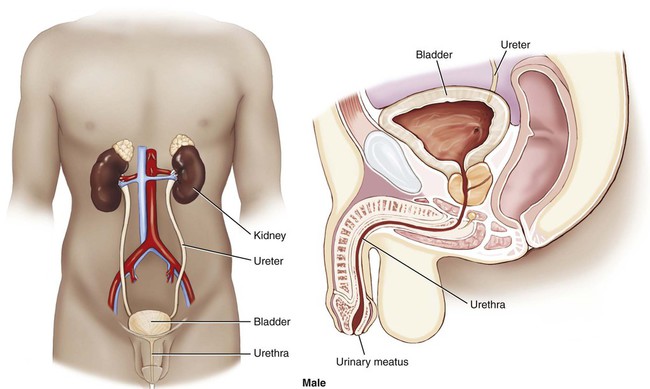
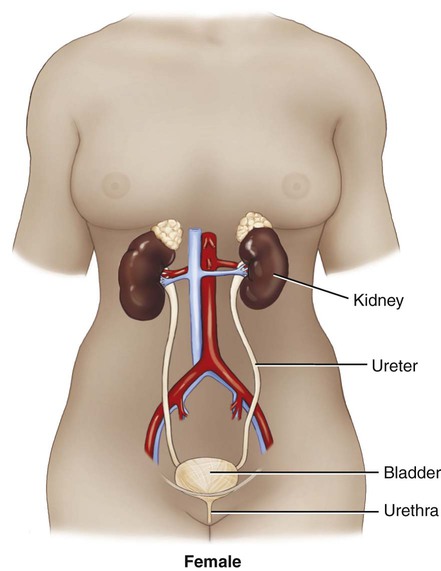
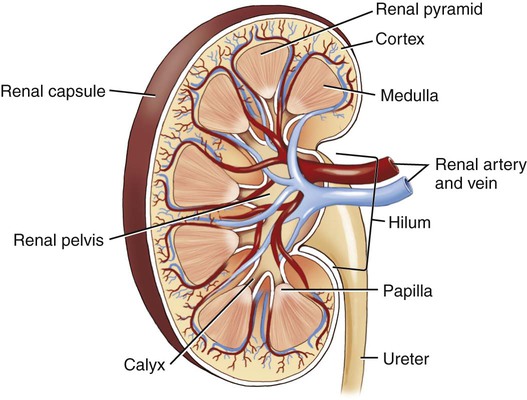
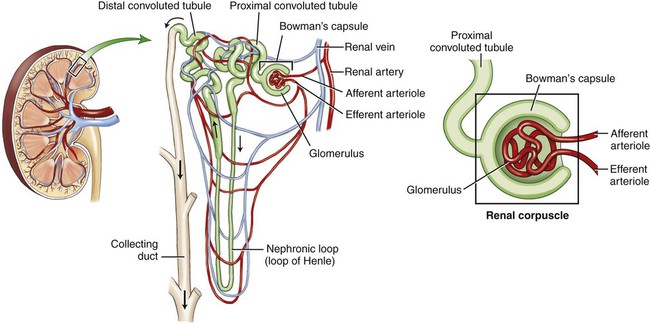
Use additional code to identify infectious agent (B95-B97) Excludes1 prostatocystitis (N41.3) The urinary system is composed of two kidneys, two ureters, a urinary bladder, and a urethra (Figs. 6-1 and 6-2). The work of the urinary system is done by a specialized tissue in the kidneys called parenchymal tissue. The kidneys function to filter the blood and eliminate waste through the passage of urine. The ureters are thin, muscular tubes that move urine in peristaltic waves from the kidneys to the bladder. The urinary bladder is the sac that stores the urine until it is excreted. The bladder is lined with an epithelial mucous membrane of transitional cells. Underneath, a layer termed the lamina propria is composed of connective tissue that holds the blood vessels and nerves. The detrusor muscle is the final coat; it normally contracts to expel urine. The urethra is the tube that conducts the urine out of the bladder. The opening of the urethra is called the urinary meatus. The triangular area in the bladder between the ureters’ entrance and the urethral outlet is called the trigone. The ureters, bladder, and urethra are all stromal tissue, which is a supportive tissue. Because the kidneys are primarily responsible for the functioning of the urinary system, it is helpful to look at them in greater detail. Each of the two kidneys is located high in the abdominal cavity, tucked under the ribs in the back and behind the lining of the abdominal cavity (retroperitoneal). The normal human kidney is about the size of a fist. The tough outer covering of the kidney is the renal capsule. If a kidney were sliced open, the outer portion, the cortex (pl. cortices), and the inner portion, called the medulla (pl. medullae), would be visible (Fig. 6-3). The renal pelvis and calyces (sing. calyx) are an extension of the ureter inside the kidney. The renal pyramids are triangular sections that extend from the renal medulla toward the renal pelvis. The downward point of the pyramid is referred to as the papilla. The term renal means “pertaining to the kidneys.” The ureteropelvic junction (UPJ) is the area where the ureter joins the renal pelvis. It is a common site of obstruction of the outward flow of urine from the kidney. The hilum (pl. hila) is the location on the kidney where the ureter and renal vein leave the kidney and the renal artery enters. The cortex contains tissue with millions of microscopic units called nephrons (Fig. 6-4). Here in the tiny nephrons, blood passes through a continuous system of urinary filtration, reabsorption, and secretion that measures, monitors, and adjusts the levels of substances in the extracellular fluid. Combining Forms for the Anatomy of the Urinary System Prefixes for the Anatomy of the Urinary System Suffixes for the Anatomy of the Urinary System Terms Related to Symptoms and Signs Involving the Genitourinary System (R3Ø-R39) Terms Related to Glomerular Diseases (NØØ-NØ8) Terms Related to Renal Tubulo-interstitial Diseases (N1Ø-N16) Terms Related to Acute Kidney Failure and Chronic Kidney Failure (N17-N19) Terms Related to Urolithiasis (N2Ø-N23) Terms Related to Other Disorders of the Kidney and Ureter (N25-N29)
Genitourinary System
 Recognize and use terms related to the anatomy and physiology of the genitourinary system.
Recognize and use terms related to the anatomy and physiology of the genitourinary system.
 Recognize and use terms related to the pathology of the genitourinary system.
Recognize and use terms related to the pathology of the genitourinary system.
 Recognize and use terms related to the procedures for the genitourinary system.
Recognize and use terms related to the procedures for the genitourinary system.
ICD-10-CM Example from Tabular
N30 Cystitis
Urinary System
Anatomy and Physiology
The Kidney
The Nephron
Meaning
Combining Form
artery
arteri/o
bladder
cyst/o, vesic/o
calyx
calic/o, cali/o, calyc/o
cell
cellul/o
cortex
cortic/o
glomerulus
glomerul/o
hilum
hil/o
kidney
nephr/o, ren/o
meatus
meat/o
medulla
medull/o
parenchyma
parenchym/o
peritoneum
peritone/o
renal pelvis
pyel/o
stroma
strom/o
trigone
trigon/o
ureter
ureter/o
urethra
urethr/o
urine, urinary system
urin/o, ur/o
Prefix
Meaning
extra-
outside
en-
in
par-
beside, near
retro-
backward
Suffix
Meaning
-al, -ar, -ic
pertaining to
-ation, -ion
process of
Pathology
Term
Word Origin
Definition
anuria
an- without
-uria urinary condition
Condition of no urine.
dysuria
dys- painful, abnormal
-uria urinary condition
Condition of painful urination.
enuresis
en- in
ur/o urine
-esis state of
Also commonly known as “bed-wetting,” enuresis can be nocturnal (at night) or diurnal (during the day).
extrarenal uremia
extra- outside
ren/o kidney
-al pertaining to
ur/o urine
-emia blood condition
Excessive urea in blood (uremia) due to kidney failure caused by disease outside of the kidney (e.g., congestive heart failure).
extravasation of urine
extra- outside
vas/o vessel
-ation process of
Condition of urine leaking outside of the bladder and into surrounding tissues. May be due to trauma or a stone.
hematuria
hemat/o blood
-uria urinary condition
Blood in the urine.
incontinence, urinary
Inability to hold urine.
nocturia
noct/i night
-uria urinary condition
Condition of excessive urination at night.
oliguria
olig/o scanty, few
-uria urinary condition
Condition of scanty urination.
polyuria
poly- excessive, frequent
-uria urinary condition
Condition of excessive urination.
retention, urinary
Inability to release urine.
vesical tenesmus
vesic/o bladder
-al pertaining to
Bladder spasms.
Term
Word Origins
Definition
acute nephritic syndrome
nephr/o kidney
-itic pertaining to
Hypertension, hematuria, and proteinuria (protein in the urine) resulting from damage to the glomeruli.
nephrotic syndrome
nephr/o kidney
-tic pertaining to
Abnormal group of signs in the kidney, characterized by proteinuria, hypoalbuminemia (abnormally low levels of albumin in the blood), and edema; may occur in glomerular disease and as a complication of many systemic diseases (e.g., diabetes mellitus). Also called nephrosis.
Term
Word Origin
Definition
hydronephrosis
hydr/o water
nephr/o kidney
-osis abnormal condition
Dilation of the renal pelvis and calices of one or both kidneys resulting from obstruction of the flow of urine.
pyelonephritis
pyel/o renal pelvis
nephr/o kidney
-itis inflammation
Bacterial or viral infection of the kidneys and renal pelvis.
pyonephrosis
py/o pus
nephr/o kidney
-osis abnormal condition
Pyogenic (pus-producing) infection of the kidney.
vesicoureteral reflux
vesic/o urinary bladder
ureter/o ureter
-al pertaining to
re- back
-flux flow
Abnormal backflow of urine from the bladder to the ureter.
Term
Word Origin
Definition
renal failure
ren/o kidney
-al pertaining to
Inability of the kidneys to excrete wastes, concentrate urine, and conserve electrolytes. May be acute or chronic.
acute renal failure (ARF)
Sudden inability of the kidneys to excrete wastes, resulting from hemorrhage, trauma, burns, toxic injury to the kidney, pyelonephritis or glomerulonephritis, or lower urinary tract obstruction. Characterized by oliguria and rapid azotemia.
chronic kidney disease (CKD) (formerly chronic renal failure)
CKD is measured in stages of increasing severity, from 1 (mild damage with a normal glomerular filtration rate) to 5 (complete kidney failure requiring either dialysis or a renal transplant). Stage 5 is also called end-stage renal disease (ESRD) and is the most extreme form of CKD.
Term
Word Origin
Definition
urolithiasis
ur/o urine, urinary system
lith/o stone
-iasis condition, presence of
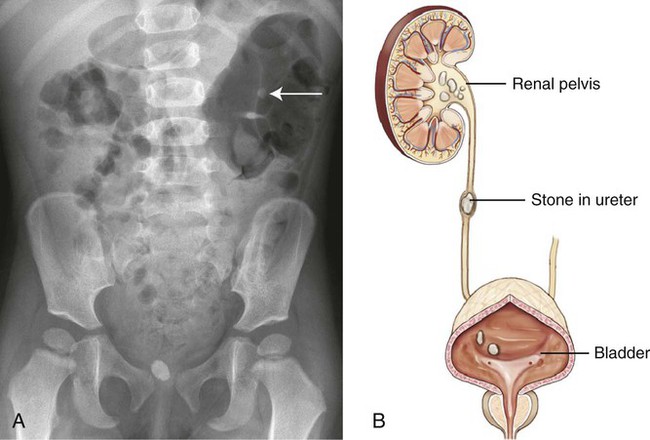
Stones (calculi) anywhere in the urinary tract, but usually in the renal pelvis or urinary bladder. Depending on where the stone is located, the term is nephrolithiasis (kidney), ureterolithiasis (ureter), cystolithiasis (urinary bladder), or urethrolithiasis (urethra). Usually formed in patients with an excess of the mineral calcium. Also called urinary calculi (Fig. 6-5).
Term
Word Origin
Definition
nephrogenic diabetes insipidus
nephr/o kidney
-genic pertaining to producing
Diabetes insipidus caused by a defect in the renal tubules causing them to be unresponsive to antidiuretic hormone (ADH).
nephropathy
nephr/o kidney
-pathy disease process
Disease of the kidneys; a general term that does not specify a disorder.
nephroptosis
nephr/o kidney
-ptosis drooping, sagging
Prolapse or sagging of the kidney. ![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree

 Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access