Radiolucent cholesterol stones
 Risk factors: Chronic hemolysis, biliary infection, and gastrointestinal diseases affecting bile salt reabsorption
Risk factors: Chronic hemolysis, biliary infection, and gastrointestinal diseases affecting bile salt reabsorptionDiagnostic Checklist
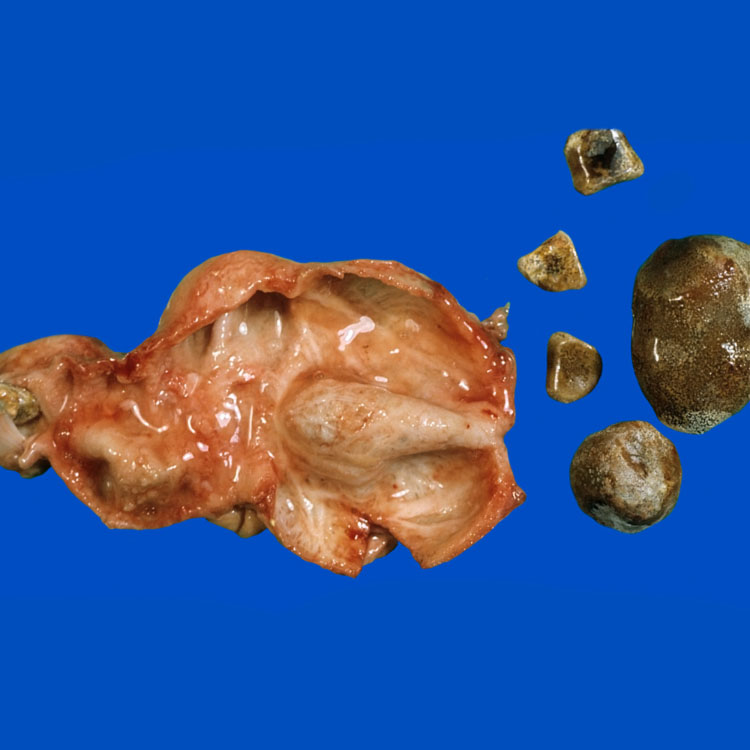
Gallbladder with multiple mixed stones is shown. Most chronic cholecystitis cases are associated with stones; however, symptomatic stones can be present in histologically normal gallbladder.
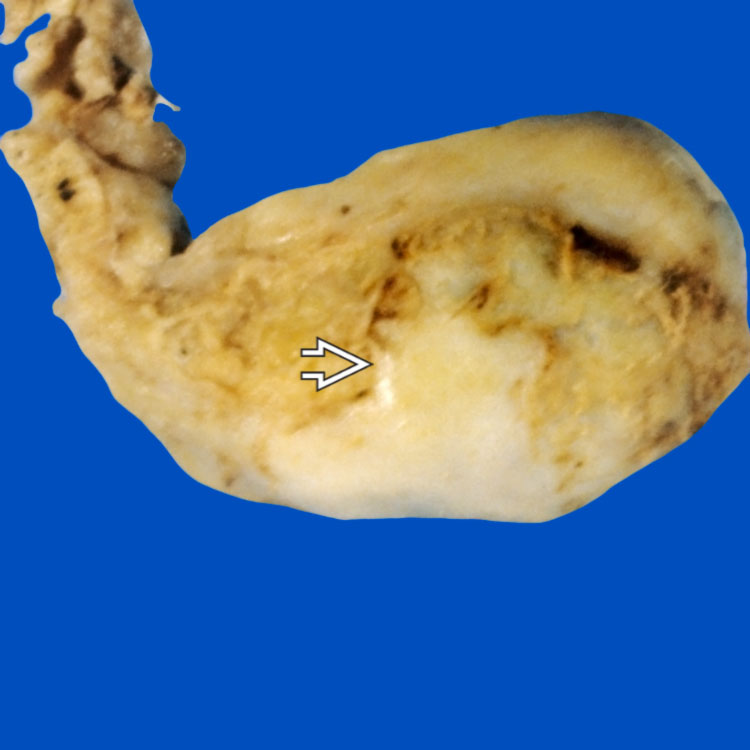
Thick, fibrotic gallbladder shows dystrophic calcification
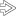 reminiscent of porcelain. This variant is associated with an increased risk of adenocarcinoma.
reminiscent of porcelain. This variant is associated with an increased risk of adenocarcinoma.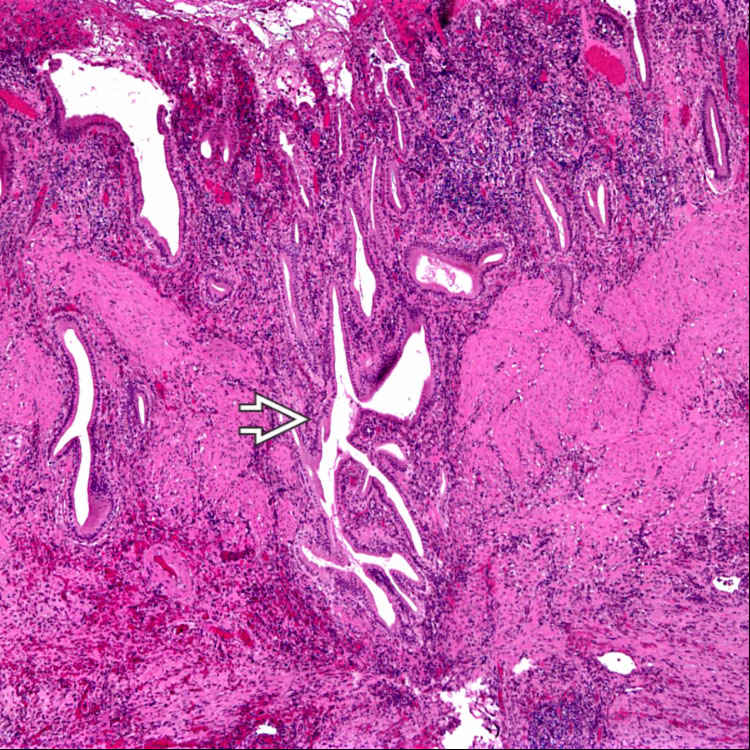
The mucosa herniates through the muscularis propria, resulting in Rokitansky-Aschoff sinuses
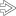 . This is a common finding in chronic cholecystitis, but is not sufficient for the diagnosis by itself.
. This is a common finding in chronic cholecystitis, but is not sufficient for the diagnosis by itself.ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Pathogenesis
• Almost always associated with gallstones




Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree







 . In some cases, these follicles can have a polypoid appearance on gross examination.
. In some cases, these follicles can have a polypoid appearance on gross examination.
