QUESTION 31.2
A. Allergy
B. Infection
C. Malformation
D. Neoplasia
E. Reflux
3. An esophageal biopsy from a 25-year-old man with retrosternal pain shows the histopathologic changes in this picture. This form of esophagitis is due to:
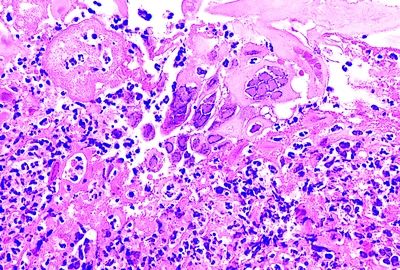
QUESTION 31.3
A. Cytomegalovirus
B. Herpes simplex virus (HSV)
C. Measles
D. Tropheryma whipplei
E. Varicella–zoster virus
4. A histologic change that definitively supports a diagnosis of Barrett esophagus within an esophageal biopsy is:
A. Cardiac-type glands
B. Columnar cells with neutral mucin
C. Endocrine cells
D. Goblet cells with acid mucin
E. Villous surface of the mucosa
5. An esophageal biopsy is taken from a patient with history of GERD. The most significant histopathologic changes are shown in this photomicrograph. Which of the following diagnostic categories is most appropriate to this case?
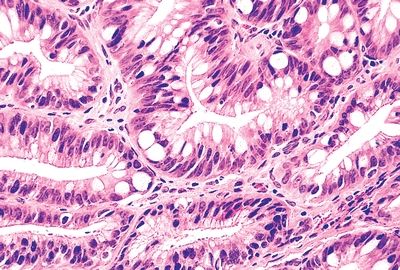
QUESTION 31.5
A. Negative for dysplasia
B. Indefinite for dysplasia
C. Positive for low-grade dysplasia
D. Positive for high-grade dysplasia
E. Intramucosal carcinoma
6. An esophageal biopsy is taken from a patient with history of GERD. The most significant histopathologic changes are shown in this photomicrograph. Which of the following diagnostic categories is most appropriate to this case?
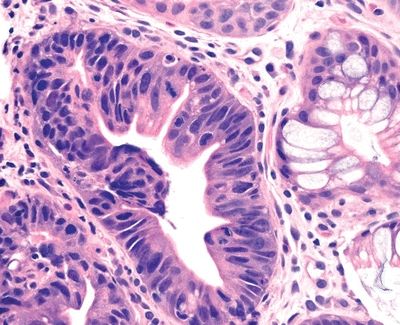
QUESTION 31.6
A. Negative for dysplasia
B. Indefinite for dysplasia
C. Positive for low-grade dysplasia
D. Positive for high-grade dysplasia
E. Intramucosal carcinoma
7. The histopathologic changes seen in this esophageal biopsy from a patient with Barrett esophagus are most consistent with:
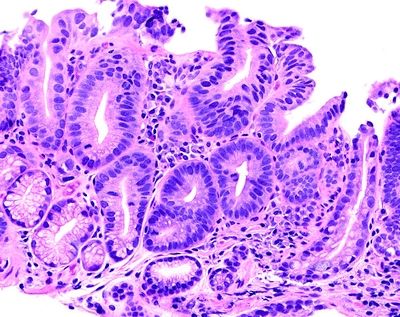
QUESTION 31.7
A. Adenocarcinoma
B. Cardiac-type mucosa
C. Gastric foveolar-type dysplasia
D. Intestinal-type dysplasia
E. Reactive changes
8. Superficial squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus is defined by:
A. Circumferential involvement of the esophagus
B. Distal invasion of the gastric wall
C. Growth confined to submucosa, regardless of nodal involvement
D. Infiltration limited to lamina propria
E. Invasion limited to mucosa and submucosa, with negative nodes
9. A 54-year-old man presents with dysphagia. Endoscopy reveals a large fungating mass in the middle third of the esophagus. This photomicrograph shows its histologic appearance. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
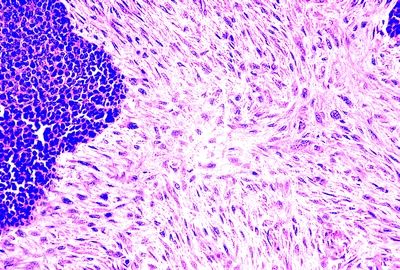
QUESTION 31.9
A. Adenosquamous carcinoma
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


