Chapter 23 Drugs to Treat Heart Failure
| Abbreviations | |
|---|---|
| ACE | Angiotensin-converting enzyme |
| ARB | Angiotensin receptor blocker |
| ATP | Adenosine triphosphate |
| AV | Atrioventricular |
| BNP | B-natriuretic peptide |
| cAMP | Cyclic adenosine monophosphate |
| CHF | Congestive heart failure |
| CNS | Central nervous system |
| Epi | Epinephrine |
| GI | Gastrointestinal |
| NE | Norepinephrine |
| NO | Nitric Oxide |
| PDE | Phosphodiesterase |
| RAAS | Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system |
| SA | Sinoatrial |
| SNS | Sympathetic nervous system |
Therapeutic Overview
| Therapeutic Overview |
|---|
| Problem |
| Reduced force of contraction |
| Decreased cardiac output |
| Increased total peripheral resistance |
| Inadequate organ perfusion |
| Development of edema |
| Decreased exercise tolerance |
| Ischemic heart disease |
| Sudden death |
| Ventricular remodeling and decreased function |
| Goals |
| Alleviation of symptoms, improve quality of life |
| Arrest ventricular remodeling |
| Prevent sudden death |
| Nondrug Therapy |
| Reduce cardiac work; rest, weight loss, low sodium diet |
| Drug Therapy |
| Acute heart failure |
| Intravenous diuretics, inotropic agents, phosphodiesterase inhibitors, vasodilators |
| Chronic heart failure |
| ACE inhibitors, β adrenergic receptor blockers, angiotensin receptor blockers, aldosterone antagonists, digoxin, diuretics |
nearly 21%, whereas the death rate during that period declined by 2%.
Mechanisms of Action
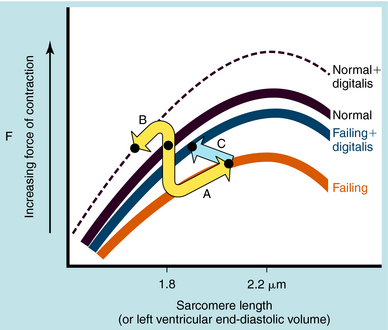
Remodeling of the heart occurs through complex structural changes in one or more cardiac chambers, especially the ventricles. These result in an increase in end-diastolic and end-systolic volume along with changes in cardiac shape and left ventricular mass (Frank-Starling curves are shown in Figure 23-1). Impaired contractility was previously thought to be responsible for heart failure, although a specific biochemical abnormality could not be identified. This idea has given way to the concept that heart failure involves endogenous neurohormones and cytokines in response to an initial “index event,” usually an acute injury to the heart or genetic mutation. Coronary artery disease and hypertension account for most cases, with myocardial infarction being a major contributor. Any insult, whether acute myocardial infarction, essential hypertension, aortic stenosis, or volume overload caused by aortic insufficiency, idiopathic cardiomyopathy, or inflammatory disease, leads to activation of specific mediators involved in the remodeling process.
Neurohormonal systems defend against changes in intravascular volume and act to maintain regional blood flow and regulate systemic blood pressure. Initially, they compensate for the decline in ventricular function and mask the underlying deficiency. Chronic activation of multiple compensatory mechanisms perpetuates progression to irreversible myocyte injury and worsening of cardiac function. Initiating factors include: stretch of the ventricular myocardium, increased cytokine and growth factor production, nitric oxide (NO) production, tumor necrosis factor, natriuretic peptides, free radical-mediated oxidative stress, ischemia, activation of myocardial metalloproteinases, proapoptotic factors, and chronic inflammation. Heart failure is usually accompanied by an increase in sympathetic nervous system (SNS) activation along with chronic up regulation of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) and effects of aldosterone on heart, vessels, and kidneys. CHF should be viewed as a complex, interrelated sequence of events involving hemodynamic, nonhemodynamic, genetic, energetic, and neurohormonal events.
In the failing heart, the loss of contractile function leads to a decline in cardiac output and a decrease in arterial blood pressure. The baroreceptors sense the hemodynamic changes and initiate countermeasures to maintain support of the circulatory system. Activation of the SNS serves as a compensatory mechanism in response to a decline in left ventricular stroke volume. This helps maintain adequate cardiac output by increasing myocardial contractility and heart rate (β1 adrenergic receptors) and by increasing vasomotor tone (α1 adrenergic receptors) to maintain systemic blood pressure (see Chapters 11 and Chapters 19). Over the long term, this hyperadrenergic state leads to irreversible myocyte damage, cell death, and fibrosis. In addition, the augmentation in peripheral vasomotor tone increases left ventricular afterload, placing an added stress upon the left ventricle and an increase in myocardial O2 demand, factors involved in ventricular remodeling. The frequency and severity of cardiac arrhythmias are enhanced in the failing heart, in part as a result of the increased adrenergic tone.
The most frequent cause for chronic systolic dysfunction is ischemic cardiomyopathy, characterized by a reduction in the ventricular ejection fraction and enlargement of the left ventricle, due to a failure of the left ventricle to empty as a result of impaired myocardial contractility or pressure overload. This results from destruction of myocytes, impaired myocyte function, or fibrosis. Chronic pressure overload, caused by untreated long-standing hypertension or aortic stenosis, decreases the left ventricular ejection fraction by increasing resistance to forward flow. Initially, the increase in the left ventricular end-diastolic pressure (volume) results in a compensatory enhancement in stroke volume due to the pressure-induced lengthening of the sarcomeres that invokes the Frank-Starling mechanism (see Fig. 23-1), thereby partially compensating for the failing ventricle. The marked diastolic derangement in filling and the decreased ventricular distensibility do not permit adequate stretch of the myocytes because it occurs under conditions that require an increase in cardiac output. Therefore, in the presence of systolic heart failure, the Frank-Starling mechanism fails to adequately increase stroke volume in response to exercise.
Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors
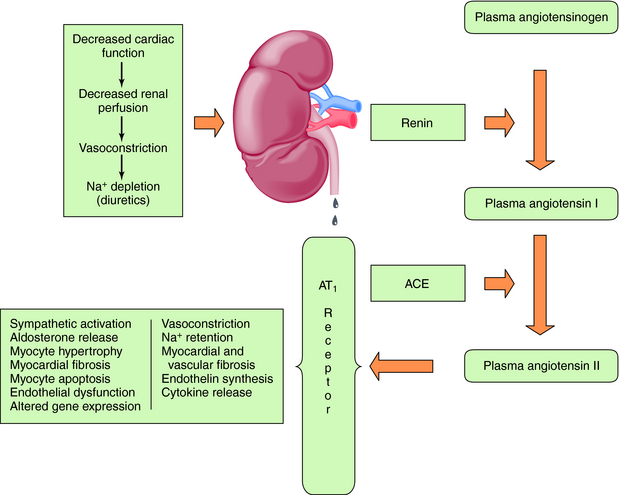
Baroreceptor-mediated activation of the SNS leads to an increase in renin release and formation of angiotensin II (see Chapter 19), which causes intense vasoconstriction and stimulates aldosterone production (Fig. 23-2). This is decreased by the angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, which inhibit formation of angiotensin II from angiotensin I, as discussed in Chapter 20.
Angiotensin II acts through AT1 and AT2 receptors, although most of its actions occur through AT1 receptor activation. Although the AT2 receptor is distributed widely in fetal tissues, its distribution is limited in adults. Angiotensin II mediates cell growth, vasoconstriction, Na+ and fluid retention, and sympathetic activation (Table 23-1). The central role of the RAAS in the development and progression of cardiovascular disease and, in particular, CHF is well established. In addition to regulation of blood pressure and maintenance of fluid and electrolyte balance, short-term activation of the RAAS in heart failure improves cardiac output through fluid and Na+ retention (increased preload), whereas long-term activation results in vasoconstriction, increased afterload, and decreased cardiac output. These mechanisms, together with SNS activation, induce a vicious cycle of increased preload, afterload, and cardiac workload, leading to increased myocardial O2 consumption, loss of myocytes through apoptosis, and progressive worsening heart failure.
TABLE 23–1 Effects of Angiotensin II
| Site of Action | Response |
|---|---|
| Vascular smooth muscle | Vasoconstriction—increased renal and peripheral resistance, increased left ventricular afterload, vessel wall hyperplasia, hypertrophy initiated by AT1 receptors |
| Heart | Positive inotropic effect by opening voltage-gated Ca++ channels, myocardial hypertrophy, activation of matrix metalloproteinases, myocardial fibrosis initiated by AT1 receptors, increase in release of norepinephrine |
| Adrenal cortex | Increased aldosterone synthesis and release, release of catecholamines from adrenal medulla |
| Kidney | Reduction in renal blood flow and excretory functions, increase in Na+ channels in the apical membrane of renal tubules, increased activity of Na+,K+-ATPase in the basal lateral membrane, increased renal tubular reabsorption of Na+, increased K+ excretion |
| Sympathetic nervous system | Increased norepinephrine release and inhibition of reuptake (increase in peripheral resistance, stimulation of renin release) |
| Central nervous system | Release of vasopressin, increased fluid retention, activation of the sympathetic nervous system |
β Adrenergic Receptor Blocking Drugs
The β receptor blockers inhibit the adverse effects of the SNS in patients with heart failure. Whereas cardiac adrenergic drive initially serves as a compensatory mechanism to support the failing heart, long-term activation leads to a down regulation of β1 receptors and an uncoupling from adenylyl cyclase (see Chapter 1), thereby reducing myocardial contractility. The β receptor blockers may be beneficial through resensitization of the down regulated receptor, improving myocardial contractility.
Another approach is to block AT1 receptors with the use of angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs). The currently available drugs selectively block AT1 receptors and replicate many of the actions of ACE inhibitors; they do not block AT2 receptors. Activation of AT2 receptors may cause vasodilation, preventing hypertrophy of vascular smooth muscle and cardiomyocytes, production of bradykinin, and release of NO. There is also overexpression of AT2 receptors in the failing heart. There may also be non-ACE-dependent formation of angiotensin II by enzymes, such as chymase, cathepsin G, trypsin, and tissue plasminogen activator. An ARB might block the deleterious actions mediated by AT1 receptors while preserving the desirable effects of AT2 receptor activation. Although the hemodynamic and clinical effects may appear similar, ACE inhibitors and ARBs should not be regarded as being identical.
The elevated circulating angiotensin II levels in the patient with CHF lead to greatly increased production of aldosterone (see Chapter 39), an important mediator in the progressive development of CHF. Aldosterone binds to mineralocorticoid receptors in renal epithelial cells and promotes Na+ retention, Mg++ and K+ loss, sympathetic activation, parasympathetic inhibition, myocardial and vascular fibrosis, baroreceptor dysfunction, impaired arterial compliance, and vascular damage. Aldosterone antagonists include spironolactone and eplerenone, which may reduce norepinephrine (NE) release from cardiac sympathetic nerves and increase plasma K+. The elevated concentrations of aldosterone in CHF led to the concept that inhibition of aldosterone receptors could be beneficial, and competitive aldosterone antagonists are now part of the therapeutic armamentarium.
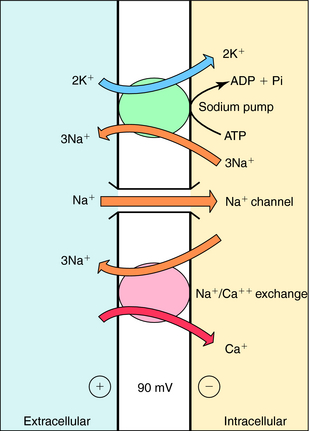
The cardiac glycosides increase the force of myocardial contraction, alter electrophysiological properties in specialized regions, and have extracardiac actions associated with toxicity. Cardiac glycosides influence the heart through a direct inhibition of membrane Na+,K+-ATPase and an indirect increase in vagal tone (Table 23-2). Their cardiotoxic effects are an overextension of the same mechanisms responsible for their positive inotropic actions.
TABLE 23–2 Effects of Cardiac Glycosides on Electrophysiological Properties of the Heart
| Direct | Indirect (increased vagal tone) | |
|---|---|---|
| SA node | No effect at therapeutic dose | No effect at therapeutic dose |
| Atrial muscle | High dose increases rate of spontaneous depolarization | High dose decreases rate of spontaneous depolarization |
| AV node | Increased refractory period | Decreased conduction velocity |
| Decreased conduction velocity | Increased refractory period | |
| His-Purkinje system | Increased refractory period | Increased refractory period |
| Decreased conduction velocity | Decreased conduction velocity | |
| High dose increases triggered activity | None | |
| Toxic doses enhance pacemaker |
Cardiac glycosides increase contractile force; however, unlike catecholamines, they do not increase the rate of relaxation. By decreasing the activity of the Na+,K+-ATPase, they cause a progressive gain in intracellular Na+ with each cardiac cycle. This increase promotes Ca++ influx by Na+/Ca++ exchange (Fig. 23-3). The net result is an increased intracellular Ca++, enhancing the Ca++ transient resulting from an augmented Ca++ loading of the sarcoplasmic reticulum. In the presence of a digitalis glycoside, a new steady state is achieved where an increased amount of Ca++ is released after depolarization, increasing force development (stroke volume; see Fig. 23-1).
Electrophysiological effects of cardiac glycosides vary among different regions of the heart. They decrease automaticity within the sinoatrial (SA) and atrioventricular (AV) nodes as a result of an increase in parasympathetic tone along with a concomitant decrease in sympathetic tone. The increase in parasympathetic tone on the AV node leads to a decrease in conduction velocity and an increase in effective refractory period. Thus digitalis glycosides indirectly decrease heart rate and impair impulse transmission across the AV node.
The major direct effects are in the atrial muscle, AV node, and ventricles (see Table 23-2). In atria, they prolong the effective refractory period and decrease conduction velocity, effects opposite to those elicited by their indirect actions. However, the direct effects in the AV node summate with the indirect actions to further impair conduction velocity and increase the refractory period.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree