Epithelioid Hemangioma
Steven D. Billings, MD
Key Facts
Terminology
Angiolymphoid hyperplasia with eosinophilia, histiocytoid hemangioma
Benign vascular tumor with epithelioid endothelial cells, usually accompanied by lymphoid aggregates and eosinophils
Clinical Issues
Most commonly involves head and neck, especially around ear
Microscopic Pathology
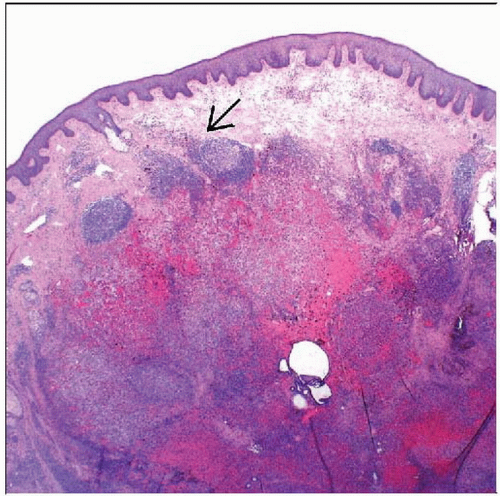
Lobular proliferation of capillaries usually surrounding central vessel
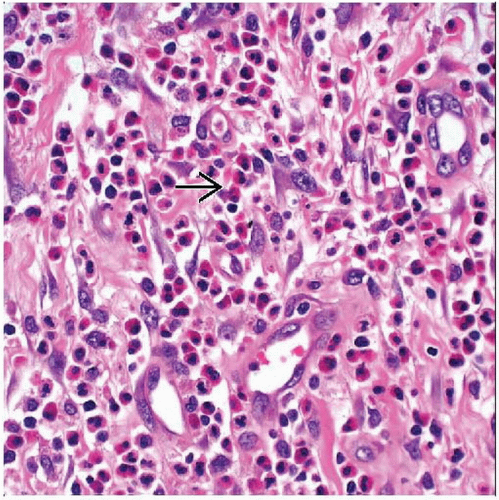
Capillaries lined by epithelioid endothelial cells
Lymphoid aggregates
Density of lymphoid aggregates can obscure underlying vascular proliferation on low-power examination
Abundant eosinophils
Lacks complex vasculature of angiosarcoma
Lacks nuclear pleomorphism of epithelioid angiosarcoma
Not all tumor vessels are necessarily lined by epithelioid endothelial cells
Usually superficial dermal tumors
Endothelial cells positive for CD31 and CD34
Immunohistochemical stains can bring out hard-to-see vascular component in cases with obscuring lymphoid aggregates
TERMINOLOGY
Synonyms
Angiolymphoid hyperplasia with eosinophilia, histiocytoid hemangioma
Definitions
Benign vascular tumor with epithelioid endothelial cells, usually accompanied by lymphoid aggregates and eosinophils
CLINICAL ISSUES
Presentation
Dermal or subcutaneous nodules
Most commonly involves head and neck, especially around ear
Usually solitary but may be multiple in same region
Prognosis
Benign
Local recurrence in up to 1/3
No metastasis
MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY
Histologic Features
Lobular proliferation of capillaries usually surrounding central vessel
Capillaries lined by epithelioid endothelial cells
Epithelioid endothelial cells with abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm
Not all vessels necessarily have epithelioid endothelial cells
Lymphoid aggregates
May show germinal center formation
Abundant eosinophils
Usually superficial dermal tumors
Rare deep or intravascular tumors
Endothelial cells positive for CD31 and CD34
Immunohistochemical stains can bring out hard-to-see vascular component in cases with obscuring lymphoid aggregates
Predominant Cell/Compartment Type
Vascular
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree