This is a skin biopsy specimen with extramedullary hematopoiesis (EMH), as evidenced by the large megakaryocyte  .
.
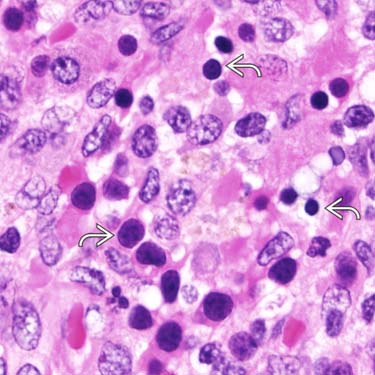
This cutaneous lesion contains small clusters of nucleated red blood cells
 , which were positive for a hemoglobin A immunostain (not shown).
, which were positive for a hemoglobin A immunostain (not shown).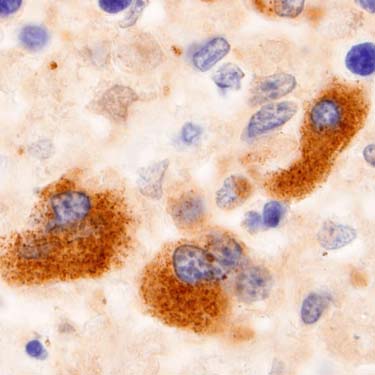
This is a factor VIII immunostain in EMH of the skin. The megakaryocytes are positive for factor VIII. Other megakaryocyte markers include CD61, CD34, and LMP.
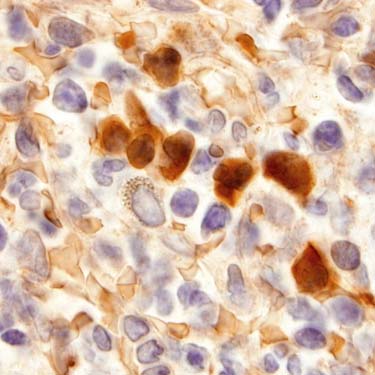
This is a hemoglobin A immunostain in a skin biopsy specimen with EMH; the stain is highlighting erythroid cells.
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Viral Infection
Hematopoietic Disorders
• In adults, EMH is seen with hematopoietic disorders
 All myeloproliferative neoplasms are associated with EMH
All myeloproliferative neoplasms are associated with EMH




 All myeloproliferative neoplasms are associated with EMH
All myeloproliferative neoplasms are associated with EMHStay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree









