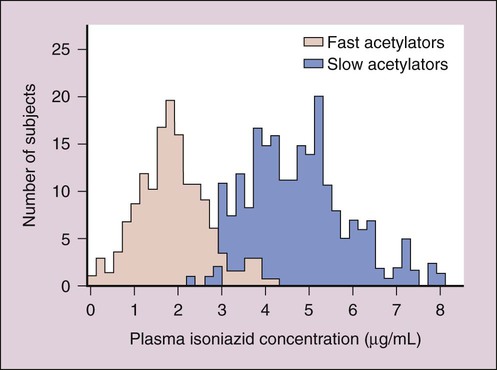
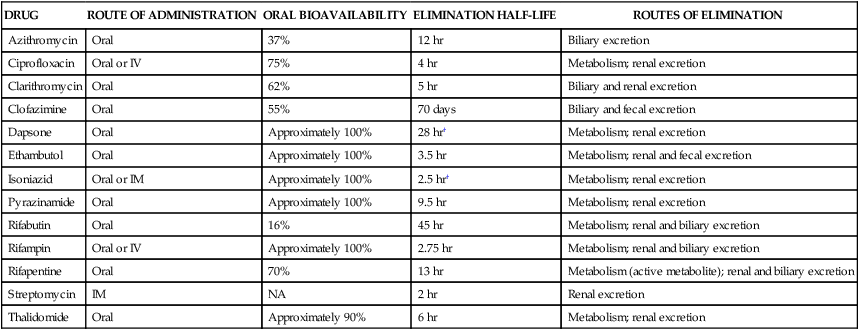
Drugs initially used to treat most patients with TB are referred to as first-line drugs. They include isoniazid, ethambutol, and pyrazinamide (which are synthetic drugs), and rifampin and streptomycin (which are antibiotics). First-line drugs are discussed later, and some of their properties are shown in Table 41-1. TABLE 41-1 Pharmacokinetic Properties of Antimycobacterial Drugs* IM, Intramuscular; IV, intravenous; NA, not applicable. *Values shown are the mean of values reported in the literature. †The half-lives of dapsone and isoniazid exhibit genetic variation. Second-line drugs are reserved to treat patients infected with organisms that are resistant to first-line drugs and patients with HIV co-infection. They include rifabutin and rifapentine (other derivatives of rifamycin), fluoroquinolone drugs (see Chapter 40), cycloserine, capreomycin, ethionamide, amikacin, and aminosalicylic acid. Most of the second-line drugs are not discussed further in this chapter. Isoniazid is extensively metabolized, and the parent compound and its metabolites are excreted in the urine. The primary metabolite, acetylisoniazid, is formed by conjugation of acetate with isoniazid in a reaction catalyzed by acetyltransferase, an enzyme whose activity is genetically determined. Slow acetylation is an autosomal recessive trait, and persons with the slow phenotype are homozygous for the slow allele. Persons with the fast phenotype are either heterozygous or homozygous dominant. Because of the different rates of acetylation of isoniazid, persons with the fast phenotype have lower plasma isoniazid concentrations than do persons with the slow phenotype (Fig. 41-1).
Antimycobacterial Drugs
Drugs for Mycobacterial Infections
Drugs for Tuberculosis
DRUG
ROUTE OF ADMINISTRATION
ORAL BIOAVAILABILITY
ELIMINATION HALF-LIFE
ROUTES OF ELIMINATION
Azithromycin
Oral
37%
12 hr
Biliary excretion
Ciprofloxacin
Oral or IV
75%
4 hr
Metabolism; renal excretion
Clarithromycin
Oral
62%
5 hr
Biliary and renal excretion
Clofazimine
Oral
55%
70 days
Biliary and fecal excretion
Dapsone
Oral
Approximately 100%
28 hr†
Metabolism; renal excretion
Ethambutol
Oral
Approximately 100%
3.5 hr
Metabolism; renal and fecal excretion
Isoniazid
Oral or IM
Approximately 100%
2.5 hr†
Metabolism; renal excretion
Pyrazinamide
Oral
Approximately 100%
9.5 hr
Metabolism; renal excretion
Rifabutin
Oral
16%
45 hr
Metabolism; renal and biliary excretion
Rifampin
Oral or IV
Approximately 100%
2.75 hr
Metabolism; renal and biliary excretion
Rifapentine
Oral
70%
13 hr
Metabolism (active metabolite); renal and biliary excretion
Streptomycin
IM
NA
2 hr
Renal excretion
Thalidomide
Oral
Approximately 90%
6 hr
Metabolism; renal excretion
Isoniazid
Pharmacokinetics.
< div class='tao-gold-member'>
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


Antimycobacterial Drugs
Only gold members can continue reading. Log In or Register to continue