gene Expression Profiling
Molecular subtypes of breast cancer include luminal A, luminal B, HER2, and basal-like cancers
HER2+BC by gene expression studies are ER negative (10-20% of cancers)
ER(+) luminal B carcinomas (15-20% of cancers) overexpress HER2 in up to 50% of cases
ER positive but often at lower levels than in luminal A carcinomas
HER2 downregulates PR, and many of these carcinomas lack PR expression
Some studies using IHC to classify breast cancers have defined all luminal B carcinomas as HER2 positive
However, up to 50% of luminal B carcinomas by gene expression studies are HER2 negative
HER2 expressing carcinomas detected clinically are included in luminal B and HER2 groups
These patients show similar benefit from HER2-targeted therapy in clinical trials
Approximately 1/2 of HER2 carcinomas are ER positive and 1/2 ER negative
HER2 expression profile includes increased expression pattern for HER2 as well as other adjacent coamplified genes
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
HER2+BC reported in 15-20% of patients
Age
HER2+BC patients are younger (˜ 53 years) than the average woman with breast cancer (˜ 61 years)
HER2+BC is not associated with BRCA1 or BRCA2
Gender
HER2+BC is less common in males than in females
Ethnicity
No significant differences in HER2+BC rates in different ethnic populations have been reported
Laboratory Tests
HER2 overexpression can be documented by evaluation of DNA, mRNA, and protein assays
DNA analysis for gene amplification is usually evaluated by fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH)
Chromogenic in situ hybridization (CISH) is alternative technique
2nd probe often used to evaluate number of copies of centromere 17
Criteria for gene amplification utilize total number of genes or ratio of genes to number of centromere copies
In majority of cases, both methods of evaluation yield same interpretation
If the 2 methods give discordant results (usually due to increased centromere copies), it is not yet clear whether these carcinomas respond to HER2-directed therapy
HER2 mRNA level is evaluated and reported as part of Oncotype DX assay (Genomic Health; Redwood City, CA)
Should not be used to select patients for targeted therapy
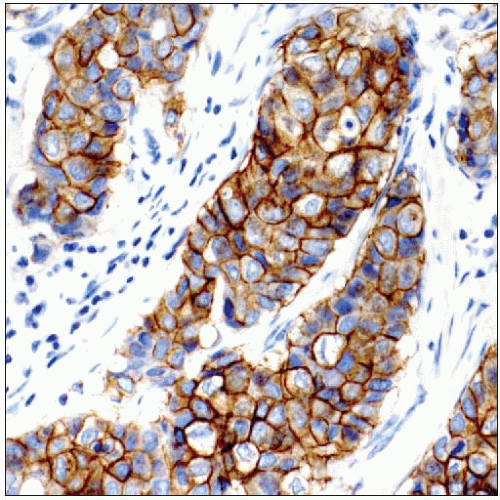
Protein overexpression is analyzed by IHC
Correlation between IHC and FISH results is > 90%
Rare carcinomas may overexpress protein due to mechanisms other than gene amplification
It is easier to detect heterogeneity in HER2 expression and discordant expression patterns for DCIS and invasive carcinoma using IHC
IHC, FISH, and CISH methods have received FDA approval for assessing HER2 status in clinical practice
If HER2(+) is discordant with histologic features (e.g., carcinoma is well differentiated or subtype unlikely to show overexpression), repeat &/or additional studies should be considered
Natural History
HER2+BC is associated with poor prognosis
Higher rate of recurrence and mortality in patients with newly diagnosed breast cancer who do not receive any adjuvant systemic therapy
Early recurrence more commonly seen compared with HER2 negative disease
Small carcinomas (< 1 cm) with negative nodes have worse prognosis if HER2(+)
HER2+BC has worse prognosis if also ER(+)
May be due to higher incidence of lymph node metastases and lower response rates to therapy
Metastatic HER2+BC usually also overexpresses HER2
In rare cases, recurrent or metastatic disease lacks HER2 expression
Likely due to heterogeneity of expression in primary carcinoma with possible selection of subclones after treatment
For example, residual disease after neoadjuvant treatment with HER2-targeted therapy can lack expression in up to 1/3 of cases
HER2+BC more likely to spread early to major visceral sites (brain, lungs, liver, adrenals, ovaries)
With HER2-targeted therapy, progressive visceral disease significantly diminished
CNS metastases more common after treatment with HER2-targeted therapy
May be related to inability of trastuzumab to cross blood-brain barrier
Treatment
Adjuvant therapy
HER2 positivity may be associated with relative, but not absolute, resistance to endocrine therapy
Effect may be specific to selective estrogen receptor modulator therapy, such as tamoxifen
HER2 status may be predictive for either resistance or sensitivity to different types of chemotherapies
HER2 positivity is associated with response to anthracycline therapy
Anthracycline sensitivity may be secondary to coamplification of HER2 with topoisomerase II α (TOP2A)
TOP2A amplification occurs in about 1/3 of HER2+BC and is associated with ER(+)
HER2-targeted therapy has demonstrated remarkable efficacy in both metastatic and adjuvant settings
Trastuzumab (humanized monoclonal antibody) targets an extracellular epitope of HER2 receptor
Trastuzumab improves response, time to progression, and survival when used alone or with chemotherapy in metastatic breast cancer
Adjuvant trastuzumab given during &/or after chemotherapy results in significant improvement in disease-free and overall survival
Lapatinib (small molecule tyrosine kinase inhibitor) improves outcome in patients with advanced disease in combination with chemotherapy
Only patients with HER2+BC are candidates for HER2-targeted therapy
HER2 is a useful marker for therapeutic decision making for patients with breast cancer
HER2(+)/ER(-) carcinomas have best response to neoadjuvant therapy
HER2(+)/ER(+) carcinomas have lesser response to neoadjuvant therapy, and response is related to degree of ER expression
MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY
Histologic Features
Majority are invasive carcinomas of no special histologic type (“ductal carcinomas”)
Majority have high nuclear grade and DNA aneuploidy
Necrosis present in ˜ 40%
Lymphocytic infiltrate in ˜ 60%
More likely to harbor P53 mutations
High mitotic rate and proliferative index
Lymph-vascular invasion more common
More likely to be associated with extensive DCIS and multiple foci of invasion
Lymph node metastasis and > 4 lymph node metastases more common
Some subtypes of breast carcinoma have higher rates of HER2 positivity
Apocrine carcinoma: ˜ 50%
Inflammatory carcinoma: 40-50%
Invasive micropapillary carcinoma: 30-50%
Some subtypes of breast carcinoma do not overexpress HER2 or have very low rate of HER2 positivity (< 5%)
Tubular carcinoma
Mucinous carcinoma
Invasive papillary carcinoma
Triple negative carcinomas (including medullary carcinoma, basal-like carcinoma, adenoid cystic carcinoma, low-grade adenosquamous carcinoma, and metaplastic carcinoma)
Frequency of HER2 expression in invasive lobular carcinoma is dependent on grade
Well- and moderately differentiated lobular carcinomas: < 5%
Edge enhancement can mimic appearance of HER2 positivity
FISH should be used to confirm amplification
Poorly differentiated lobular carcinomas: 50-80%
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree