Extramedullary Hematopoiesis
Aaron Auerbach, MD, PhD
Key Facts
Terminology
Formation of blood cells (erythroid cells, myeloid cells, megakaryocytes) outside bone marrow
Most common in liver and spleen
Hematopoiesis occurs in skin in early embryonic life Etiology/Pathogenesis
Associated with viral infections, hematopoietic disorders, and neoplasms
Microscopic Pathology
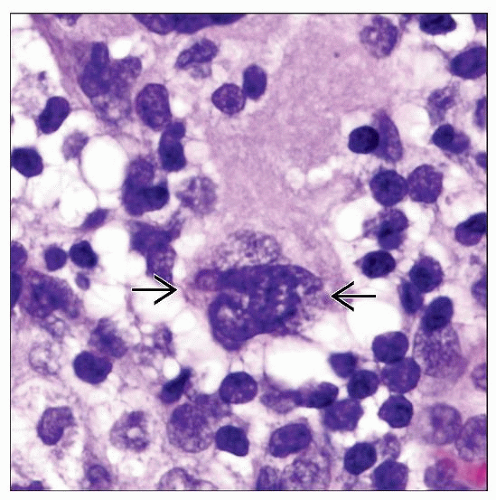
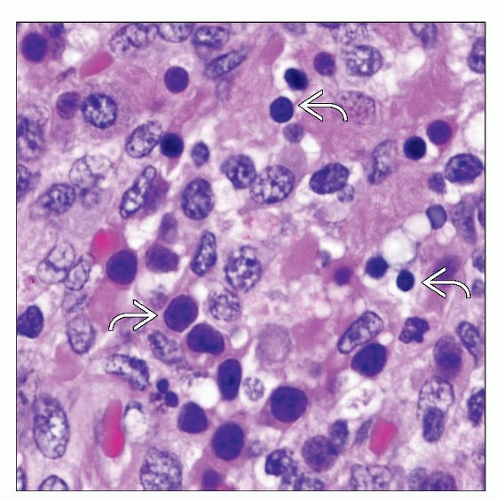
Dermis with myeloid cells, erythroid cells, and megakaryocytes at all stages of maturation
Ancillary Tests
Myeloid cells positive for CD33, CD13, CD43, and CD15
Erythroid cells positive for hemoglobin A
Megakaryocytes express factor VIII and CD61
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Extramedullary hematopoiesis (EMH)
Definitions
Formation of blood cells (including nucleated red blood cells, lymphocytes, and megakaryocytes) outside of bone marrow
Occurs most commonly in liver and spleen
Also found in other organs including lymph nodes, kidney, adrenal, gastrointestinal tract, lung, breast, central nervous system
Hematopoiesis occurs in skin early in embryonic life
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Viral Infection
Has been reported in skin in neonates with intrauterine viral infections including
Cytomegalovirus (CMV)
Coxsackievirus
Rubella
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree