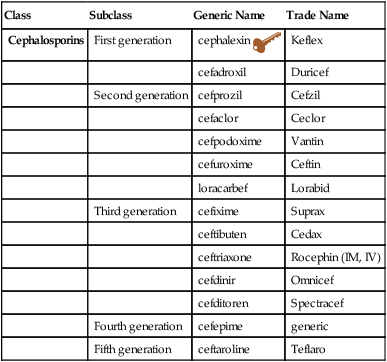
Chapter 60 The mold Cephalosporin acremonium (now Acremonium chrysogenum) was discovered in sewage in Sardinia, Italy, in 1945. In 1964, the first cephalosporin, cephalothin, was marketed. Cephalosporins now comprise a large category of antimicrobials, with a wide spectrum of activity that is superior to the penicillins (Table 60-1). The generations are loosely based on antimicrobial spectrum of activity. This chapter discusses the most common oral cephalosporins, with one exception—ceftriaxone—which can be given IM in the primary care setting. Many first-, second-, third-, and fourth-generation cephalosporins are used IM or IV for serious infections and are not discussed. The primary care provider should be familiar with one oral cephalosporin from each generation. The most widely used cephalosporins for the primary care provider consist of cephalexin (Keflex), cefprozil (Cefzil), cefuroxime (Ceftin), and ceftriaxone (Rocephin). TABLE 60-1 Cephalosporin Indications With Dosage and Administration
Cephalosporins
Class
Subclass
Generic Name
Trade Name
Cephalosporins
First generation
cephalexin ![]()
Keflex
cefadroxil
Duricef
Second generation
cefprozil
Cefzil
cefaclor
Ceclor
cefpodoxime
Vantin
cefuroxime
Ceftin
loracarbef
Lorabid
Third generation
cefixime
Suprax
ceftibuten
Cedax
ceftriaxone
Rocephin (IM, IV)
cefdinir
Omnicef
cefditoren
Spectracef
Fourth generation
cefepime
generic
Fifth generation
ceftaroline
Teflaro
Drug
Bacteria
Site/Disease
Dosage
FIRST GENERATION
cephalexin (Keflex)
GABHS, S. pneumoniae, staph, H. influenzae, E. coli, Klebsiella, Proteus
URI, UTI, skin
Adult: 250-500 mg q6h
Child: 25-50 mg/kg/day in divided doses
Otitis media: 75-100 mg/kg/day in 3 or 4 divided doses
cefadroxil (Duricef)
GABHS, S. pneumoniae, staph, H. influenzae
E. coli, Klebsiella, Proteus
Pharyngitis, tonsillitis
UTI, skin
Adult: 1 g/day in single or two divided doses × 10 days
Child: 30 mg/kg/day in single or two divided doses × 10 days
Adult: 1-2 g/day in single or two divided doses (2 g/day complicated UTI)
Child: 30 mg/kg/day in single or two divided doses
SECOND GENERATION
cefuroxime (Ceftin)
GABHS, staph
Pharyngitis, tonsillitis
Adult: 250 mg bid × 10 days
Child (3 mo-12 yr): 20 mg/kg/day (maximum, 500 mg/day) divided bid × 10 days
GABHS, S. pneumoniae, H. influenzae, M. catarrhalis
Otitis media, impetigo
Child: 30 mg/kg/day (maximum, 1 g/day) divided bid × 10 days
S. pneumoniae, H. influenzae, M. catarrhalis; strep, staph
Acute exacerbation of COPD, skin, soft tissue
Adult: 250-500 mg bid × 10 days
E. coli, Klebsiella, Proteus, Morganella, Citrobacter
UTI
Adult: 125-250 mg bid × 7 to 10 days
N. gonorrhoeae
B. burgdorferi
Gonorrhea
Early Lyme disease
Adult: 1 g single dose
Adult: 500 mg bid × 20 days
cefprozil (Cefzil)
GABHS
Pharyngitis, tonsillitis
Adult (>13 yr): 500 mg once daily × 10 days
Child (2-12 yr): 7.5-15 mg/kg (maximum, 1 g/day) q12h × 10 days
S. pneumoniae, H. influenzae, M. catarrhalis
Otitis media
Child (>6 mo-12 yr): 15 mg/kg q12h × 10 days
Same
Sinusitis
Adult: 250-500 mg q12h × 10 days
Child: 7.5-15 mg/kg q12h × 10 days
Same
Strep, staph
Exacerbation of COPD
Skin, soft tissue
Adult: 500 mg q12h × 10 days
Adult: 250-500 mg q12h × 10 days
Child (2-12 yr): 20 mg/kg (maximum, 1 g) q24h × 10 days
cefaclor (Ceclor)
Strep, staph
Mild to moderate infection
Acute exacerbation of COPD
Pharyngitis, tonsillitis
Adult: 250-500 mg q8h
Adult: 500 mg q12h × 7 days
Adult: 375 mg (ER) q12h × 10 days
Child: 20 mg-40 kg/day (maximum, 1 g/day) in divided doses q8h
cefpodoxime (Vantin)
S. pneumoniae, H. influenzae, M. catarrhalis, S. pyogenes
Pneumonia, bronchitis
Pharyngitis, tonsillitis
Skin
Otitis media
Pharyngitis/tonsillitis
Adult: 200 mg q12h × 14 days
Adult: 100 mg q12h × 5 to 10 days
Adult: 400 mg q12h × 7 to 14 days
Child (2 mo-12 yr): 10 mg/kg/day (maximum, 400 mg/day) divided q12h × 5 days
Child (2 mo-12 yr): 10 mg/kg/day (maximum, 200 mg/day) in two divided doses × 5-10 days
loracarbef (Lorabid)
S. pyogenes, S. pneumoniae, H. influenzae, M. catarrhalis
Pharyngitis/tonsillitis
Sinusitis
Lower respiratory tract
Adult: 200 mg q12h × 10 days
Adult: 400 mg q12h × 10 days
Adult: 400 mg q12h × 7-14 days
Strep, staph
Same
Skin
UTI
Adult: 200 mg q12h × 7 days
Adult: 200-400 mg q12h × 7 days
THIRD GENERATION
cefixime (Suprax)
H. influenzae, M. catarrhalis, S. pyogenes
Otitis media, pharyngitis, tonsillitis, acute exacerbations of COPD
Adult: 400 mg/day as single dose or 200 mg bid × 10 days
Child (<50 kg or <12 yr): 8 mg/kg/day suspension as single daily dose or a 4 mg/kg q12h × 10 days
ceftriaxone (Rocephin)
S. pneumoniae, S. aureus, H. influenzae, H. parainfluenzae, K. pneumoniae, S. marcescens, E. coli, E. aerogenes, P. mirabilis, S. pyogenes
Lower respiratory, skin and skin structure, UTI
Adult: 1-2 g once daily × 4-14 days IM
Child: 50-75 mg/kg/day in divided doses q12h IM × 10-14 days
N. gonorrhoeae
Gonorrhea
Single IM dose of 250 mg
cefdinir (Omnicef)
Same
Pharyngitis, tonsillitis, sinusitis
Adult: 300 mg q12h or 600 mg once daily × 10 days
Child (6 mo-12 yr): 7 mg/kg q12h or 14 mg/kg once daily × 10 days (maximum, 600 mg/day)
Acute exacerbation of COPD
Pneumonia, skin, soft tissue
Otitis media
Adult: 300 mg q12h or 600 mg once daily × 10 days
Adult: 300 mg q12h × 10 days
Child (6 mo-12 yr): 7 mg/kg q12h × 10 days (maximum, 600 mg/day)
Child (6 mo-12 yr): 7 mg/kg q12h or 14 mg/kg once daily × 10 days (maximum, 600 mg/day)
cefditoren (Spectracef)
S. pyogenes, S. aureus
H. influenzae, H. parainfluenzae,
S. pneumoniae, M. catarrhalis
Pharyngitis, tonsillitis, skin, soft tissue
Acute exacerbation of COPD, pneumonia
Adult: 200 mg bid × 10 days
Adult: 400 mg bid × 10 days; pneumonia: 14 days![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


