Atypical Vascular Lesion
Thomas Mentzel, MD
Key Facts
Terminology
Vascular proliferation after radiotherapy, excluding obvious angiosarcoma, arising predominantly in breast
Clinical Issues
Exact incidence is difficult to establish
Small papules, usually < 5 mm
Papules are red to brown colored
All lesions must be excised completely
Wide age range; median in late 50s
Microscopic Pathology
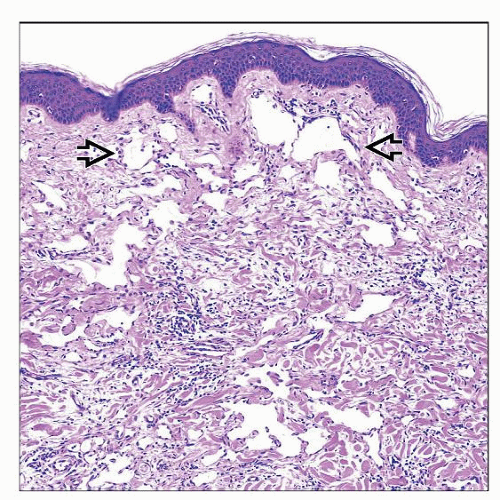
Usually well-circumscribed, superficial dermal-based lesions
Small, symmetrical, and wedge-shaped lesions
Dilated &/or narrow vascular structures
Single layer of slightly enlarged endothelial cells
No endothelial multilayering should be seen
No prominent cytologic atypia or mitoses
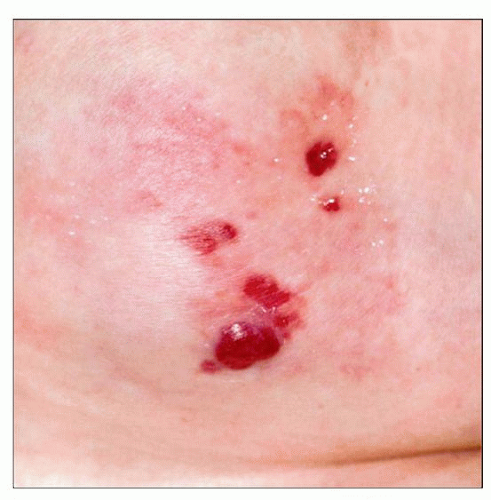 Multiple red papules and nodules on the chest are seen in a patient with an atypical vascular lesion after radiotherapy. |
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Atypical vascular lesion (AVL)
Synonyms
Atypical vascular proliferation (AVP)
Benign lymphangiomatous papule (BLAP)
Definitions
Vascular proliferation after radiotherapy excluding obvious angiosarcoma, arising predominantly in breast
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Environmental Exposure
Occur after radiotherapy (40-60 Gy)
Develop a median of 3 years after radiotherapy
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
Exact incidence difficult to establish
Relative risk is increased about 10x following radiation therapy
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree