Cryptococcal Lymphadenitis
Tariq Muzzafar, MBBS
Key Facts
Etiology/Pathogenesis
Infection by Cryptococcus neoformans
Most cases are associated with immunosuppression
> 80% of cases associated with AIDS
Microscopic Pathology
Cryptococcus neoformans
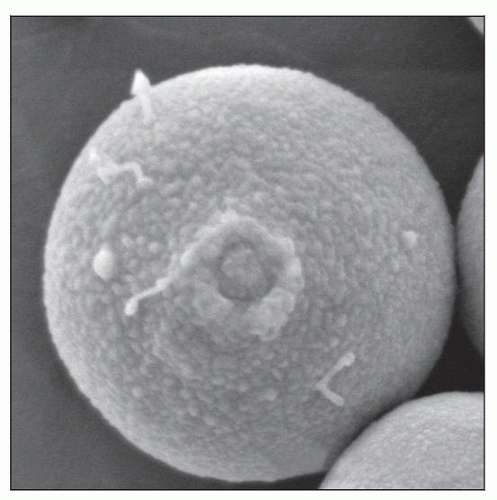
Single yeasts with narrow-based buds
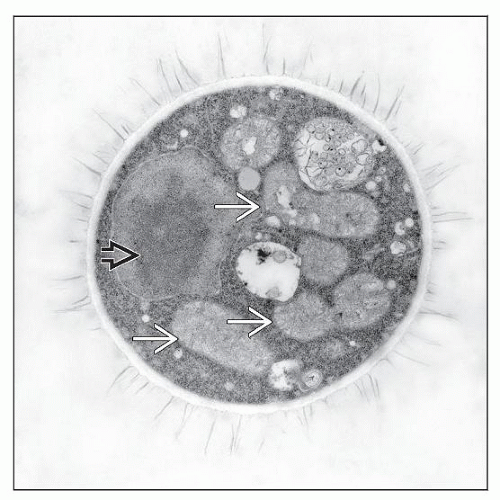
Clear, concentric spaces on H&E due to 3-5 µm thick mucopolysaccharide capsule
Fungal organisms highlighted by PAS, GMS, mucicarmine, Fontana-Masson stains
Tissue reaction
Scattered or confluent noncaseous granulomas
Cystic spaces composed of gelatinous fluid enclosed by fibrosis
Often less/minimal reaction in patients with marked immunodeficiency
Cytologic findings
FNA of lymph nodes useful for diagnosis
Bronchoalveolar lavage useful for diagnosing lung disease
India ink preparation of CSF demonstrates spherical, encapsulated yeast cells, 5-20 µm
Ancillary Tests
Culture essential for definitive identification
Fungal antigen in serum and other body fluids can aid in diagnosis
Top Differential Diagnoses
Tuberculous lymphadenitis
Histoplasma lymphadenitis
TERMINOLOGY
Definitions
Inflammation of lymph nodes due to Cryptococcus neoformans
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Infection by Cryptococcus neoformans
Saprophytic fungus; not highly pathogenic
C. neoformans has worldwide distribution
Found in bird nests, pigeon feces
Transmission occurs via aerosols into lungs
Infection spreads from lungs to regional lymph nodes; subsequent dissemination
Underlying immunosuppression very common in infected patients
> 80% of cases associated with AIDS
7-15% of all AIDS patients have cryptococcal infection
Incidence has decreased in developed countries
With advent of highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART)
Other patient risk groups include those with
Iatrogenic immunosuppression
Organ transplant
Therapy with immunosuppressive agents
Malignancies
Connective tissue diseases
Chronic pulmonary disease
Chronic renal or hepatic diseases
Diabetes mellitus
Pregnancy
Inhalation from environmental sources can lead to
Acute disease
Latent infection with lymph node complex formation
Reactivation may occur in future
Cell-mediated immunity crucial to limiting infection
CLINICAL ISSUES
Presentation
Organs involved include
Common: Central nervous system (CNS) and respiratory tract
Meningitis; pneumonia or lung nodules
Other: Skin, prostate, eyes, bone, urinary tract, blood
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree