Choriocarcinoma and Variants
Steven S. Shen, MD, PhD
Jae Y. Ro, MD, PhD
Key Facts
Terminology
Germ cell tumor composed of mixture of mononucleate trophoblastic cells and multinucleate syncytiotrophoblasts
Clinical Issues
Pure choriocarcinoma comprises < 1% of germ cell tumor
Known for early hematogenous metastasis to lung, liver, and brain
Patients typically have very high circulating human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) (usually > 100,000 mIU/mL)
Macroscopic Features
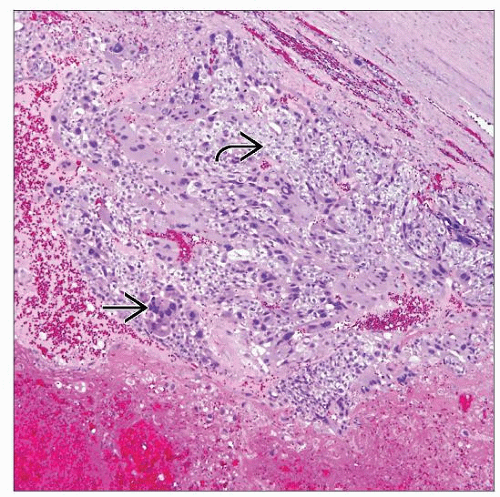
Hemorrhagic and necrotic mass with blood clot; illdefined gray to tan tissue at periphery
Microscopic Pathology
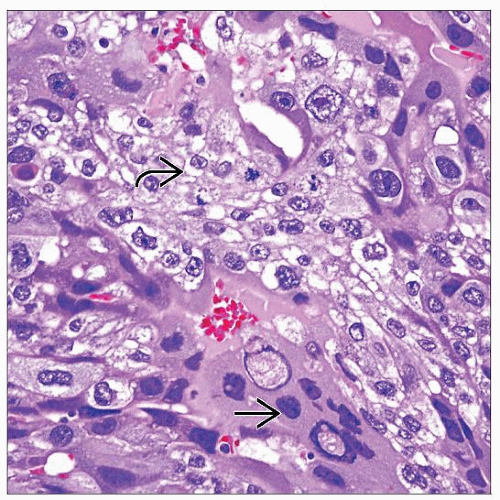
Classic choriocarcinoma consists of mixture of cytotrophoblasts and multinucleate syncytiotrophoblasts
Syncytiotrophoblasts wrapping around mononuclear cytotrophoblastic cells and forming villous configuration
Significant hemorrhage and necrosis
Intratubular germ cell neoplasia (ITGCN) in adjacent testis
Ancillary Tests
Positive for cytokeratin, HCG, HPL, EMA/MUC1 (only for syncytiotrophoblast), and SALL4
Negative for vimentin, CD30(BerH2), Podoplanin(D2-40), Oct3/4, and inhibin
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Choriocarcinoma (CC)
Synonyms
Trophoblastic tumor
Definitions
Germ cell tumor composed of admixture of mononucleate cytotrophoblastic and multinucleate syncytiotrophoblastic cells
Monophasic choriocarcinoma (rare, lacks syncytiotrophoblasts)
Placental site trophoblastic tumor (extremely rare; tumor of intermediate trophoblasts)
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
Pure choriocarcinoma accounts for < 1% of germ cell tumors
Usually mixed with other germ cell tumor components (8% of mixed germ cell tumors)
Age
25-30 years
Presentation
Testicular mass (often small)
Symptoms due to hematogenous metastasis (hemoptysis, central nervous system dysfunction, hematemesis, melena, hypotension, anemia)
May present with metastasis with subsequent detection of primary
May have gynecomastia or hyperthyroidism
Laboratory Tests
Patients typically have very high circulating human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) (usually > 100,000 mIU/mL)
Treatment
Radical orchiectomy and systemic chemotherapy
Prognosis
Worse prognosis than other germ cell tumors, if pure
Level of hCG correlates with prognosis, reflecting tumor burden
IMAGE FINDINGS
General Features
Similar to other nonseminomatous germ cell tumors, but mass is usually small or inapparent in pure CC
MACROSCOPIC FEATURES
General Features
For pure tumors
Hemorrhagic and necrotic mass with blood clot; illdefined gray to tan tissue at periphery
Primary site may be totally regressed with “burntout” focus
Size
Variable (may be quite small)
MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY
Key Descriptors
Predominant Pattern/Injury Type
Neoplastic
Predominant Cell/Compartment Type
Mononucleated cytotrophoblasts and multinucleated syncytiotrophoblasts
Histologic Features
Classic choriocarcinoma consists of mixture of cytotrophoblasts and multinucleate syncytiotrophoblasts
Cytotrophoblasts are round or polygonal cells with prominent cell borders, clear cytoplasm, and usually single bland nucleus
Syncytiotrophoblasts are large multinucleate cells, often degenerate appearing, with abundant eosinophilic and vacuolated cytoplasm
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree