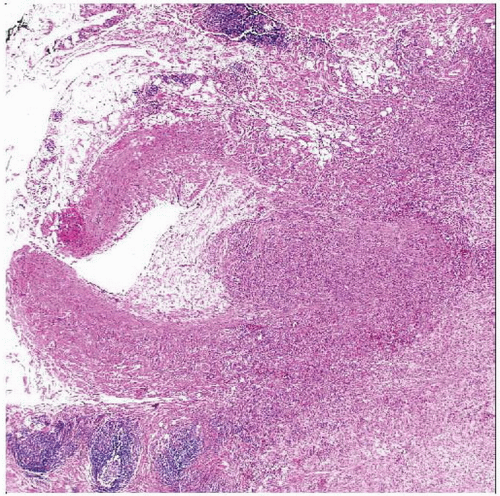
Epithelioid Hemangioendothelioma
Thomas Mentzel, MD
Key Facts
Terminology
Vascular neoplasm with metastatic potential composed of epithelioid endothelial cells
Clinical Issues
Rare vascular tumor
Superficial or deep soft tissue
Rare in skin
˜ 50% associated with preexisting vessel
Behavior intermediate between hemangioma and angiosarcoma
Metastatic rate (20-30%)
Mortality (10-20%)
Painful mass
All age groups
Wide local excision with clear margins
Adverse prognostic factors
> 3 mitoses per 50 high-power fields
Tumor size > 3 cm
Macroscopic Features
Well-circumscribed nodular lesion
Microscopic Pathology
Rare obvious vascular channels
Short strands, cords, solid nests, or single cells
Bland, epithelioid, round or slightly spindled endothelial cells
Intracytoplasmic lumina
Myxohyaline, chondroid-like stroma
Expression of endothelial markers
CD31, CD34, FLI-1
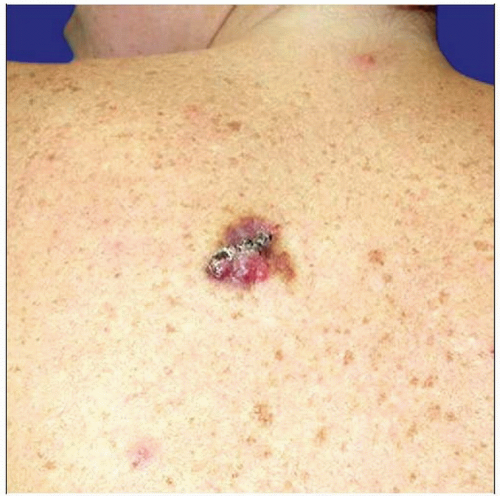 Clinical photograph shows a rare cutaneous epithelioid hemangioendothelioma presenting as an exophytic lesion. |
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma (EHE)
Synonyms
Intravascular bronchioloalveolar tumor
Angioglomoid tumor
Definitions
Angiocentric vascular neoplasm with metastatic potential composed of epithelioid endothelial cells
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
Rare vascular tumor
Age
All age groups
Rare in childhood
Gender
M = F
Site
Superficial or deep soft tissue
Extremities
Head & neck region
Rare in skin
Visceral organs (often multicentric)
Presentation
Painful mass
Solitary mass
Multicentric in a number of cases
Edema
May be present
Occlusion of vessels
1/2 of cases arise in/are associated with preexisting vessels
May cause more profound symptoms
Treatment
Surgical approaches
Wide local excision with clear margins
Adjuvant therapy
No adjuvant chemo-/radiotherapy
Prognosis
Intermediate behavior between hemangioma and angiosarcoma
Local recurrence rate (10-15%)
Metastatic rate (20-30%)
Mortality (10-20%)
Better prognosis in superficial cases
Adverse prognostic factors
> 3 mitoses per 50 high-power fields
Tumor size > 3 cm
IMAGE FINDINGS
General Features
Best diagnostic clue
May show calcifications
Location
Soft tissue of extremities
MACROSCOPIC FEATURES
General Features
Well-circumscribed nodular lesion
Fusiform intravascular mass resembling organizing thrombus
MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY
Histologic Features
Expansion of vessels in angiocentric cases
Centrifugal extension into soft tissues
Rare obvious vascular channels
Short strands, cords, solid nests, single cells
Round to slightly spindled endothelial tumor cells
Eosinophilic cytoplasm
Vesicular nuclei
Small nucleoli
Intracytoplasmic vacuoles
Represent miniature endothelial lumina
May contain erythrocytes
Bland epithelioid tumor cells
Rare mitoses
Myxohyaline stroma
Chondroid stroma
Metaplastic calcification &/or ossification in ˜ 10% of cases
Stroma contains sulfated acid mucopolysaccharides
Atypical features in ˜ 1/3 of cases
Increased cellularity
Solid nests
Marked nuclear atypia
Enlarged nuclei
Prominent nucleoli
Mitoses
Spindling of tumor cells
Necrosis
Predominant Pattern/Injury Type