Zoonotic infection caused by small, weakly gram-negative coccobacillus
Clinical Issues
• ∼ 1-2% of patients develop visceral involvement (liver, spleen, bone, central nervous system, or lung)
• Multiple hepatic lesions, sometimes accompanied by splenic lesions and lymphadenopathy, raises concern for neoplasia
Ancillary Tests
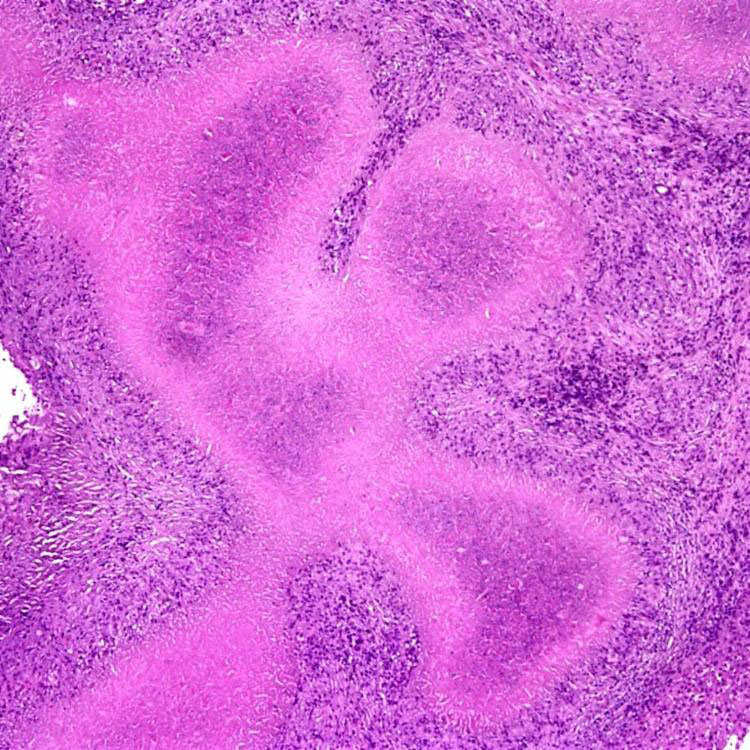
The characteristic lesion of hepatic cat-scratch disease consists of a stellate or geographic area of central necrosis surrounded by palisading histiocytes, mononuclear cells, and an outer rim of fibrosis. Younger lesions have less fibrosis and are more cellular.
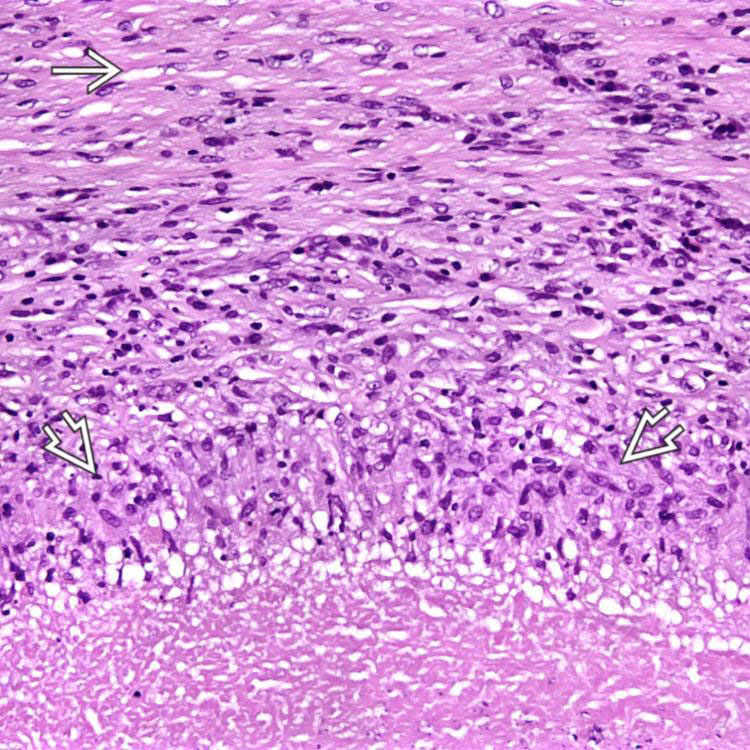
The lesion of hepatic cat-scratch disease shows distinctive layers: Central necrosis, palisading histiocytes
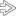 and admixed mononuclear cells, and an outer rim of fibrosis
and admixed mononuclear cells, and an outer rim of fibrosis  .
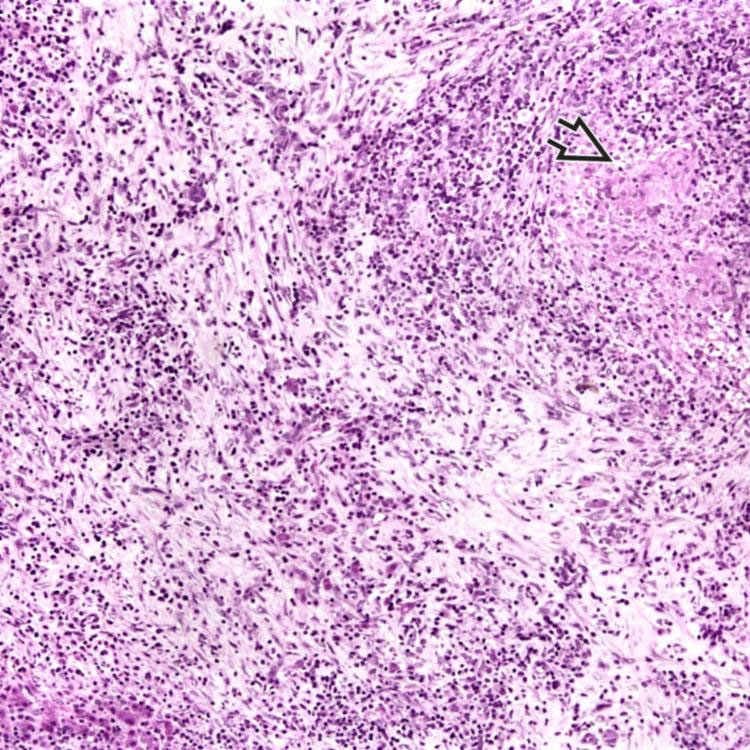
.
Older lesions of hepatic cat-scratch disease may consist primarily of fibrosis and chronic inflammation with little remaining central necrosis
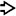 . A needle biopsy that samples only the fibrotic areas would most likely be nondiagnostic.
. A needle biopsy that samples only the fibrotic areas would most likely be nondiagnostic.TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Definitions
• Infection by Bartonella species after inoculation by cat
 Most cases are attributed to B. henselae but B. quintana and other species have been implicated in some
Most cases are attributed to B. henselae but B. quintana and other species have been implicated in some




 Most cases are attributed to B. henselae but B. quintana and other species have been implicated in some
Most cases are attributed to B. henselae but B. quintana and other species have been implicated in someStay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree













 characteristic of Bartonella can be seen on a silver impregnation stain, such as a Warthin-Starry. (Courtesy M. Scott, MD.)
characteristic of Bartonella can be seen on a silver impregnation stain, such as a Warthin-Starry. (Courtesy M. Scott, MD.)