Atypical Adenomatous Hyperplasia
Rafael E. Jimenez, MD
Gladell P. Paner, MD
Key Facts
Terminology
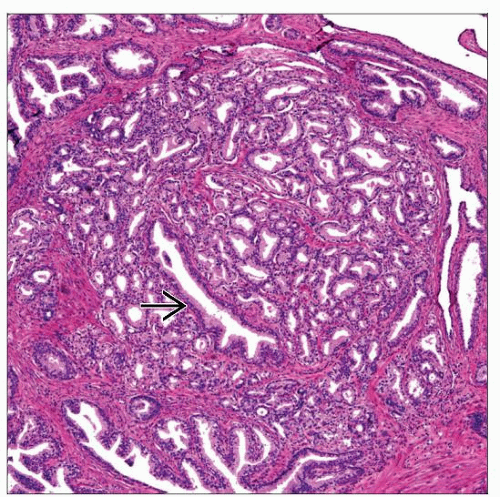
Small to medium-sized acinar proliferation usually forming well-circumscribed nodule in prostate transition zone, which does not fulfill cytologic criteria of carcinoma
Clinical Issues
Minimal evidence suggests that AAH may represent preneoplastic entity, particularly for low-grade, transition zone adenocarcinoma
Comes to attention in routine practice as prostate cancer mimic in needle biopsy or TURP
Microscopic Pathology
Well-circumscribed proliferation of small to medium-sized glands in transition zone, usually mixed with typical hyperplastic nodules in background
Variable size and shape of glands; similar cytology of surrounding hyperplastic glands
More dilated “parent” gland may be centrally located
Some peripheral AAH glands infiltrate surrounding stroma, tending to merge with adjacent benign glands
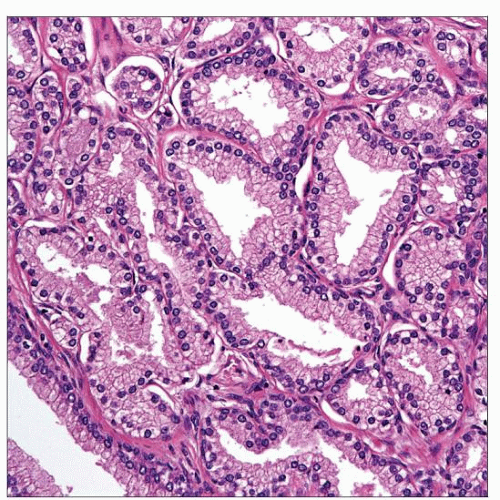
Acinar cells with clear cytoplasm, round uniform nuclei with inconspicuous nucleoli
Fragmented basal cell layer, often requires immunostains for detection
Ancillary Tests
Basal cell markers frequently show discontinuous basal cell layer
AMACR is focally positive in 7% and can be diffusely positive in up to 10% of cases
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Atypical adenomatous hyperplasia (AAH)
Synonyms
Adenosis
Atypical adenosis, small acinar atypical hyperplasia, atypical hyperplasia, atypical primary hyperplasia (outdated terms)
1994 consensus statement by expert GU pathologists recommended use of term AAH, although both AAH and adenosis are used interchangeably
Definitions
Small to medium-sized acinar proliferation usually forming well-circumscribed nodule in transition zone of prostate, which has basal cell layer and does not fulfill cytologic criteria of carcinoma
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
Present in 1.5-19.6% of transurethral resections of prostate (TURP) specimens
Seen in up to 33% of radical prostatectomies
Uncommon in needle core biopsies (< 2%), since transition zone is not often sampled
Presentation
Asymptomatic, incidental histologic finding
Comes to attention in routine practice as prostate cancer mimic in needle biopsy or TURP
Treatment
No treatment is currently warranted
Prognosis
Weak evidence suggests AAH may represent preneoplastic entity, particularly for low-grade, transition zone adenocarcinoma
Evidence is circumstantial, mostly based on morphologic findings and little molecular or clinical supporting data
MACROSCOPIC FEATURES
General Features
No gross abnormality
MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY
Histologic Features
On low power, AHH consists of relatively well-circumscribed proliferation of small to medium-sized glands in transition zone, usually mixed with typical hyperplastic nodules in background
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree