Granulomatous Lobular Mastitis
Key Facts
Terminology
Specific disease of breast occurring only in parous women and characterized by lobulocentric granulomas
Etiology/Pathogenesis
Association with prior childbirth suggests cell-mediated response to antigen within lobules arising during or after pregnancy
Clinical Issues
Average length of time between pregnancy and presentation: 2 years
Patients present with sometimes tender firm discrete palpable breast mass ranging in size from 1-8 cm
Mass can occur anywhere in breast and typically does not involve nipple
In advanced cases, multiple sinus tracts can open onto skin
Excisional biopsy is generally performed to exclude malignancy
If inflammation persists, patients have been treated successfully with corticosteroids
Top Differential Diagnoses
Squamous metaplasia of lactiferous ducts (SMOLD)
Sarcoidosis
Wegener granulomatosis (WG)
Infections with granulomas
TB and fungal infections must be excluded before making a diagnosis of GLM
Duct ectasia
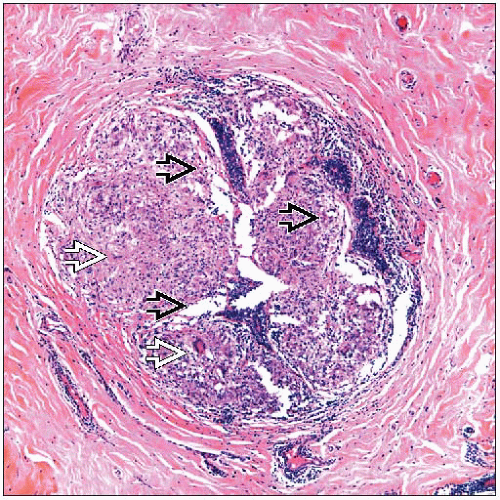
 In GLM, well-formed granulomas are present, centered on ducts and lobules. The epithelium appears distorted or engulfed by the inflammatory cells. A scattering of lymphocytes is also present. |
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Granulomatous lobular mastitis (GLM)
Synonyms
Postlactational granulomatous mastitis
Idiopathic granulomatous mastitis
Lobular granulomatous mastitis
Definitions
Specific disease of breast occurring only in parous women and characterized by lobulocentric granulomas
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Etiology
Association with prior childbirth suggests cell-mediated response to antigen within lobules arising during or after pregnancy
Many women have used oral contraceptives after pregnancy, but causal relationship has not been established
No infectious agents have been identified by special stains or by culture
CLINICAL ISSUES
Presentation
Occurs in women up to 15 years after a pregnancy
Average length of time between pregnancy and presentation: 2 years
Age range: Late teens to 40s; average age: 30s
Patients present with firm discrete palpable breast mass ranging in size from 1-8 cm
Mass can occur anywhere in breast and typically does not involve nipple
Nipple discharge is not characteristic
Mass may be tender
In advanced cases, multiple sinus tracts can open onto skin
Treatment
Excisional biopsy is generally performed to exclude malignancy
In some patients, surgery is curative
If inflammation persists, patients have been treated successfully with corticosteroids
Microorganisms must 1st be excluded as primary cause or as secondary infection
Prognosis
Majority of patients are treated successfully with combination of surgery and corticosteroids
IMAGE FINDINGS
Mammographic Findings
May show multiple small masses or ill-defined masses
Calcifications are not associated with GLM
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree