1% of all rhabdomyosarcomas occurring in children
Ancillary Tests
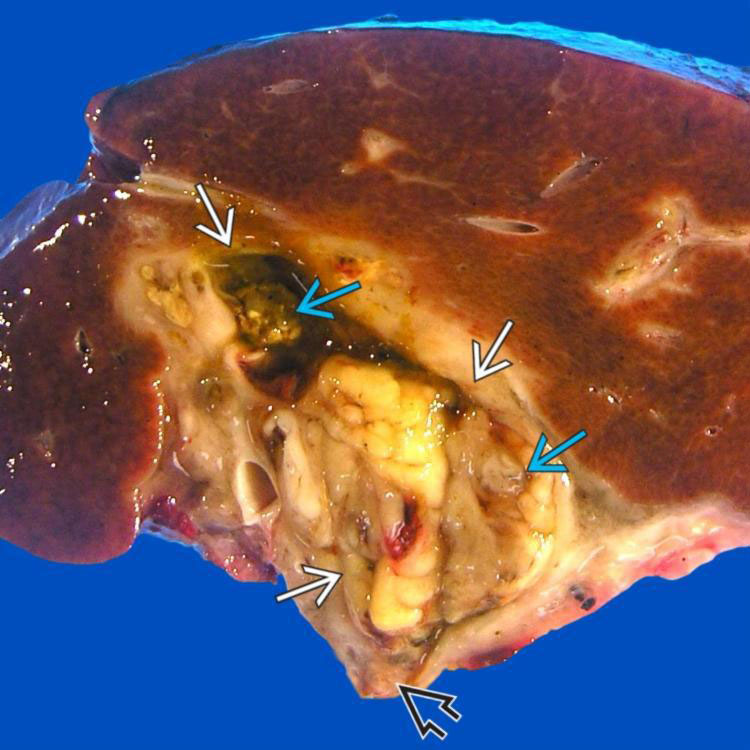
Liver of a 2-year-old girl shows a large embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS) in the porta hepatis. Mass
 obstructs common hepatic duct
obstructs common hepatic duct  and extends to hepatic duct resection margin
and extends to hepatic duct resection margin 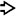 . It shows a variegated cut surface due to necrosis caused by neoadjuvant chemoradiation therapy.
. It shows a variegated cut surface due to necrosis caused by neoadjuvant chemoradiation therapy.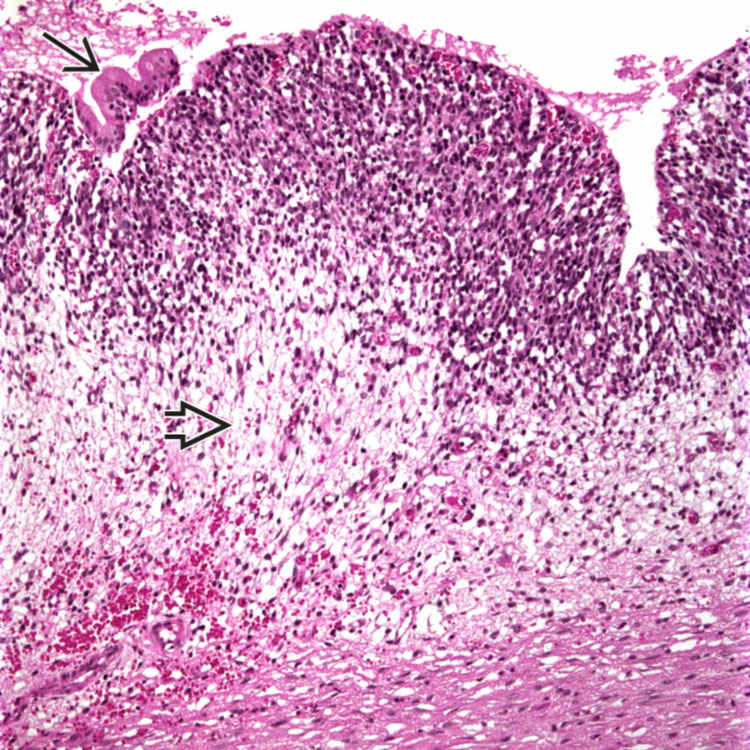
Characteristic cambium layer consists of densely packed tumor cells beneath biliary epithelium
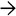 , which is largely denuded. Deeper portion of tumor is hypocellular with loose myxoid stroma
, which is largely denuded. Deeper portion of tumor is hypocellular with loose myxoid stroma 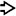 .
.
Tumor cells in embryonal RMS are typically small, round or ovoid, and hyperchromatic. Spindled cells can be present
 . Occasional rhabdomyoblasts are seen, which have abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm
. Occasional rhabdomyoblasts are seen, which have abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm 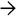 .
.






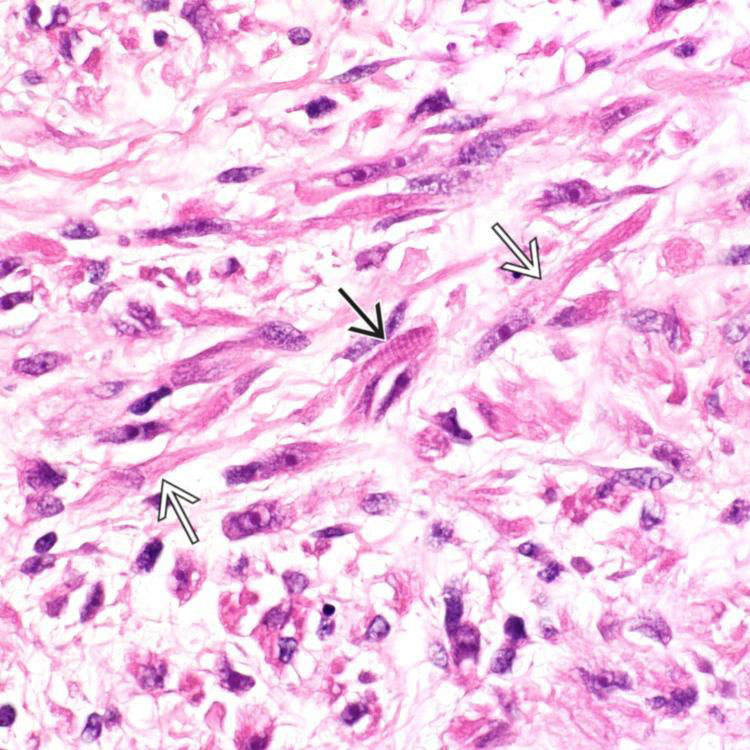
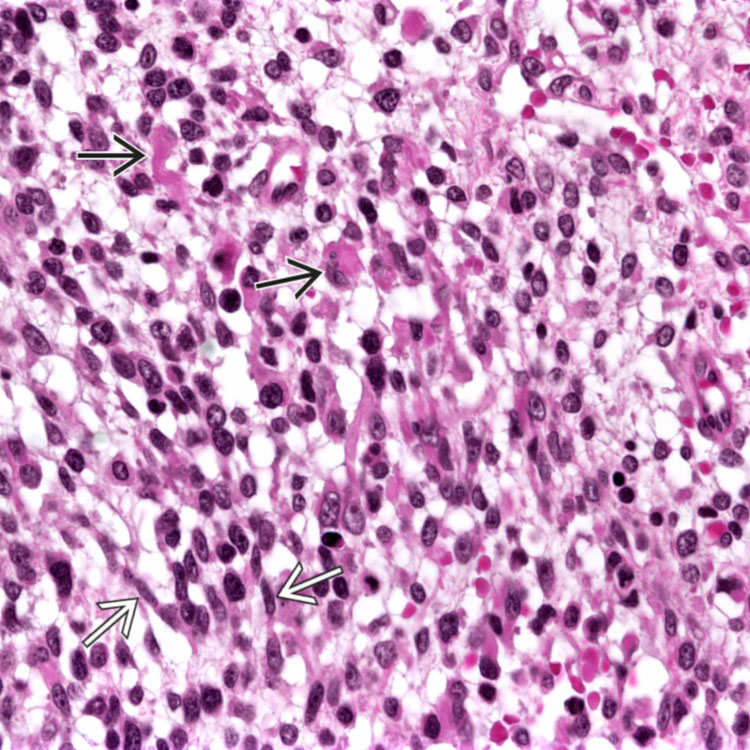
 . Cytoplasmic cross striations are noted in one cell
. Cytoplasmic cross striations are noted in one cell 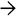 .
.



