Epidermoid and Dermoid Cysts
Steven S. Shen, MD, PhD
Jae Y. Ro, MD, PhD
Key Facts
Terminology
Specialized benign form of testicular cyst with keratinizing squamous lining without skin adnexal structures (epidermoid cyst)
Specialized benign form of monodermal cystic teratoma with keratinizing squamous lining and skin adnexal structures (dermoid cyst)
Clinical Issues
< 1% of testicular tumors
Dermoid cyst more rare than epidermoid cyst
Painless testicular enlargement over several years
Cured by surgical resection
Macroscopic Features
Unilocular intraparenchymal cystic lesion containing keratin debris
Microscopic Pathology
Epidermoid cyst: Unilocular cyst with keratinized squamous epithelial lining containing granular cell layer, no skin adnexal structures
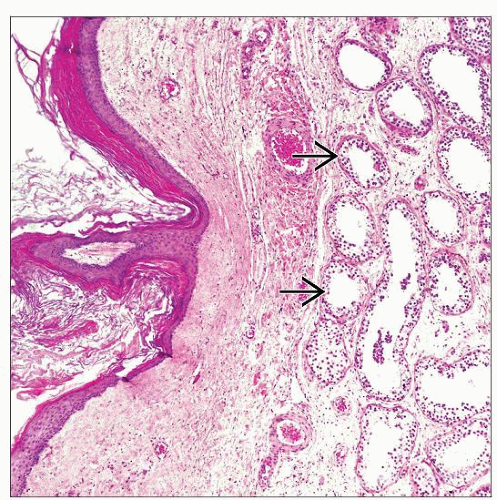
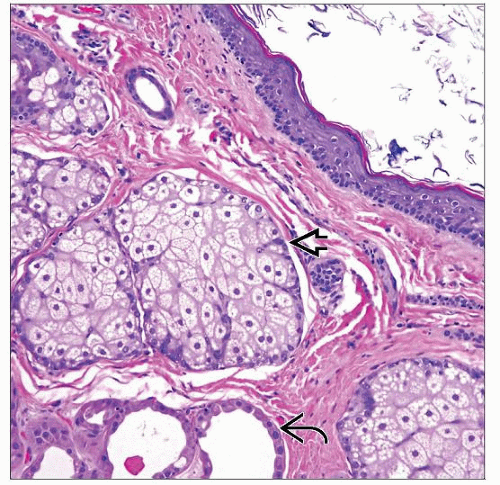
Dermoid cyst: Usually unilocular cyst lined by epidermis and dermis containing skin adnexal structures (hair follicle, sebaceous, apocrine or eccrine glands)
Other noncutaneous elements (such as ciliated epithelium, small bowel mucosa and submucosa) may be seen but maintain organoid arrangement
Lipogranulomatous reaction to cyst contents may be seen
Uninvolved testis has normal spermatogenesis with no significant atrophy or “dysgenetic features”
TERMINOLOGY
Definitions
Specialized benign form of testicular cyst with keratinizing squamous lining without skin adnexal structures (epidermoid cyst)
Specialized benign form of monodermal cystic teratoma with keratinizing squamous lining and skin adnexal structures (dermoid cyst)
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Pathogenesis
Pathogenesis of epidermoid cyst is still controversial
Some consider it as nonteratogenic, either from epithelial inclusion or from metaplastic mesothelium
Others suggest that it is teratomatous because of loss of heterozygosity for certain chromosomal loci
Dermoid cyst is considered a specialized form of teratoma
Different from mature teratoma; believed to be derived from nontransformed germ cells and is unrelated to intratubular germ cell neoplasia (ITGCN)
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
< 1% of testicular tumors
Dermoid cyst more rare than epidermoid cyst
Age
Range: 10-40 years
Presentation
Painless or painful palpable testicular enlargement over several years
May be incidental finding
Laboratory Tests
Serum tumor markers (LDH, AFP, and hCG) are not elevated
Treatment
Surgical approaches
Cured by resection
May be amenable to partial orchiectomy