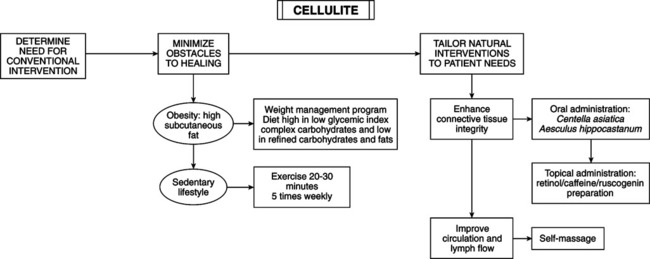
• Subcutaneous tissue of thighs has three layers of fat, with two planes of connective tissue (CT) (ground substance) between them. Construction of subcutaneous tissue of the thigh differs in men and women. In women, the uppermost subcutaneous layer consists of “standing fat cell chambers,” separated by radial and arching dividing walls of CT anchored to overlying CT of skin (corium). The uppermost subcutaneous tissue in men is thinner, with a network of crisscrossing CT walls, and the corium (CT structure between dermis and subcutaneous tissue) is thicker than in women. • Pinch test: pinching skin and subcutaneous tissue of woman’s thighs exhibits pitting, bulging, and deformation of skin. In most men, skin folds or furrows but does not bulge or pit. • With aging, corium, already thinner in women than men, becomes thinner and looser. Fat cells migrate into this layer. CT walls between fat cell chambers become thinner, allowing them to hypertrophy. Breakdown (thinning) of CT is a major contributor to cellulite and granular “buckshot” feel of cellulite. • Condition arises from alternating depressions and protrusions in the upper compartment of fat tissue. The vertical orientation of women’s fat cell compartments and weakening of tissues allows protrusion of fat cells into lower corium. • Distension of lymphatic vessels of upper corium and decrease in number of subepidermal elastic fibers. • Stage 0: skin on thighs and buttocks has smooth surface when subject is standing or lying. Pinch test: skin folds and furrows but does not pit or bulge. This is the “normal” stage of most men and slim women. • Stage 1: skin surface is smooth while standing or lying. The pinch test is clearly positive for pitting, bulging, deformity of affected areas, which is normal for most women. In men it may be a sign of deficiency of androgenic hormones. This is the best classification most can expect because of structural predisposition. • Stage 2: skin surface is smooth while lying but when standing shows pitting, bulging, and deformity of affected skin. This is common in women who are obese or older than 35-40 years of age. • Stage 3: mattress phenomenon when lying or standing. This is very common after menopause and in obesity.
Cellulite
GENERAL CONSIDERATIONS
Histologic Features
CLINICAL FEATURES
Four Major Stages
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


Cellulite
